Designing and creating a plastic product involves idea generation and invention, product engineering, technology, and the constructive fabrication of attractive and efficient-performing plastic products. As the realization of unique and environmentally friendly solutions increases in demand, designers and engineers have to go through several steps, starting with drawings on paper and ending with production. This article discusses the practical aspects of plastics engineered product design and development focusing on specific processes, decision-making factors, and areas necessary to achieve optimum results in the plastics industry.
Understanding of Plastic Product Design and Development?
Plastic Product design and development related to designing new products from plastics. They are a modern process that involves the following steps: Concept, design, and production. This involves aspects such as the choice of materials, adherence to design theories, and manufacturing requirements in coming up with products that suit a certain user need or market demand.
Different Types of Processes Used in Plastic Product Design and Development
Here are some of the common types of processes we can use for plastic product design and development;
1. Injection Molding
This method of molding plastics is one of the most frequently used technologies for creating parts for mass production. It is a process by which a desired shape is created by pouring a heated liquid material which is plastic in this case under a high-pressure chamber and appears in the plastic injection mold in a desired shape already created. In another case when the plastic remains hot, the mold opens and releases the part but the final shape remains that which is intended. It is a highly efficient technique for volume production because the process is fast, and parts can be produced with close tolerances and very little material being used up.

2. Blow Molding
Blow molding is particularly applied for the manufacturing of hollow products made of plastic materials such as bottles and containers. The first step involves softening the plastic using heat and then pouring it on a mold. Air is then forced into the mold, and the molten plastic is forced into the hollow shape of the inner surface of the mold. When it comes to the idea that blow molding is good for products that have to be lightweight, resistant to impact, and should have the ability to contain a liquid.

3. Thermoforming
It is mainly comprised of heating a plastic sheet and transforming it into a flexible form of plastic. The material is then draped over the mold and via a vacuum-forming process is drawn over the surface of the mold and leaves when the material cools. Thermoforming is more widely applied in the packaging industry, disposable trays, and containers. So, this method is characterized by relatively low costs and allows the creation of thin light products in large quantities.

4. Rotational Molding
Rotational molding or roto-molding is a slower method of molding that is more appropriate for producing large empty articles such as tanks, playing equipment, and boats such as kayaks. Here, powdered plastic is put into a mold that is then heated and is also compounded on a two-plane system. As the mold rotates the powder melts and the bonding of the powder to the interior walls of a mold is done providing a strong product without seams. It is suitable for the generation of an extensive and rather thin-walled container including varying wall thickness.

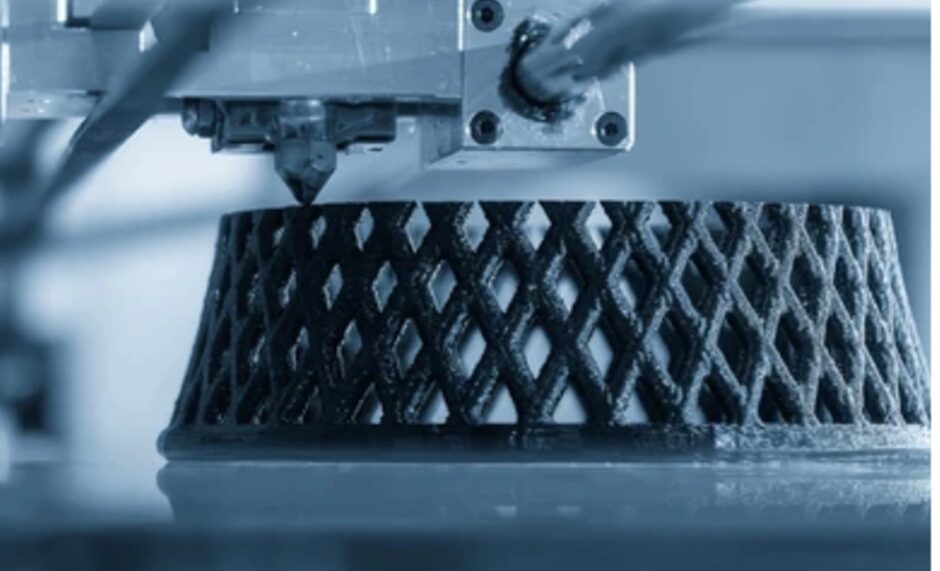
5. 3D Printing
3D printing or Additive manufacturing process involves the construction of an object using a physical model created from a computer source. While most other technologies are removal- or casting-based, 3D printing enables direct control of intricate surface geometries and voids. Because it can make a physical model of the design without the use of the costly mold, it is frequently used for prototyping. It is also appropriate to use if a production run is small or on assemblies that require specific materials.

Comparison of all Types of Processes Used in Plastic Product Design and Development
The following is a detailed comparison of all types of processes used in plastic product design and development;
| Process | Description | Ideal for | Strengths | Limitations | Cost |
| Injection Molding | Molten plastic injected into molds | High-volume parts | Consistent quality, low per-unit cost | High tooling cost | High |
| Blow Molding | Air-inflated molding for hollows | Bottles, containers | Lightweight, fast cycle | Limited to hollow shapes | Moderate |
| Thermoforming | Heated plastic sheets molded | Packaging, trays | Low tooling cost, fast setup | Thin walls, limited shapes | Low |
| Rotational Molding | Mold rotation for large hollows | Tanks, large durable items | Uniform walls, low tooling cost | Slow cycle, limited detail | Moderate |
| 3D Printing | Layer-by-layer from a digital model | Prototyping, complex shapes | Customizable, no tooling needed | Slower, limited material strength | Variable |
Complete Plastic Product Design Process
Let’s discuss all the plastic product designs and development process step-wise in depth;

1. Defining Requirements
The initial activity in the life cycle of a plastic product is the identification of form, use, and performance characteristics. This encompasses its usage, more of who will be using it, and issues like; durability, flexibility, or resistance to different environmental factors.
2. Create a Preliminary Concept Sketch
Designers then make what are called, which are in fact sketches that help in imagining the product’s appearance and the general construction. These sketches help in preliminary stakeholder meetings by providing a brief vision of the product’s appearance and utility.
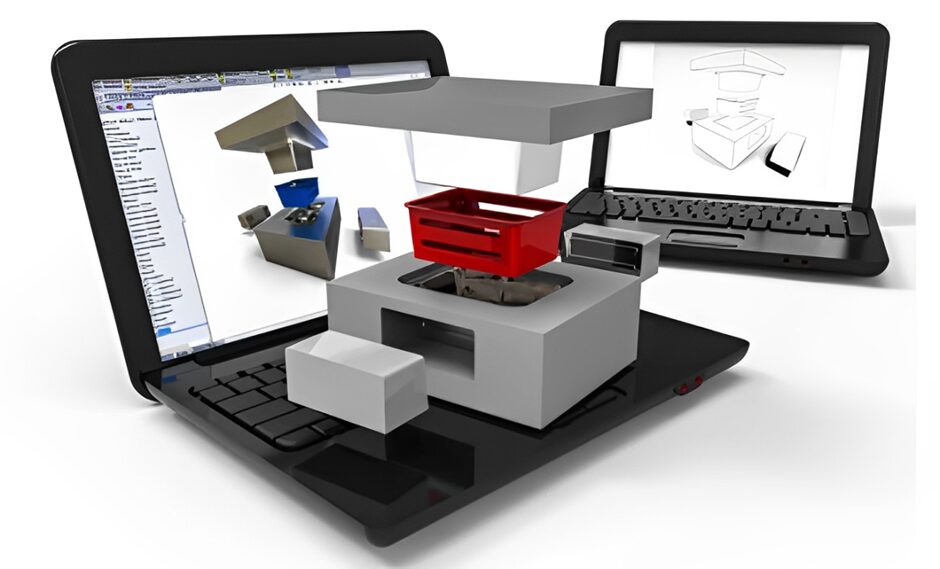

3. Initial Materials Selection
Once the concept of creation has been resolved, designers choose the possible materials depending on their characteristics such as strength, flexibility, weight, cost, and recyclability. This step helps to select material that meets the requirements and application of the final product on the market.

4. Design Part by Material Properties
At this stage, the structure of the product becomes defined concerning the properties of the chosen materials’ density, tensile strength, heat resistance, etc. This optimization guarantees that the product is capable of functioning optimally when in the field.
5. Structural Analysis
Structural analysis employs computer-aided simulations and tests to determine the ability of the product to perform as required and as designed. Potential obstacles can hinder the performance of the system and its part throughout the design process, so avoiding them would be best for the designers.

6. Final Materials Selection
After testing, the laboratory results and additional evaluations are used to solidify the designers’ decision on the most suitable materials for use. This step assists in verifying that the material chosen will meet the needs the product was intended for and its expected life cycle.
7. Modify the Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
In DFM report (design for manufacturing), concentrates on the design changes to achieve a better manufacturing process, and less cost and time. These changes may include the reduction of parts, the form design for the chosen manufacturing process, and the shapes of the parts.
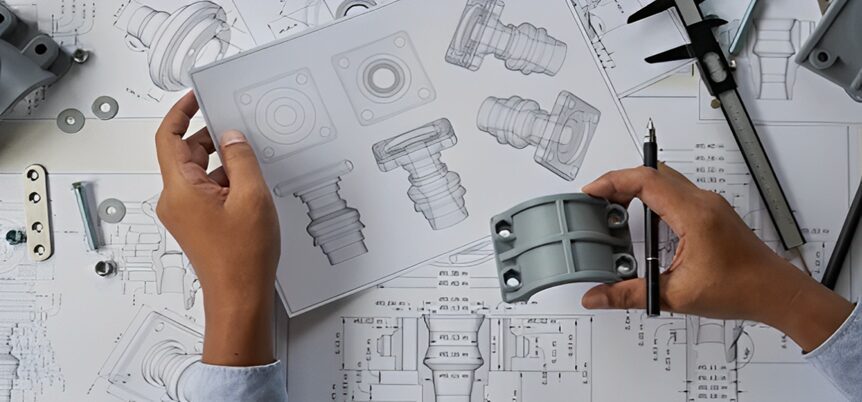
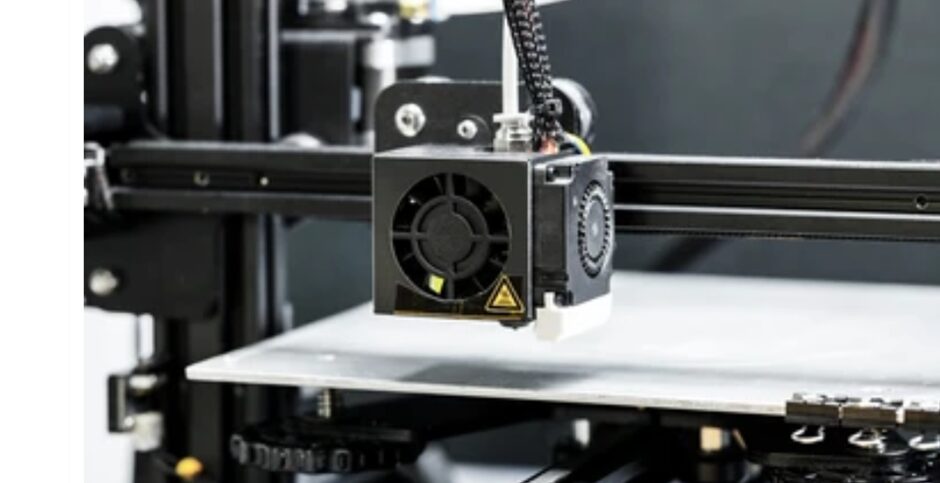
8. Prototyping
Prototyping means developing a first full-scale implementation of the design. This model enables the designer and the engineer to have an idea of how the final product looks, and operates and how it can be used. Prototyping results are useful since they dictate how the final product is modified to meet quality requirements before the mass release.
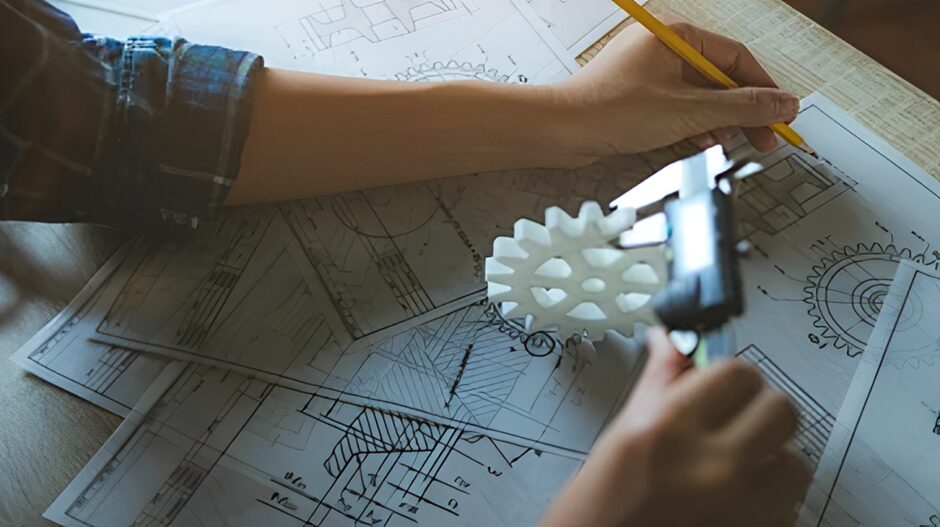

9. Tooling
Tooling is the manufacturing of tools and mold requirements before a large-scale manufacturing process begins. For plastic products, it is often making specialized dies used in forming steps such as injection molding or blow molding which depend on the shape and size of the final product required.
10. Production
Finally, production begins. In this last stage, the actual production of the plastic product is done following the design and specifications that have been considered perfect. Control of product quality is critical, especially when evaluating whether a particular product meets the relevant quality standards as well as the expected performance levels. This step also involves packing, assembling in case they were disassembled for easier handling, and preparing them for shipment.
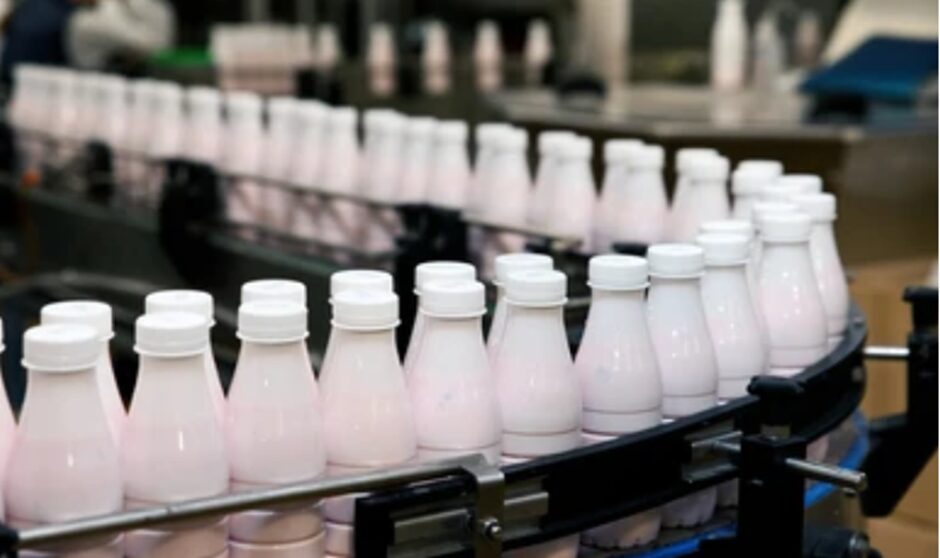

Consideration while Identifying the Appropriate Process for Plastic Product Development
So, here are some facts you must keep in mind while choosing an appropriate process;
- Product Complexity: Think of the complexity of the design and whether a certain selected process type can handle it.
- Volume Requirements: Consider the required production volume, because some processes are appropriate for low- or high-volume production.
- Material Compatibility: This means that the chosen manufacturing process must align with the desired range of materials to be used.
- Cost Implications: Consult over tooling costs, as well as material and production costs, in order to determine how high quality correspondingly is valued on this production line.
- Lead Time: Estimate the time taken to transit from design to production and select a process that best suits the project’s time frame.
Pros of the Optimal Process for Plastic Product Design and Development
The following are different pros of using optimal processes for plastic product design and development;
- Cost Efficiency: There is always the maxim that if processes are designed properly there can always be a way of making products cheaper and hence making more money.
- Design Flexibility: Solutions enable distinct designs and the ability to make changes more rapidly.
- Scalability: Such a flow chart promotes efficiency in production as the processes can easily scale through the production line to meet the market needs.
- Quality Control: This implies that well-organised operations lead to product standardisation hence improving product quality.
- Sustainability: It can be made environment friendly, using recycled things and waste reduction in the processes.
Limitations of the Process for Plastic Product Design and Development
The following are some limitations of Plastic Product Design and Development;
- High Initial Investment: There are a few processes where tooling can be expensive, for example, injection molding.
- Material Limitations: Not all processes should be able to accept or process all types of plastic material.
- Complexity in Design Changes: Changes made after the tooling phase can be very expensive and time-consuming.
- Production Constraints: Some of the methods are restricted by the size or shape of the product that is being produced.
- Waste Generation: Certain activities that are carried out may generate some waste that needs to be dealt with in the right manner.
Applications of the Optimal Process for Plastic Product Development
Some of the most common uses of the Optimal Process in the manufacture of plastic products are as follows:
- Consumer Electronics: Designing casings and parts for such portable gadgets as mobile phones and notebooks.
- Automotive Parts: Producing high-strength and low-weight materials that would help improve vehicle performance.
- Medical Devices: Manufacturing clean and accurate parts for medical applications.
- Packaging Solutions: Creating new and environmentally friendly packaging solutions for different products.
- Home Goods: Creating bowls and other kitchen utensils, chairs, tables, and cupboards among other household necessary items.
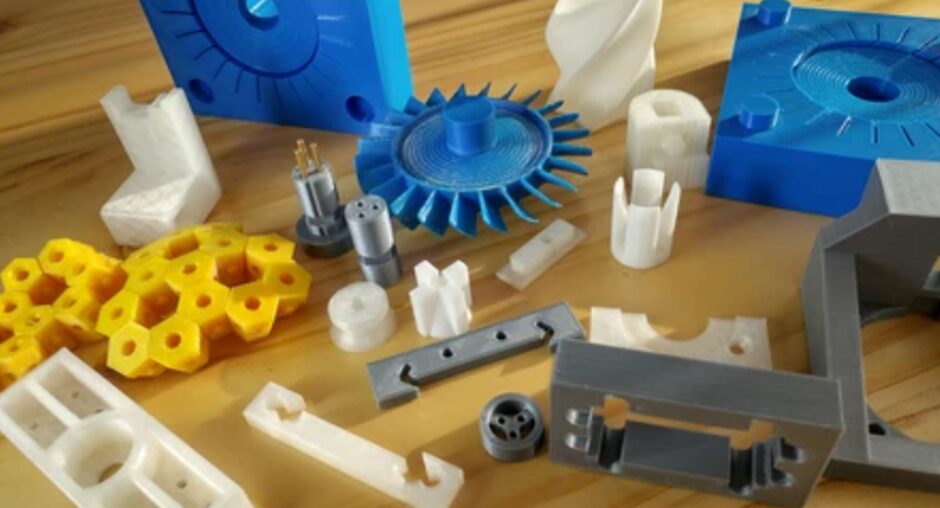

Conclusion
In conclusion, the design and development of plastic products is an important step for designing functional products that meet market requirements for enhanced performance. This is why it is necessary to consider the specific stages and important factors of the process as the case demonstrates, with the right approach companies will be able to successfully navigate a competitive environment. Therefore, one must stay current knowledge about future progress in plastic product design as far as new technologies and materials are concerned.
There are many plastic products that will design with electric components, like PCB borad and many other electronic related product, on this electronic product design and development will more complex then single plastic product design and development, if your project that will have electronic components in it, welcome to contact, we are professional in this field.
FAQs
Identify what material selection does to plastic product design.
It is also an important element of product development since material choice dictates the product’s lifespan, use, and effectiveness.
How long does it take for a new plastic product to go through its developmental stages?
This may take from several weeks to several months depending on the complexity of the product design but may take at least 3 months from concept to production.
What are the typical substrates in plastic product design?
They include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride also known as PVC. So all of them have these characteristics and are therefore suitable for various uses.
Can design changes be made after the tooling phase?
Yes, it’s possible to make changes. However, it will cost more time and money, so it is better to do the last changes before tooling.
What role does prototyping play in product design?
It involves creating a model of the proposed product. So, the principal problems can be diagnosed before actual production.
Is it possible for plastic products to be developed sustainably?
Yes, most processes have embraced the use of recycled products to reduce the adverse effects on the environment.

