Polystyrene injection molding, or PS injection molding, is a common manufacturing technique and is famous for its ability to create large volumes of identical components at a fast rate. Polystyrene is a very suitable thermoplastic. Because it is cheap, easily moldable and it has numerous applications in various sectors. This article will help explain procedures followed in polystyrene injection molding along with such areas as the material used, designing guidelines, details of processing parameters, and the pros and cons of this method.
What is Polystyrene Molding?
Polystyrene molding is one of the techniques for forming polystyrene, a thermoplastic polymer with numerous applications. This is usually achieved through the injection molding processes. Here molten polystyrene is injected into a mold cavity to form complicated shapes with high accuracy. Polystyrene injection molding is popular in many industries because the material is cheap and relatively easy to process. Besides this, it has well-desired properties such as rigidity and clarity. The process is consistent and intensive, making it appropriate for mass production.
Why is Polystyrene So Commonly Used?
Polystyrene’s widespread use can be attributed to several factors. Such as;
- Cost-effectiveness: PS is cheap to manufacture, and the production costs are considerably low when getting to a huge scale.
- Versatility: It can be easily shaped into several forms. So, it is applicable in product nudges, i.e. cans and other consumer durables.
- Clarity and rigidity: PS produces a clear, bright, glossy finish. This finishing is rigid but also very light.
- Ease of processing: It has a low melting point and good flow characteristics. So, this enables it to process easily in injection molding.
- Recyclability: PS can be recycled so it promotes a sustainable manufacturing system.
Properties of Polystyrene (PS)
The following table shows the different properties of polystyrene.

| Property | General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) | High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) |
| Density | 1.04 – 1.06 g/cm³ | 1.03 – 1.06 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 30 – 60 MPa | 15 – 35 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 70 – 110 MPa | 25 – 55 MPa |
| Impact Strength (Notched Izod) | 20 – 35 J/m | 150 – 300 J/m |
| Elongation at Break | 1 – 2% | 30 – 50% |
| Melting Point | 210°C – 250°C | 200°C – 230°C |
| Shrinkage | 0.4 – 0.7% | 0.3 – 0.8% |
| Water Absorption (24 hours) | 0.03% | 0.03% |
| Transparency | Transparent | Opaque |
| Applications | Packaging, Disposable Cutlery | Automotive Parts, Toys |
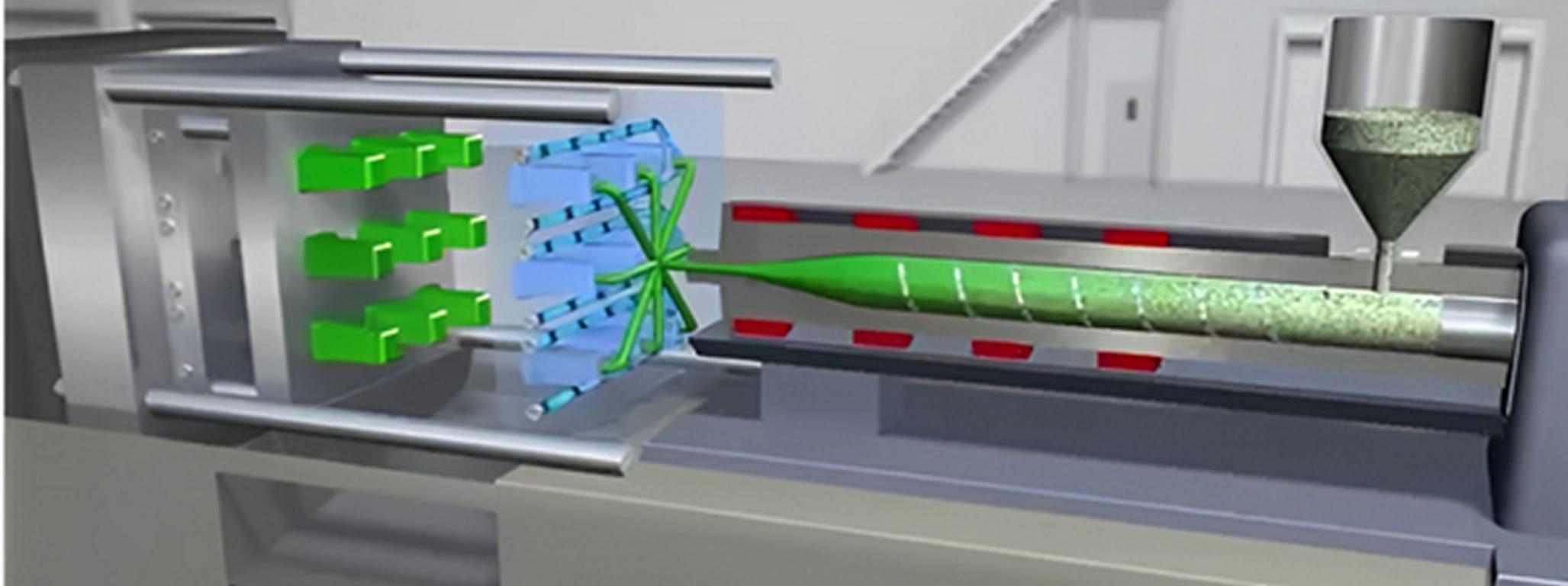
Step-by-step Process of Polystyrene Injection Molding (PS injection molding)
Injection molding with polystyrene is a standard procedure of mass production of detail parts made from the body polystyrene (PS) material. It comprises some critical stages. This may include material preparation, melting of material, and final part discharge. Here is a detailed explanation of each step in the polystyrene injection molding process:
1. Material Preparation
This step is mainly comprised of sub-processes. So let’s discuss them all briefly.
- Raw Material Selection: We choose granules or polystyrene pellets depending on the final product. This may include, for example, polystyrene for transparent products (GPPS), or high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) for products that take sharp impacts.
- Drying: Generally, polystyrene does not tend to absorb water. But for high humidity, the material requires just mini-drying to avoid moisture defects in the molding process. If required the material is dried to remove any of the moisture from the material.
2. Melting the Polystyrene
Similarly, this stage also involves certain sub-processes, i.e.;
- Hopper Loading: Here we dry the pellets then they are in turn fed through a hopper into the injection molding machine. Above the feeder is the hopper which supplies the material to the barrel of the machine.
- Heating and Melting: It is provided with heating coils to melt the polystyrene to its softened state, i.e. around 200°C to 250°C. Screw thereat rotates and pushes the material ahead and at the same time mixes and melts the polymer uniformly.
3. Injection Phase
This phase may include the following processes;
- Injection: After the polystyrene has to undergo the second phase. Here it melts and mixes uniformly and becomes homogenized. Then the screw shifts forward swiftly and presses the melt into the mold cavity. The pressure makes sure that the molten polystyrene fills the mold cavity right to the finest detail. So, it can easily achieve the respective part shape.
- Filling the Mold: Mold is made of two halves, which are the core half of the mold and the cavity half. Then these two halves need to be pressed tightly together. The molten polystyrene is then injected into the cavity up to the limits of the mold. This design indicates gates, runners, and vents must be properly designed. So, they can allow even, filling and flow of the polymer melt.
4. Cooling and Solidification
Here the main processes are;
- Cooling Phase: Once the mold cavity is filled with the material it has to cool and solidify. We maintain the temperature using coolant, i.e. water channels. So, it enables the polystyrene to cool fast.
- Solidification: When the polystyrene cools it changes its physical state from a molten state to a solid and assumes the shape of the mold. The cooling time is important because it impacts the geometry and surface finish of the end product.
5. Removal of the Molded Part
- Mold Opening: When the part has been cooled and solidified sufficiently the mold halves (core and cavity) effectively part.
- Ejection: Core pins or plates are used to force the finished part to be ejected from the mold cavity. Special caution should be taken to see that the part is ejected without causing it to be spoilt in some way or the other.
6. Post-Processing
- Trimming and Finishing: It is chocked and after ejection has some extra material like sprues or runners which is usually shaved off. This can be performed manually or through the use of automated equipment.
- Inspection and Quality Control: The molded parts are inspected for any signs of slight warping, sink marks visible through the skin, or improperly filled-in areas. Quality control guarantees that each of the parts received is to the standard needed to complete the whole product.
7. Recycling of Scraps
- Regrinding: Any remains of the material that results from trimming, or any faulty parts, can be crushed up and used in a melt. They can also be mixed with pure polystyrene pellets to reuse the molding processes hence there is little material waste.
Polystyrene Injection Molding Design Guidelines
Designing for polystyrene injection molding requires attention to detail to ensure quality and functionality: So, focus on the following guidelines;
- Wall Thickness: There should always be a standard thickness of the walls. So, it can avoid warping or the structure sinking. Anything between 2-4mm would suffice, but the ultimate thickness is at the manufacturers’ discretion.
- Draft Angles: The draft angles should be included at a range of 1-2° for quick removal of parts from the mold.
- Ribs and Bosses: You should add ribs to support the thin sections and make provision for the location of bosses where screws are to be fitted. So, it can ensure they also have support.
- Corner Radii: Employ large radii of corners in the design part. So, the drastic variations of the material can be kept minimum in the design.
- Gate Location: Locate the position gates at the widest or the thickest part of the product. So, it can ensure that the mold will be filled to the brim and minimize shrinkage.
Polystyrene Material Characteristics and Comparison with Other Materials
Here is the detailed table that provides a detailed comparison of polystyrene and other materials, those include PP, PE, ABS, etc, you can go to how to choose the best injection molding materials page to know more plastics materials.
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) | ABS |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.04 – 1.06 | 0.90 – 0.91 | 0.91 – 0.96 | 1.03 – 1.06 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 240 | 160 – 170 | 130 – 145 | 220 – 230 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 40 – 60 | 25 – 35 | 20 – 30 | 40 – 50 |
| Impact Resistance | Low | High | Medium | High |
| Cost | Low | Low | Low | Medium |
Advantages and Disadvantages of using Polystyrene
Advantages:
Here are some of the advantages include;
- Cost-effective and readily available.
- Very high clarity for completely transparent tasks.
- Non-complex and takes no time to process a large amount of energy.
- It is lightweight with a good dimensional stability class.
- It is a kind of recyclable material that puts it in an environmentally friendly basket.
Disadvantages:
Similarly, the following are the limitations or disadvantages of Polystyrene.
- Poor impact strength and quite vulnerable to cracking.
- Not heat resistant. So, it becomes soft at high heat temperatures.
- UV light resistance is low, and it becomes discolored easily.
- This is a brittle material and it is easy to fracture under pressure.
- Not biodegradable hence is a threat to the environment if discarded or not recycled.
Precautions for the PS injection molding:
So, here are the precautions for the PS injection molding:
- Drying: See that PS is free from moisture to avoid moisture contamination.
- Temperature Control: It is also important to keep a consistent processing temperature to prevent the degradation of the material.
- Mold Design: While designing the structure, incorporate the right angles on the draft. Besides this, make a good provision on how to vent the building to avoid imperfections.
- Ejection: Due to part deforming force concern, you must apply a correct amount of ejection force.
- Cooling Time: The warp and shrinkage are influenced by the time the component spends cooling. So, a good balance must be struck to ensure that it does not impact the part.
Polystyrene Processing Temperature in Injection Molding
The temperature used in injection molding is usually between 200 and 250°C to process the polystyrene. It helps the proper flow of the materials and avoids degrading the material to a level that is not manageable. If the temperature of the polystyrene is too low, the material may not melt properly. So, the mold might not be filled optimally resulting in defects like short shots or underfilled parts.
On the other hand, when the temperature is high the material tends to break and lose its color, and mechanical properties as well as give out poisonous gases. The molding temperature is well-regulated to enable the material to flow well into the cavity. So, it reproduces the part design and provides high-quality products.
Why Sincere Tech Company for Your Polystyrene Injection Molding Parts
Sicnere Tech is one of top 10 plastic injection molding companies in China that offers polystyrene injection molds and custom plastic injection molding parts for wide range to materials, our sinple advantages are listed below:
- Durability: Our injection plastic molds are durable and they hardly get worn out as compared to other materials used in the making of molds.
- Precision: Our provision of high accuracy in mold manufacturing can ensure consistency in every part.
- Cost-Effective: Our services are in the middle of the range where the cost and the quality are uncompromisable.
- Quick Turnaround: We have a rapid turnaround with 101% satisfaction.
- Experienced Team and Staff: We have a large number of staff with hands-on experience in polystyrene injection molding services. They are masters in providing highly precise and best-quality products.
- Customized Solution: We also help with custom design parts.
If you are looking for highly precise and accurate polystyrene injection molding services. Do not go anywhere. Contact us today.

Conclusion
Polystyrene injection molding is a relatively efficient and reasonably priced manufacturing process. It applies to many products. Besides this, PS molding at its best provides good parts with a high degree of clarity and stiffness with proper mold design and processing. However, it has some biases like low impact strength and heat stability of the material. By using the design guidelines, you can gainfully utilize the polystyrene injection molding process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the polystyrene temperature range?
The processing temperature of the polystyrene normally falls between the conditions of 200°C – 250°C.
Q2. Why is polystyrene used in injection molding?
It is mainly used because it is cheap and easy to process. Because it provides rigidity and improved clarity.
Q3. What are the key weaknesses of polystyrene as a material?
The main disadvantage is that it has a low index of rebound. So, it cannot resist heat and it is very brittle.
Q4. Can polystyrene be recycled?
Of course Yes! polystyrene can be recycled, which means the production of such a product can be considered an environmentally friendly process.
Q5. What is the widespread usage of polystyrene?
It is used in packaging, consumer goods, insulation materials, medical applications, automotive elements, and others.






