We are one of the top 10 plastic injection molding companies in China that provides custom injection mould and injection moulding manufacturing services for a variety of plastic products around the world. We offer part design, mold design, PCB design, prototypes, mold making, massive production, testing, certificates, painting, plating, silkscreening, printing, assembly, and delivery, all in one-stop services.
Do you know the name of the process by which most plastic-solid materials are produced? It is called injection moulding. It is one of the best molding processes to make millions of injection-molded parts in a very short time. However, the initial injection mold tooling cost is pretty high compared to other machining methods, but this injection tooling cost will be recovered by the large production later, and this process has a low or even no waste rate.

What is injection molding
Injection molding (or injection moulding) is a manufacturing technology for producing products from plastics. Injecting the molten plastic resin at high pressure into an injection mould, which the mold is made according to the desired part shape, which was created by a designer using some CAD design software (such as UG, Solidworks, etc.).
The mould is made by a mold company (or mold maker) from metal material or aluminum and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part by some high-tech machines like CNC machines, EDM machines, lather machines, grinding machines, wire-cutting machines, etc., step by step to make the final mould cavity base on exactly the desired part shape and size, which we called an injection mold.
The injection moulding process is widely used for producing a variety of plastic products, from the smallest component to the big bumpers of cars. It is the most common technology to produce molding products in the world today, with some commonly made products including food containers, buckets, storage bins, house cooking equipment, outdoor furniture, automotive components, medical components, molding toys, and more.

Types of Injection Moulding – Basically 7 types of injection molding process as below
- Reaction injection molding
- Liquid injection molding
- Gas-assist injection molding
- Co-injection molding
- 2-Shot Injection Molding (or double injection molding)
- Fusible core injection molding
- Rapid injection molding
Injection moulding equipment
Injection molding machine
Injection molding machines, normally called injection presses, fasten our custom-made injection mold in the machine. The injection machine is rated by tonnage, which indicates the amount of clamping force that the press can generate. This clamping force keeps the mold closed during the injection molding process. There are various specifications for injection molding machines, from less than 5 tons to 6,000 tons or even bigger.
In general, the basic injection molding machine consists of a mold system, control system, injection system, hydraulic system, and Pinpin system. The tonnage clamp and shot size are used to identify the dimensions of a thermoplastic injection molding machine, which is a major factor in the overall process. Another consideration is the thickness of the mold, pressure, injection rate, the distance between the binding rod, and the screw design.
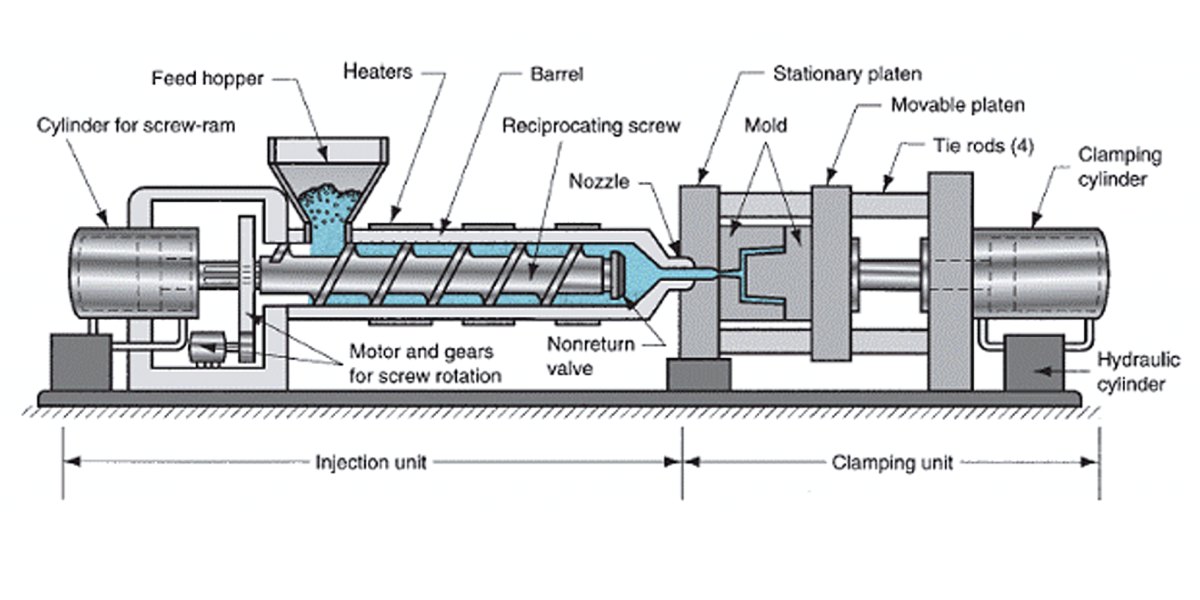
Horizontal Injection-molding-machine
Horizontal or vertical machines
There are normally two types of injection molding machines: horizontal and vertical molding machines.
This means molding machines fasten the mold in either a horizontal or vertical position. The majority are horizontal injection molding machines, but vertical machines are used in some niche applications such as cable insert molding, filter injection molding, insert molding, or some special molding process requirements.Some injection machines can produce two, three, or four colored molded parts at one step; we call them double-shot injection molding machines or 2K injection molding machines (more color will be 3K or 4K molding machines).
Clamping unit
Machines are classified primarily by the type of driving systems they use: hydraulic, electric, or hybrid. Hydraulic presses have historically been the only option available to molders until Nissei introduced the first all-electric machine in 1983. The electric press, also known as Electric Machine Technology (EMT), reduces operation costs by cutting energy consumption and also addresses some of the environmental concerns surrounding the hydraulic press.
Electric injectino molding presses have been shown to be quieter, faster, and have higher accuracy; however, the machines are more expensive. Hybrid injection molding machines take advantage of the best features of both hydraulic and electric systems. Hydraulic machines are the predominant type in most of the world, with the exception of Japan.
Final sumrize for injection molding machine: Injection molding machine converts raw plastic granules or granules into final mold parts using thermoplastic smelting, injection, conditioning, and cooling cycles.
Injection Mold- Types of injection molds
Simply explain that the injection mold is custom made of the desired part shape by cutting the steel or aluminum and producing the mold that can be used in the injection molding machine, which we called injection mold or plastic injection mold. Go to our plastic molding section to learn more about plastic injection mold manufacturing. But making injection mould actually not easy; you need to have a professional team (a mold maker, a mold designer) and mold manufacturing equipment like CNC machines, EDM machines, wire-cutting machines, etc.
There are two main types of injection molds: cold runner mold (two plate and three plate designs) and hot runner molds (the more common of the runner-less molds). The significant difference is the presence of sprue and runner with every molded part in the cold runner type. This extra molded component must be separated from the desired molded par;, the hot runner basically does not have any runner wasteore small runner waste.
Cold runner mold
Developed to provide for injection of thermoset material either directly into the cavity or through sprue and a small sub-runner and gate into the mold cavity, there are basically two types of the cold runner which mostly used in the mold industry, two plate mold and Three plate mold.
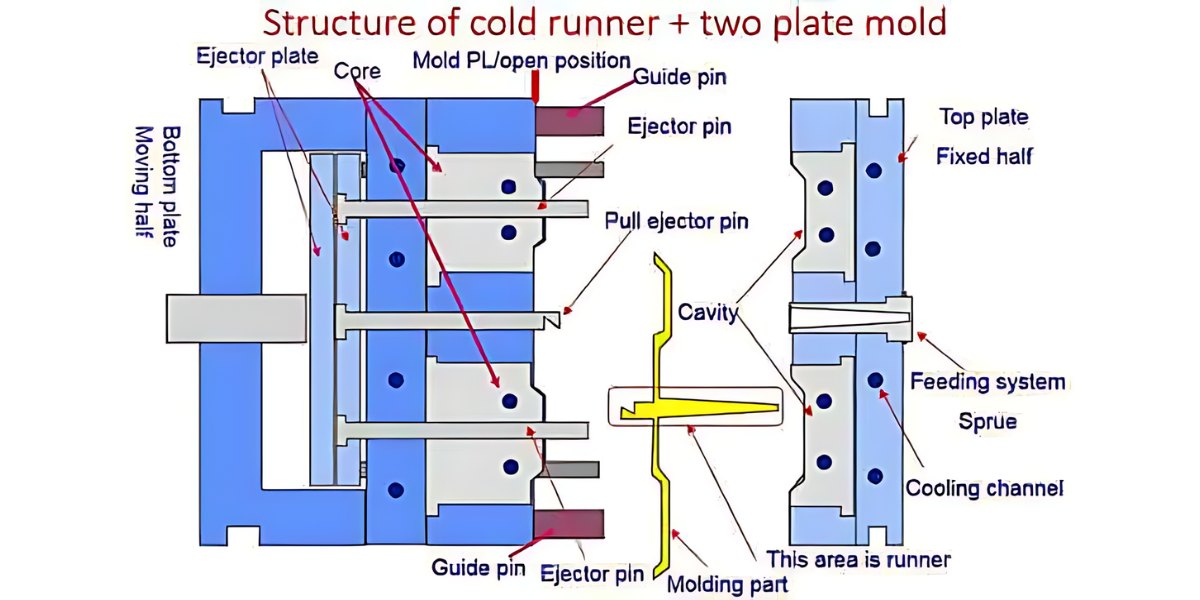
Two plate mold
The conventional two-plate mold consists of two halves fastened to the two platens of the molding machine’s clamping unit. When the clamping unit is opened, the two mold halves open, as shown in (b). The most obvious feature of the mold is the cavity, which is usually formed by removing metal from the mating surfaces of the two halves. Molds can contain a single cavity or multiple cavities to produce more than one part in a single shot. The figure shows a mold with two cavities. The parting surfaces (or parting line in a cross-sectional view of the mold) are where the mold opens to remove the part(s).
In addition to the cavity, there are other features of the mold that serve indispensable functions during the molding cycle. The mold must have a distribution channel through which the polymer melt flows from the nozzle of the injection barrel into the mold cavity. The distribution channel consists of (1) a sprue, which leads from the nozzle into the mold; (2) runners, which lead from the sprue to the cavity (or cavities); and (3) gates that constrict the flow of plastic into the cavity. There are one or more gates for each cavity in the mold.
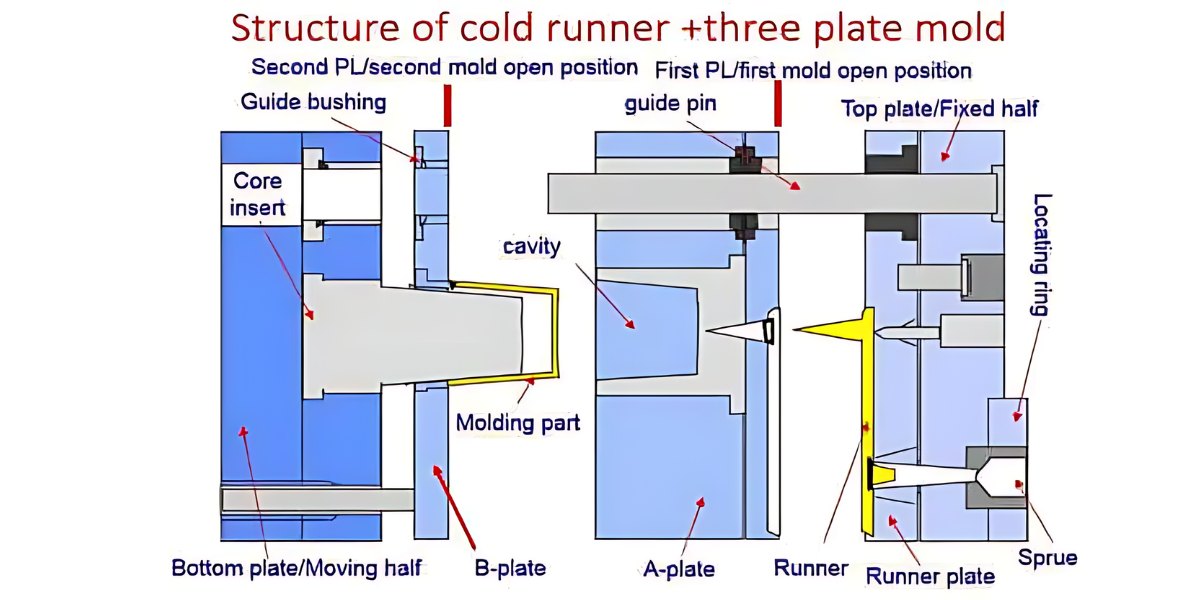
Three plate mold
The two-plate mold is the most common mold in injection molding. An alternative is a three-plate injection mold. There are advantages to this mold design. First, the flow of molten plastic is through a gate located at the base of the cup-shaped part rather than at the side. This allows for a for a more even distribution of melt along the sides of the cup. In the side gate design of the two-plate, the plastic must flow around the core and join on the opposite side, possibly creating a weakness at the weld line.
Second, the three-plate mold allows more automatic operation of the molding machine. As the mold opens, it divides into three plates with two openings between them. This forces the disconnection of runners and parts, which drop by gravity (with possible assistance from blown air or a robotic arm) into different containers beneath the mold.
Hot Runner Mold
Hot-runner molding has parts that are physically heated. These types of molding help transfer the molten plastic quickly from the machine, directly feeding it into the mold cavity. It can also be known as the runner-less mold. The hot runner system is very useful for some of the high volumes of products that will save huge production costs by using the hot runner mold system. The sprue and runner in a conventional two-plate or three-plate mold represent waste material.
In many instances, they can be ground and reused; however, in some cases, the product must be made of “virgin” plastic (original raw plastic material) or there is multiple cavity mold (such as 24 cavities or 48 cavities, 96 cavities, 128 cavities, or even more cavities). The hot-runner mold eliminates the solidification of the sprue and runner by locating heaters around the corresponding runner channels. While the plastic in the mold cavity solidifies, the material in the sprue and runner channels remains molten, ready to be injected into the cavity in the next cycle.
Type of hot runner system.
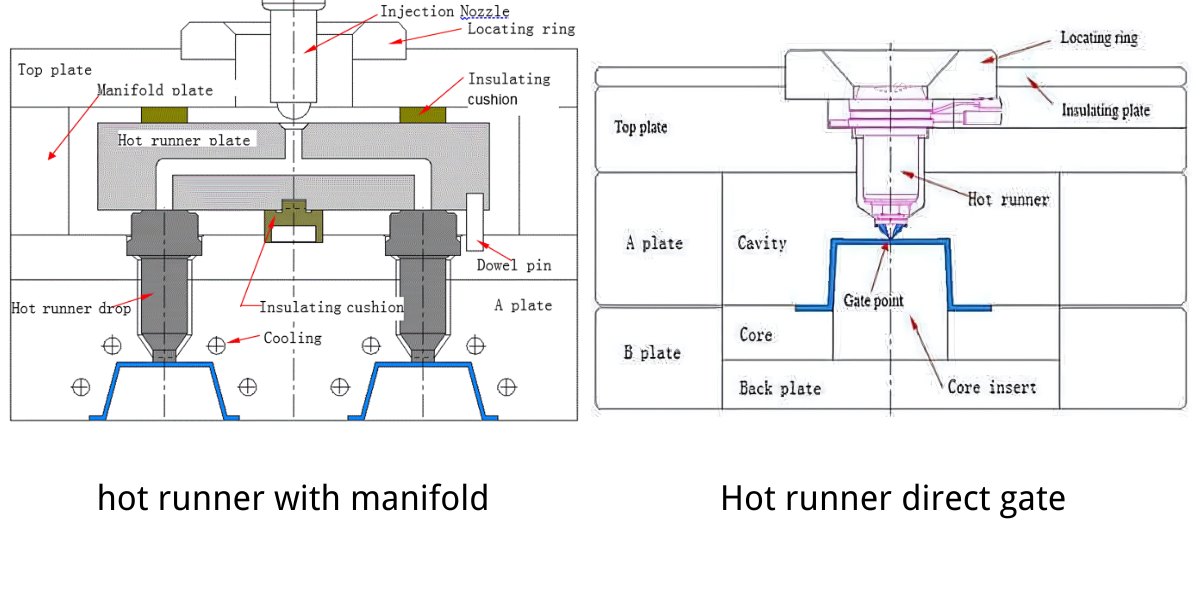
Basically, there are two types of hot runner systems: one called hot sprue mold (without the manifold plate and hot runner plate), and one called hot runner mold (with the manifold plate and hot runner plate).
Hot sprue mold (without the manifold plate and hot runner plate) uses the hot nozzle (sprue) to feed the material into the mold cavity, either directly or indirectly.
The hot runner mold (with the manifold plate and hot runner plate) means the hot runner system has the hot runner plate, manifold plate, and sub-hot runner sprue. The below pictures are simple explanations for two types of hot runner systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Runner Molding
There are a few amazing advantages to cold-runner molding, such as:
- Cold-runner molding is cheaper and easier to maintain.
- You are able to quickly change colors.
- It has a faster cycle time.
- It is more flexible than hot-runner molding.
- The gate locations can easily be changed or fixed.
Although there are many advantages, there are also some disadvantages. The disadvantages of cold-runner molding are:
- You have to have thicker dimensions compared to the hot runner mold.
- You can only use certain types of nozzles, fittings, and manifolds.
- Cold-runner molding can result in slower production time when you remove sprues and runners.
- You must manually separate the runners and parts after molding.
- You may waste the plastic materials if you do not reset after each run.
If you want to know more information, please go to the cold runner mold page to check out more details.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Runner Molding
Hot-runner molding has a few advantages, such as:
- Hot-runner molding has a very quick cycle time.
- You can save production costs by using hot-runner molding.
- Less pressure is needed to inject the molding.
- You have more control over the hot-runner molding.
- Hot-runner molding can fit a wide variety of gates.
- Multiple cavities of mold can be easily filled by using the hot runner system.
The disadvantages of using hot-runner moldings are:
- It is more expensive to make the hot runner mold than the cold runner mold.
- It is difficult to maintain and fix the hot runner mold.
- You are not able to use hot-runner molding on materials that are thermally sensitive.
- You will need to get your machines inspected more often than cold-runner molding machines.
- It is hard to change the colors in the hot runner mold system.
Want to know more information? Welcome to the hot runner mold section.
Injection Moulding Processing?
Injection moulding is one of the best ways to shape plastic products by injecting a thermoplastic material. During the process of injection molding, the plastic material is placed in the injection molding machine and the melt system of the injection unit is used to melt the plastic into the liquid. The liquid material is then high-pressure-injected into a mold (a custom manufacturing mold) that is assembled in that injection molding machine. The mold is made of any metal, such as steel or aluminum. The molten form is then allowed to cool down and set into a solid form.
The plastic material thus formed is then ejected out of the plastic mold. The actual process of plastic molding is just an expansion of this basic mechanism. The plastic is let into a barrel or chamber under gravity or is force-fed. As it moves down, the increasing temperature melts the plastic resin. Then, the molten plastic is forcibly injected into the mold under the barrel with an appropriate volume. As the plastic cools, it solidifies. The injection-molded parts like this have a reverse shape from the mold. A variety of shapes, both 2D and 3D, can be produced by the process.
The process of plastic molding is cheap due to the simplicity involved, and the quality of the plastic material is modifiable by changing the factors involved in the custom injection molding process. The pressure of injection can be changed to change the hardness of the final product. The thickness of the mold also governs the quality of the article produced.
The temperature for melting and cooling determines the quality of the plastic formed. ADVANTAGES The major advantage of injection molding is that it is very cost-effective and fast. Apart from this, unlike the cutting processes, this process rules out any undesired sharp edges. Also, this process produces smooth and finished products that require no further finishing. Check below for the detailed advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of injection moulding
Although injection molding is used by many different companies, and there is no doubt this is one of the most popular methods to produce injection molding products, there are some advantages to using it, such as:
- Precision and aesthetics—because in this injection molding process you can make your plastic part with any shape and surface finish (texture and high gloss finishing), some of the special surface finishing can still be met by the secondary surface finishing process. The injection molding part is the repeatability of their shapes and dimensions.
- Efficiency and speed: a single production process, even for the most complex products, lasts from a few to several dozen seconds.
The possibility of full automation of the production process, which in the case of companies dealing with the production of plastic components translates into low production effort and the possibility of mass production,. - Ecology: because, compared to metalworking, we are dealing with a significant reduction in the number of technological operations, less direct energy and water consumption, and low emissions of compounds harmful to the environment.
Plastics are materials that, although known relatively recently, have even become indispensable in our lives, and thanks to increasingly modern production processes from year to year, they will contribute even more to saving energy and other natural resources.
Disadvantages of injection molding
- The high cost of injection molding machines and often the cost of tooling (molds) that equals it result in extended depreciation time and high costs of starting production.
- Due to the above, injection technology is only cost-effective for mass production.
- The need for high-qualification technical supervision employees who must know the specifics of injection molding processing.
- The need for high technical requirements for injection mold making
- The need to maintain narrow tolerances for processing parameters.
- A long time of preparation for the production due to the labor-intensive implementation of the injection molds.
Injection molding cycle time
The basic injection cycle time includes mold close, injection carriage forward, plastics filling time, metering, carriage retracts, holding pressure, cooling time, mold open, and eject part(s).
The mold is closed shut by the injection molding machine, and the melted plastic is forced by the pressure of the injection screw to inject into the mold. The cooling channels then assist in cooling the mold, and the liquid plastics become solid into the desired plastic part. The cooling system is one of the most important parts of the mold; inappropriate cooling can result in distorted molding products, and the cycle time will be increased, which will increase the injection molding cost as well.
Molding Trial
When the injection plastic mold has been made by the mold maker, the first thing we need to do is do the mold trial. This is the only way to check the mold quality to see if it was made according to the custom requirement or not. To test the mold, we normally fill the plastics with the molding step by step, using short-shot filling at first, and increasing the material weight little by little until the mold is 95 to 99% full.
After meeting this status, a small amount of holding pressure will be added and holding time increased until the gate freeze-off has occurred. Holding pressure is then increased until the molding part is free of sink marks and the part weight has been stable. Once the part is good enough and has passed any specific technical tests, a machine parameter sheet needs to be recorded for massive production in the future.
Plastic injection molding defects
Injection molding is a complex technology, and problems may happen every time. A new custom made of an injection mold has some issues, which is very normal. To solve the mold issue, we need to fix and test the mold several times. Normally, two or three trials can completely solve all the issues, but in some cases, only a one-time mold trial can approve the samples. And finally, all of the issues are solved completely. Below are most of the injection molding defects and the troubleshooting skills to solve those issues.
Issue No. I: Short shot defects- What is a short shot issue?
When injecting material into the cavity, molten material does not completely fill the cavity, resulting in the product lacking material. This is called short molding or short shot, as shown in the picture. There are lots of reasons to cause short shot issues.

Fault Analysis and Method for Correction the defects
- Improper selection of injection molding machine: When choosing plastic injection machines, the maximum shot weight of the plastic injection machine must be greater than the weight of the product. During verification, the total injection volume (including the plastic product, runner, and trimming) shall not be more than 85% of the plasticizing capacity of the machine.
- Insufficient supply of material: the bottom of the feed position might have “bridging the hole” phenomena. The shot stroke of the injection plunger should be added to increase the supply of material.
- Poor flow factor of raw material: improve mold injection system, for example, by proper design of runner location, by enlarging gates, runner, and feeder size, and by using a bigger nozzle, etc. In the meantime, the additive can be added to the raw material to improve the flow rate of the resin or change the material to have a better flow rate.
- Overdose of using the lubricant: reduce the lubricant and adjust the gap between the barrel and injection plunger to recover the machine, or fix the mold so that there is no need for any lubricant during the molding process.
- Cold foreign substances blocked the runner. This issue normally happens with hot-runner systems. Dismount and clear the nozzle of the hot runner tip, or enlarge the cold material cavity and runner cross-section area.
- Improper design of injection feeding system: When designing the injection system, pay attention to gate balance; the product weight of each cavity should be in proportion to the gate size, so that each cavity can be fully filled simultaneously, and gates should be positioned in thick walls. A balanced separate runners scheme can also be adopted. If the gate or runner is small, thin, or long, the molten material pressure will be reduced too much during feeding, and the flow rate will be blocked, which will result in poor filling. To solve this problem, the cross-sections of the gate and runner should be enlarged, and multiple gates should be used when necessary.
- Lack of venting: check if there is a cold-slug well or if the position of the cold-slug well is correct. For mold with a deep cavity or deep ribs, venting slots or venting grooves should be added at positions of short molding (end of feeding area). Basically, there are always venting grooves on the parting line; the size of the venting grooves can be 0.02-0.04mm and 5-10mm in width, 3mm close to the sealing area, and the venting opening should be at the end of filling the position.
When using raw materials with excessive moisture and volatile content, a large amount of gas (air) will also be generated, causing air trap issues in the mold cavity. In this case, raw materials should be dried and cleared of volatile substances. In addition, during the injection process operation, poor venting can be addressed through increasing mold temperature, low injection speed, reducing injection system obstruction and mold clamping force, and enlarging gaps between molds. But the short shot issue happens to the deep rib area. To release the air out, you need to add a venting insert to solve this air trap and short shot issues. - The mold temperature is too low. Before starting molding production, the mold should be heated up to the required temperature. In the beginning, you should connect all of the cooling channels and check if the cooling line is working well, especially for some special materials like PC, PA66, PA66+GF, PPS, etc. The perfect cooling design is a must for those special plastic materials.
- Molten material temperature is too low. In a proper molding process window, the temperature of the material is in proportion to the filling length. Low-temperature molten material is poor in fluidity, and the filling length is shortened. It should be noted that after the feed barrel is heated to the required temperature, it should stay constant for a while before starting molding production.
In the event that low-temperature injection must be used to prevent molten material from being resolved, the injection cycle time can be prolonged to overcome the short shot. If you have a professional molding operator, he should know this very well. - Nozzle temperature is too low. When open mold, the nozzle should be part away from the mold spure to reduce the influence of mold temperature on the nozzle temperature and keep the nozzle temperature within the range of what the molding process requires.
- Insufficient injection pressure or holding pressure: injection pressure is close to a positive proportion to the filling distance. The injection pressure is too low, the filling distance is short, and the cavity cannot be fully filled. Increasing the injection pressure and holding pressure can improve this issue.
- Injection speed is too slow. Mold filling speed is directly related to injection speed. If injection speed is too low, filling of molten material is slow while slow-flowing molten is easy to cool, hence the flow properties further decrease and result in a short injection. For this reason, the injection speed should be enhanced properly.
- Plastic product design is not reasonable. If the wall thickness is out of proportion to the length of the plastic product, the product shape is very complex, and the forming area is large, melt material is easily blocked at the thin wall of the product, leading to insufficient filling. Therefore, when designing the shape and structure of the plastic products, note that wall thickness is directly related to melting limit filling length. During injection molding, product thickness should range between 1-3 mm and 3-6 mm for large products. Generally, it is not good for injection molding if the wall thickness is over 8 mm or less than 0.4 mm, so this kind of thickness should be avoided in design.
Issue No. II: Trimming (Flashing or burrs) Defects
I. What is the flashing or Burrs?
When extra plastic melt material is forced out of the mold cavity from the mold joint and forms a thin sheet, trimming is generated. If the thin sheet is large, it is called flashing.

Molding Flash or burrs
II. Fault Analysis and Method for Correction
- Mold clamping force is not sufficient. Check whether the booster is overpressurizing and verify whether the product of the projected area of the plastic part and the forming pressure exceed the clamping force of the equipment. Forming pressure is the average pressure in the mold; normally, it is 40 MPa. If the calculation product is larger than the mold clamping force, it indicates that the clamping force is insufficient or the injection positioning pressure is too high. In this case, the injection pressure or section area of the injection gate should be reduced; pressure keeping and pressurization time can also be shortened; injection plunger strokes can be reduced; the number of injection cavities can be reduced; or a mold injection machine with a larger tonnage can be used.
- The material temperature is too high. The temperature of the feed barrel, nozzle, and mold should be decreased properly to reduce the injection cycle. For melts of low viscosity, like polyamide, it is difficult to solve overflow flashing defects by simply changing injection molding parameters. To solve this issue completely, fixing the mold is the best way, like doing better mold fitting and making the parting line and shot-off area more precise.
- Mold defect. Mold defects are the main reason for overflow flashing. The mold must be carefully examined and the mold parting line re-verified to ensure the pre-centering of the mold. Check whether the parting line fits well, whether the gap between sliding parts in the cavity and core is out of tolerance, whether there is adhesion of foreign matter on the parting line, whether the mold plates are flat and whether there is bending or deformation, whether the distance between mold pate is adjusted to fit the thickness of the mold, whether the surface mold block is damaged, whether the pull rod is deformed unevenly, and whether the venting slot or grooves is too large or too deep.
- Improperness of the molding process. If injection speed is too high, injection time is too long, injection pressure in the mold cavity is unbalanced, mold filling speed is not constant, or there is overfeeding of material, an overdose of lubricant can lead to flashing; therefore, corresponding measures should be taken according to the specific situation during operation.
Issue No. III. Welding Line (Joint Line) Defects
I. What is the welding line defect?

Welding line
When filling the mold cavity with molten plastic material, if two or more flows of molten material have cooled down in advance before confluence t the joint area, the flows will not be able to totally integrate and a liner is produced at the confluence, thereby a welding line is formed, also called joint line
II. Fault Analysis and Method for Correction
- The material temperature is too low. Low-temperature molten material flows have poor confluence performance, and the welding line is easily formed. If welding marks appear at the same position on both the interior and exterior of a plastic product, it is usually inappropriate welding caused by the low temperature of the material. To address this problem, the feeding barrel and nozzle temperatures can be properly increased, or the injection cycle can be prolonged to increase the material temperature. In the meantime, the coolant flow inside the mold should be regulated to properly increase the mold temperature.
Generally, the strength of the plastic product welding line is relatively low. If the position of the mold with the welding line can be partially heated to partially increase the temperature at the welding position, the strength at the welding line can be enhanced. When a low-temperature injection molding process is used for special needs, injection speed and injection pressure can be increased to improve confluence performance. A small dosage of lubricant can also be added to the raw material formula to increase molten flow performance. - Mold Defect. The fewer numbers of the gate should be adopted, and the position of the gate should be reasonable to avoid inconsistent filling speed and interruption of molten flow. Where possible, a one-point gate should be adopted. To prevent low-temperature molten material from generating a welding mark after being injected into the mold cavity, lower the mold temperature and add more cold water to the mold.
- Poor mold venting solution. Check whether the venting slot is blocked by solidified plastic or another substance at first (especially some glass fiber material), and check whether there is a foreign substance at the gate. If there are still carbonation spots after removing the extra blocks, add a venting groove at the flow convergence in the mold or change the gate location. Reduce the mold clamping force and increase venting intervals to speed up the convergence of material flows. In terms of the molding process, reducing material temperature and mold temperature, shortening high-pressure injection time, and decreasing injection pressure can be taken.
- Improper use of release agents. In injection molding, usually, a small quantity of release agent is evenly applied at the thread and other positions that are not easy to demold. In principle, the use of the release agent should be reduced as much as possible. In massive production, you should never use a release agent.
- The structure of plastic products is not reasonably designed. If the wall of the plastic product is too thin, the thickness differs greatly, or there are too many inserts, it will cause poor welding. When designing a plastic product, it shall be ensured that the thinnest part of the product must be greater than the minimum wall thickness allowed during forming. In addition, reduce the number of inserts and make the wall thickness as uniform as possible.
- The welding angle is too small. Each kind of plastic has its own unique welding angle. When two flows of molten plastic converge, the welding mark will appear if the converging angle is smaller than the limit welding angle and will disappear if the converging angle is bigger than the limit welding angle. Usually, the limit welding angle is around 135 degrees.
- Other causes. Different degrees of poor welding can be caused by the use of raw materials with excessive moisture and volatile content, oil stains in the mold that are not cleaned up, cold material in the mold cavity or uneven distribution of fiber filler in the molten material, an unreasonable design of the mold cooling system, fast solidification of the melt, a low temperature of the insert, a small nozzle hole, an insufficient plasticizing capacity of the injection machine, or a large pressure loss in the plunger or barrel of the machine.
To solve these problems, different measures, such as pre-drying of raw materials, regular cleaning of mold, changing the design of mold cooling channels, controlling the flow of cooling water, increasing the temperature of inserts, replacing nozzles with larger apertures, and using injection machines with larger specifications, can be taken in the process of operation.
Issue No. IV: Warp Distortion – What is warp distortion?
Due to internal shrinkage of the product is inconsistent, the internal stress is different and distortion occurs.
Fault Analysis and Method for Correction
1. The molecular orientation is unbalanced. In order to minimize warp distortion caused by diversification of molecular orientation, create conditions to reduce flow orientation and relax orientation stress. The most effective method is to reduce molten material temperature and mold temperature. When this method is used, it is better to combine it with heat treatment of the plastic parts; otherwise, the effect of reducing molecular orientation diversification is often of short duration. The method of heat treatment is: after demoulding, keep the plastic product at a high temperature for some time and then cool to room temperature gradually. In this way, the orientation stress in the plastic product can be largely eliminated.
2. Improper cooling. When designing a plastic product structure, the cross-section of each position should be consistent. Plastic must be kept in the mold for a sufficient time for cooling and forming. For the design of a mold cooling system, cooling pipelines should be at positions where the temperature is easy to rise and the heat is relatively concentrated. As for the positions that easily cool down, gradual cooling should be adopted to ensure balanced cooling of each position of the product.
3. The gating system of mold is not properly designed. When determining the gate position, be aware that the molten material will not directly impact the core, and be sure the stress on both sides of the core is the same. For large flat rectangular plastic parts, a membrane gate or multi-point gate shall be used for resin raw materials with wide molecular orientation and shrinkage, and a side gate shall not be used; for ring parts, a disk gate or wheel gate shall be used, and a side gate or pinpoint gate shall not be used; for housing parts, a straight gate shall be used, and a side gate shall not be used as far as possible.
4. The demolding and venting system is not properly designed. In-mold design, draft angle, position, and the number of ejectors should be reasonably designed to improve mold strength and positioning accuracy. For small and medium-sized molds, anti-warping molds can be designed and made according to their warping behavior. In respect of mold operation, ejection speed or ejection stroke should be properly reduced.
5. Improper operation process. The process parameter shall be adjusted according to the actual situation.
Issue No. V: Sink Mark Defects – What is the sink mark?
Sink marks are unevenly shrinking of the surface caused by the inconsistent wall thickness of the plastic product.
Fault Analysis and Method for Correction
- The injection molding condition is not properly controlled. Properly increase injection pressure and speed, increase molten material compression density, prolong injection and pressure-keeping time, compensate for the sinking of the molten, and increase the buffering capacity of injection. However, the pressure should not be too high; otherwise, the convex mark will appear. If sink marks are around the gate, prolonging the pressure keeping time can eliminate the sink marks; if sink marks are at the thick wall, prolonging the cooling time of the plastic product in the mold; if sink marks around the insert are caused by partial shrinkage of molten, the main reason is that the temperature of the insert is too low; try to increase the temperature of the insert to eliminate the sink marks; if sink marks are caused by insufficient material feeding, increase the material. Besides all of this, the plastic product must be fully cooled in the mold.
- Mold defects. According to the actual situation, properly enlarge the gate and runner cross-section, and the gate should be in a symmetrical position. The feed inlet should be in the thick wall. If sink marks appear away from the gate, the cause usually is that the flow of molten material is not smooth at some position of the mold, which hampers the transmission of pressure. To solve this problem, enlarge the injection system to allow the runner to extend to the position of the sink marks. For products with thick walls, a wing-type gate is preferred.
- Raw materials cannot meet molding requirements. For plastic products with high finish standards, resin with low shrinkage shall be used, or the appropriate dosage of lubricant can also be added to the raw material.
- Improper design of product structure. The wall thickness of the product shall be uniform; if the wall thickness differs a lot, the structure parameter of the injection system or the wall thickness shall be adjusted.
Issue No. VI: Flow Mark-What is Flow Mark?
Flow mark is a linear trace on the surface of a molding product that shows the flow direction of molten material.
Fault Analysis and Method for Correction
- Ring-shaped flow marks on the surface of the plastic part with the gate as the center are caused by poor flow motion. To address this kind of flow mark, increase the temperature of the mold and nozzle, increase the injection rate and filling speed, prolong the pressure-keeping time, or add a heater at the gate to raise the temperature around the gate. Appropriately expanding the gate and runner area can also work, while the gate and runner section is preferably circular, which can guarantee the best filling. However, if the gate is in the weak area of the plastic part, it will be square. In addition, a large cold-slug well should be set at the bottom of the injection port and at the end of the runner; the greater the influence of material temperature on the flow performance of the melt, the more attention should be paid to the size of the cold-slug well. The cold-slug well must be set at the end of the melt flow direction from the injection port.
- Whirl flow marks on the surface of the plastic part are caused by the unsmooth flow of molten material in the runner. When the molten material flows from the runner with a narrow section to the cavity with a larger section or the mold runner is narrow and the finish is poor, the material flow is easy to form turbulence, resulting in a whirl flow mark on the surface of the plastic part. To address this kind of flow mark, reduce injection speed appropriately or control the injection speed in slow-fast-slow mode. The mold gate shall be in the thick wall and preferably in the form of a handle type, a fan type, or a film type. The runner and gate can be enlarged to reduce material flow resistance.
- Cloud-like flow marks on the surface of the plastic part are caused by volatile gas. When ABS or other copolymerized resins are used, if the processing temperature is high, the volatile gas produced by the resin and lubricant will form cloud-like ripple marks on the surface of the product. In order to solve this problem, it is necessary to reduce the temperature of the mold and barrel, improve the venting of the mold, reduce the material temperature and filling speed, enlarge the gate section properly, and consider changing the type of lubricant or reducing the use of lubricant.
Issue No. VII: Glass fiber streaks – What is Glass fiber streaks
Surface Appearance: Plastic molding products with glass fiber have various surface defects, such as dim and dreary in color, coarse in texture, and metal bright spots, etc. These are especially obvious in the convex part of the material flow area, close to the joint line where the fluid meets again.
Physical cause
If the injection temperature and the mold temperature are too low, the material containing glass fiber tends to solidify fast on the mold surface, and the glass fiber will not melt in the material again. When two flows meet, the orientation of glass fiber is in the direction of each flow, which will lead to irregular surface texture at the intersection, resulting in the formation of joint seams or flow lines.
This type of defect is more obvious if the molted material is not fully mixed in the barrel. For example, if the stroke of the screw is too long, it will cause the undermixed material to also be injected.
Causes related to process parameters and improvements can be identified:
- The injection speed is too low. To increase injection speed, consider using a multi-step injection method like slow-fast mode.
- The temperature of the mold is low; increasing the mold temperature could improve the glass fiber streaks.
- Molten material temperature is too low; increase barrel temperature and screw back pressure to improve.
- The temperature of molten material varies a lot: if the molten material is not fully mixed, increase screw back pressure, reduce screw speed, and use the longer barrel to shorten stroke.
Issue No. VIII: Ejector Marks: What are ejector marks?
Surface Appearance: Stress whitening and stress rising phenomena are found on the side of the product that is facing the nozzle, i.e., where the ejector rod is located on the ejector side of the mold.
Physical cause
If the demoulding force is too high or the surface of the ejector rod is relatively small, the surface pressure here will be very high, causing deformation and eventually whitening at the ejection area.
Causes related to process parameters and improvements can be applied:
- Holding pressure is too high; decrease pressure while keeping pressure.
- Holding pressure time is too long; shorten holding pressure time.
- Holding pressure switch time is too late. advance the pressure-keeping switch
- The cooling time is too short; increasing the cooling time
Causes related to mold design and improvements can be applied:
- The draft angle is not enough; increase the draft angle according to specification, especially in the area of the ejector mark.
- The surface finish is too rough; the mold shall be well polished in the demolding direction.
- A vacuum is formed on the ejection side. Install an air valve in the cor
Conclusion
Due to the specific properties of plastics, injection molding is a very complex technological process; unlike the seemingly related process of metal die casting, it is not a mechanical process but a mechanical-physical one. In the injection molding process, a molded piece is obtained. It is characterized not only by a specific shape but also by a specific structure resulting from the flow of the plasticized material in the mold and the course of its solidification.
Because these processes occur in the form of injection, the designer of this tool must take into account, in addition to typically mechanical issues, issues related to the physical nature of the material transformation. Constructing a rationally working form requires, at the same time, from the designer a thorough knowledge of the technical capabilities of the injection molding machine, because it is a machine with extremely rich possibilities provided by its equipment and numerous work programs.
If you want to know more, please go to our other plastic mold page. If you are looking for injection molding services, you are welcome to send us your requirements for a quotation.
If you have a new project or current project that needs a China injection molding company to support you, we are happy to help. Please call us or send us an email.