Nylon 66 has 30% glass fiber reinforcement and is recognized as an engineering plastic material. It has high mechanical strength, thermal stability, and high chemical resistance. This material is produced with 30% glass fiber content and strengthens the performance of basic nylon material for several industries’ high application demands. Besides this, it is used extensively for automotive parts, electrical connectors, hardware, bearings, gears, etc., PA66 GF30 is at the cornerstone of most engineering applications today,
There is another similar pa6 gf30 material which is related to this material, soemtimes when you have low budget nylon6+gf30 will be one of most options, go to PA6 GF30 page to know more about this smiliar materials.
So, knowledge of its characteristics and processing methods will help choose the most suitable material for a particular use and get the best outcomes with longevity.

What Does PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 GF30) mean?
PA66 GF30 or Polyamide 66 with 30% glass fiber reinforcement shows high-performance thermoplastics, used in engineering industries. It has incorporated the best attributes of Nylon 66 including strength and high toughness and the additional quality of glass fiber reinforcement which increases the mechanical characteristics of the composite material. Those outgoing layers are specifically appreciated for their capacity to operate in miserable conditions.
This feature helps qualify the material for use in any setting that demands solidity. PA66 GF30 is used frequently in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications since the product’s highest reinforcement grade is crucial. However, it has numerous applications that require the highest performance and durability.
Step-by-Step Process of Manufacturing PA66 GF30
So, here is a complete steps procedure for manufacturing PA66 GF30 plastic;
1. Raw Material Selection
- Nylon 66 Resin: The first and most important type is the Nylon 66 (polyamide 66) due to its inherent mechanical properties.
- Glass Fibers: Only choose a high-quality glass fiber; normally glass fibers form 30% of the total composition, for strength and thermal characteristics.
2. Compounding
- Blending: N66 resin and glass fibers are mixed uniformly in a high-velocity, high-shear mixer using a twin screw extruder. This helps achieve proper dispersion of glass fibers uniformity in a nylon matrix.
- Additives: Add ingredients (i.e. stabilizers, colors, or agents to enhance processing and application properties).
3. Melt Processing
- Extrusion: The material is again mixed with the blending material heated and passes through die-making strands or pellets. This step is crucial since it helps establish a uniform distribution for the glass fibers within the nylon matrix.
- Cooling: Most strands are immersed in water to cool them and harden the material before breaking them into pellets.
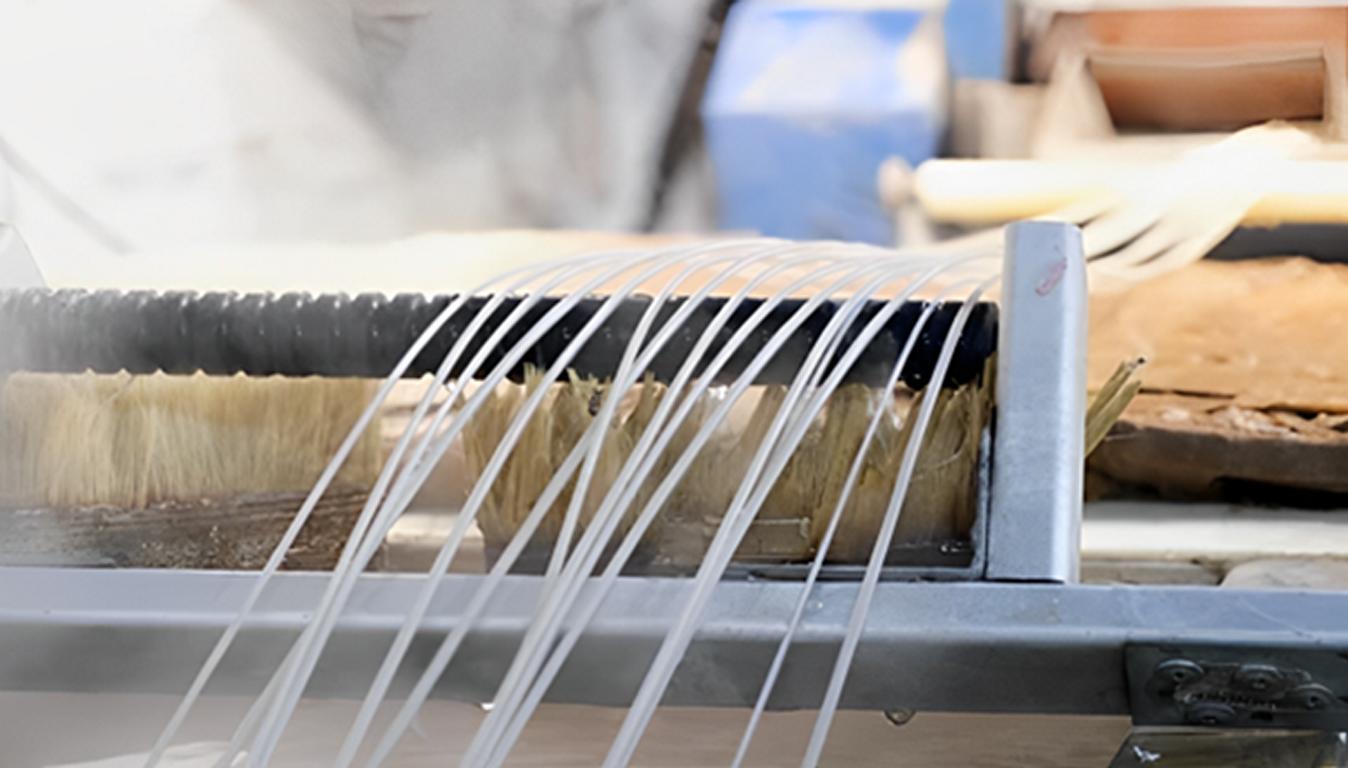

extrusion PA66 GF30 material
4. Pelletizing
- Cutting: After cooling the filaments are chopped into packaged solid cylindrical tumblers which are then gathered to be stocked or processed.
- Quality Control: The final pellets also pass through a quality test in a bid to meet the set standard by size, moisture content as well as mechanical test.
- Injection Molding or Other Forming Techniques:
- Molding: The PA66 GF30 pellets are heated and injected in the Injection molding machines and are poured into molds. This process favors the formation of parts such as automotive injection molding parts, electrical plastic housings, custom molded prodcuts and among others from the material.
- Alternative Forming: Other processing techniques used may include blow molding or compression molding where the application demands.
5. Cooling and Demolding
- Cooling: Once the mold is filled the material is left to set until the molding process is repeated or the product is removed. The time that passes while cooling determines the shape and size of the produced bread.
- Demolding: Once the parts have been polymerized, the molds are cooled and then the completed parts are ‘usian’.
- Post-Processing:
- Trimming and Finishing: Mold flash or sprue that accompanies the molding process might be removed. More other final coatings operations, including; cutting or surface conditioning.
Different grades and variants of PA66 GF30
Here are different PA66 GF30 Plastic grades and their variants available in the market; Let; ‘s explore their composition and applications in different industries;
| Grade/Variant | Glass Fiber Content (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Continuous Service Temperature (°C) | Applications |
| PA66 GF30 | 30 | 80-100 | 120-150 | Automotive components, electrical housings, industrial machinery parts |
| PA66 GF15 | 15 | 70-90 | 120-140 | Consumer goods, structural components, electronic devices |
| PA66 (unreinforced) | 0 | 60-80 | 90-110 | General-purpose applications, low-load components |
| PA66 GF50 | 50 | 90-130 | 130-160 | High-stress components, automotive parts exposed to extreme conditions |
| PA66 GF20 | 20 | 75-95 | 120-145 | Medium-load components, industrial applications, housing for tools |
Basic Properties of PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 GF30)
Let’s discuss some of the important characteristics of PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 GF30)
1. Mechanical Properties:
- Tensile Strength: It usually varies between 80 and 100 MPa, thus providing stronger resisting pulling forces.
- Flexural Modulus: These constitute 10-15 GPa meaning that the material exhibits good stiffness and offers good resistance to bending.
- Notched Izod Impact Strength: Rises in the range of 5-10 kJ/m² which allows the material to possess a moderate ability to withstand impacts.
2. Thermal Properties
- Continuous Service Temperature: These yarns possess mildew-resistant properties thus suitable for heat endurance up to 120°C to 150°C.
- Heat Deflection Temperature: In general, it is stable at about 220°C and thus favors heat stability.
3. Chemical Resistance
- Solvent Resistance: Resistant to oils, greases, and fuels, the composite material will find uses and applications in harsh usage conditions.
- Moisture Absorption: Rich in moisture and it can swell, which sometimes may affect the culinary mechanical characteristics and dimensional stability.
4. Dimensional Stability
Low Warpage: Glass fibers impart improved dimensional stability; and reduce warpage and shrinkage during processing and usage.
5. Processing Characteristics
Melt Flow Index: Normally ranges between 10 to 30 g/10-min which characterizes its flow behavior during processing, especially in injection molding.
Ease of Molding: It can be processed employing the conventional techniques for top processing including injection molding and extrusion.
6. Electrical Properties:
Dielectric Strength: It possesses a high dielectric strength the product is ideal for applications where electricity is involved and insulation.
7. Density
Density: About 1.3 to 1.4 g/cm³ – a little more than the unfilled nylon, which adds to the strength of the product.
Critical Material Standards And Specifications For PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 Gf30)
So, the following are commonly used material standards and specs for PA66 GF30
| Standard/Specification | Description |
| ASTM D638 | Measures tensile properties (strength, elongation, modulus). |
| ASTM D790 | Assesses flexural strength and modulus. |
| ASTM D256 | Evaluate Izod impact resistance for durability. |
| ISO 527 | International standard for tensile properties. |
| ISO 178 | Provides flexural properties data for structural applications. |
| ISO 180 | Determines Izod impact strength internationally. |
| UL 94 | Tests flammability ratings (e.g., V-0, V-1, V-2). |
| RoHS Compliance | Ensures materials are free from hazardous substances. |
| REACH Compliance | Ensures chemical safety in the EU. |
| FDA Compliance | Ensures safety for food contact applications. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 GF30)
The following are the pros and cons of PA66 GF30 (Nylon 66 GF30);
Pros
- High Mechanical Strength: Extremely good tensile strength with high rigidity properties that are useful for load bearing.
- Thermal Stability: This is compatible with properties at higher temperatures, properties that can be used up to 120°C (248°F).
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to different forms of chemicals, oil, and solvents in the market.
- Dimensional Stability: Little warpage close to the bulb and the cylinder retains its shape under changes in conditions.
- Versatility: Readily formed into intricate forms and shapes by most conventional procedures.
Cons
- Higher Production Costs: Evidence suggests that they are more costly to produce than the unreinforced nylons.
- Limited Flexibility: Organo sheet is not suitable for applications wherein the material may be required to be flexible or possess high impact strength.
- Moisture Absorption: May swell and cause a change in the mechanical properties of the material.
- Recycling Challenges: Restrictions in external recyclability and potential harm to the environment.
- Processing Difficulties: Difficult to work with due to glass fiber reinforcement, this material also takes a considerable toll on molds and machines.
Applications of PA66 GF30
PA66 GF30 is well known for its good mechanical performance and it can be used in a lot of fields. Here are some common applications:
- Automotive Components:
- Brackets and Supports: Applied in structural parts that need high strength and stiffness.
- Housings for Electrical Systems: Especially for parts that are exposed to heat and vibration.
- Under-the-Hood Applications: Structural parts such as the air intake manifold and engine cover can also benefit from the uncomplicated thermal balance of PA66 GF30.
- Electrical Connectors: They offer excellent dielectric properties, and mechanical strength good for use in the manufacture of electronic equipment and gadgets.
- Industrial Machinery Parts: In gears, bearings, and all other applications where high wear resistance and load-carrying capacity are desired.
- Consumer Goods: Used in products that have to be long-lasting, tough, and relatively light structures, for example, automobiles, power tools, sports equipment, and home appliances.
- Aerospace Applications: Appropriate for light and highly loaded parts that are resistant to severe environmental conditions.

Environmental Factors of PA66 GF30
The following are common environmental factors for PA66 GF30 Plastic;
- Production Emissions: Emissions resulting from the production process.
- Resource Consumption: Think about the durability of the raw materials.
- Biodegradability: PA66 GF30 is a non-biodegradable polymer and therefore the next step is to determine the feasibility of recycling it.
- Lifecycle Assessment (LCA): Perform an LCA in order to determine the environmental load from the product’s life cycle.
- Impact of Additives: Consider the environmental effects of all the additives that the enterprise may incorporate into its products.
When Should I Use PA66 GF30?
Use PA66 GF30 in applications where the following criteria are important:
- High Mechanical Strength: Whenever the application is likely to have pa66 gf30 parts that must endure high levels of stress and load.
- Thermal Stability: When components will be subjected to combined; operation conditions like in automobiles and industrial practices.
- Chemical Resistance: If the material is to be used in applications where contact with strong acids, oil, solvents, etc.
- Dimensional Stability: The applications such as dimensional accuracy and stability of structures used in varying temperatures and humidity environments call for tolerance control.
When Not to Use PA66 GF30
Consider avoiding PA66 GF30 in the following scenarios:
- High Flexibility Requirements: PA66 GF30 may be too rigid to meet the application needs in a situation where the nature of the application demands materials that can flex or bend to a large extent.
- Extreme Moisture Environments: It is moderately resistant to water but when exposed to water prolonged changes the dimension of the material and mechanic properties are affected.
- Cost-Sensitive Applications: If cost is a concern, explore options since PA66 GF30 can be more costly than unreinforced nylon or other materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this material has high strength and thermal and chemical resistances and is therefore referred to as PA66 GF30 or Nylon 66 GF30. It is also used in automotive, electronics, and in the production of other consumer goods. Despite these benefits, however, there are limitations to its use and users should consider these limitations, as well as the nature of the application for which it intends to be used, in order to achieve the best possible results.
FAQs
What is the application of this material in industries?
PA66 GF30 has a vast application in automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Is it safe to use PA66 GF30 for food contact applications in the food industry?
PA66 GF30 does not come standard within FDA guidelines for direct food contact so it should not be used in applications that involve direct food contact unless otherwise designated, you can go to food grade plastic page to check the materials which are sued for food industry.
How much of a temperature can PA66 GF30 undergo before breaking?
Depending on the formulation, PA66 GF30 has the capability of holding continuous service temperature of up to roughly 120°C (248°F).
Is PA66 GF30 recyclable?
Availability of recyclers accepted PA66 GF30 is still scarce and when disposing of merchandise made from this material its environmental effects should be considered, when you use plastic injection mold technology with PA66 G30 to make the plastic injection molding parts, PA66 GF30 can be recycled.
How does this PA66 GF30 grade perform in comparison with other types of nylon?
In mechanical properties and thermal performance, PA66 GF30 is superior to unreinforced nylon and among nylon materials PA6.

