Medical Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Overview
Medical injection molding is critical when it comes to creating medical plastic parts. Especially, when these parts need to be thin-walled and free from defects because of their applications in areas like syringes and implants. The medical injection molding process provides a cost-effective, productive, and repetitive manufacturing solution. But it has some issues such as high injection mold cost. Nevertheless, effective patient communication is essential to meet healthcare standards. It ultimately helps enhance the patient’s health status. So, in this article, we will explore everything about medical injection molding.
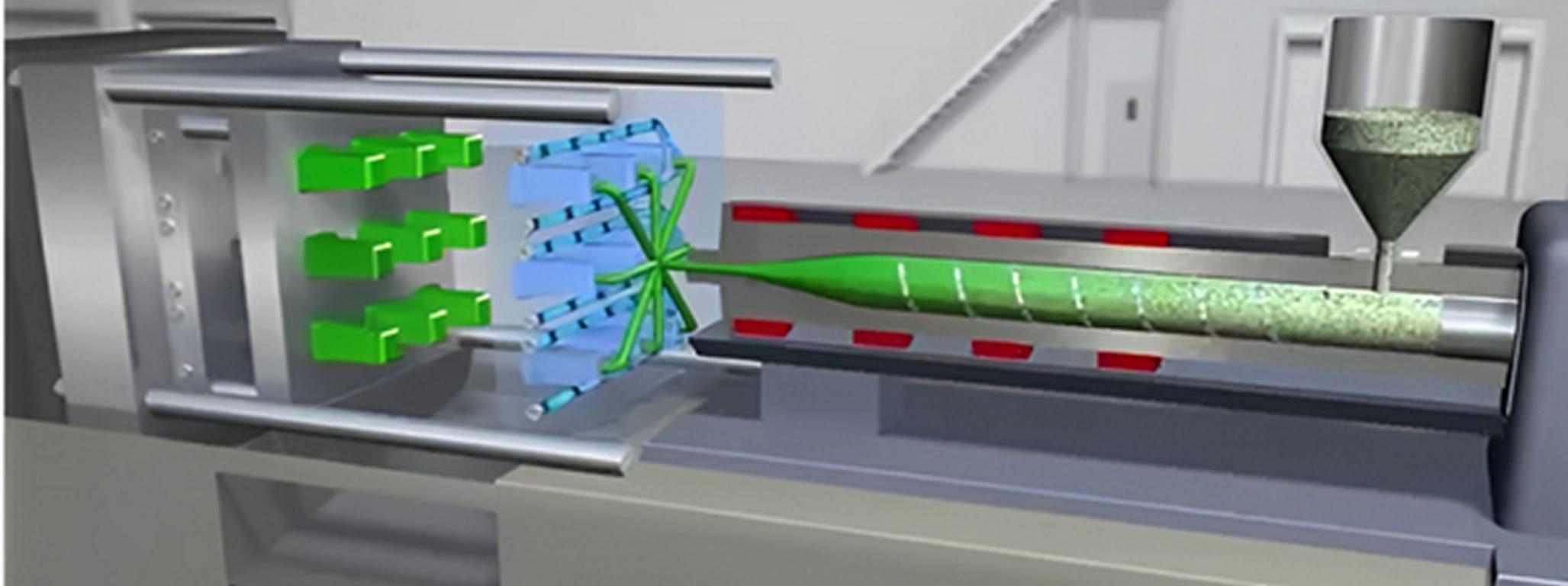
What is Medical Injection Molding?
Medical palstic injection molding constitutes one of the vital operations required to manufacture plastic medical devices and parts. It remains significant for the healthcare sector because of the prospect to manufacture accurate, top-notch, and reliable medical device plastic parts and instruments. It is also known as plastic injection molding when it shapes plastic material. Its application value ranges from accuracy, speed, material compatibility, cheapness, and accordance with highly stringent medical standards.
Complete Injection Molding Process
The medical injection molding process includes several key steps, each important for producing high-quality medical plastic parts and components.
1. Design and Prototyping
One of the processes in medical plastic injection molding is to design the expected medical plastic part and make a prototype of the design. An important requirement of the design of a medical device is its functional requirements such as dimension, form, and limit of error. CAD is widely employed to produce design documentation of the part to realize the vision of the design. Prototyping is beneficial in the testing of the design before implementation of the design in large-scale production.
2. Medical Mold Creation
Another part after deciding on the design is to cast a medical mold around it. They are usually constructed of high-tensile steel ( 1.2343, S136, 8407, etc.) to withstand the operational pressure and temperatures. The medical injection Mold is then cut to exact specifications in terms of the DESIGN and ALL the features and details that the mold requires.
3. Injection
After medical mold have been manufacutring, then medical injection molding process begain, during the injection phase, the selected material (often plastic) is melted to increase its temperature to make it molten. This molten material is again injected into the mold’s cavity under high pressure. This pressure the material assumes the shape and gets molded into the details of the mold as required. For metal injection molding as the name suggests, the material used is powdered metal and this is injected.
4. Cooling
Once the medical mold caivty is completely full filled then cooling system will start to cool the cavity, this will solid the melt plastics in the cavity to get the medical shape plastic parts. Cooling time for each material or a single material depends on the part complexity. Temperature control is important since mold failure including warping or insufficient filling may occur.
5. Ejection
After the material has set and attained room temperature, the mold is then opened and the medical plastic part is removed by ejectiion system. It can include ejector pins or other techniques that ensure the part is safely removed without it getting spoilt.
6. Post-Processing
If required, several post-processing steps are needed and would be described according to the specifics of the particular analysis conducted. These involve cutting off unwanted material, putting in extra elements, or performing tests on the product. It involves the final refinement to meet all the necessary standards and requirements.

Material Selection for Medical Plastic Injection Molding
Proper materials for Medical Injection Molding are chosen based on different factors. These may include biocompatibility, toughness, and capacity to answer medical requirements. So, the common materials include:
- Polyethylene (PE): It is highly used for tubing, catheters, and fluid transfer parts and components because of the flexibility of this material added to its chemical resistance property. Go to polyethylene injection molding page to know more detail.
- Polypropylene (PP): Perfect for syringes, medical containers, and surgical tools. Because they are hard wearing and can be easily sterilized. Go to polypropylene injection molding to know more about PP materials
- Polycarbonate (PC): It has wide applications in oxygenators, infusion connectors, and surgical tools. It is mainly due to its high tensile strength and clarity. Go to polycarbonate injection molding to know more details.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): They offer flexibility and softness; it is ideal for making seals, grips as well as components with a soft touch on medical devices. Please go to TPE injection molding and is TPE safe page to know more about TPE and TPE molding parts.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): Bright metal that has found numerous applications in manufacturing implants, spinal appliances, and other call functions. It is based on its mechanical characteristics and application compatibility. Got to PEEK plastic injection molding page to knore more details.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): This is often used in deformable tubes, Blood bags, and other products that deal in the management of fluids.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Frequently applied for housings and enclosures of medical devices due to its characteristics, including impact resistance as well as easy to molding. Go to ABS injection molding and is ABS plastic safe page to know more about ABS.
- Polyurethane (PU): It is used in medical applications that need elasticity like uses in wound dressing, catheters, and surgical drapes among others.

Applications of Medical Injection Molding
Medical injection molding is applied to manufacture several medical apparatus and parts. The attractiveness of the method is in its high accuracy and ability to produce very detailed parts, which is crucial for the elements of the modern healthcare sector. Key applications include:
1. Syringes and Needles
Syringes and needles are necessities in the medical profession in the administration of drugs and blood samples. Injection molding guarantees the production of such products with high accuracy to eliminate occasions like leakage or fluctuation in dose. The process allows the production of slick, slim, and non-tapered needles and syringes which are critical for patients’ well-being.
2. Diagnostic Devices
Diagnostic devices in the assortments of test kits and image form are produced through injection molding of critical and intricate parts to ensure they will function as intended. For instance, the elements incorporated in the blood glucose meters, or pregnancy tests, are manufactured through injection molding. The complexity of the formation of certain details and small tolerances should predetermine the work and the accuracy of the readings of these devices.
3. Surgical Instruments
Some injection molding products include handles, grips, and housings of surgical instruments. Exploiting the concept means that designs with ergonomic features adaptable to the user’s needs can be developed and incorporated into healthcare settings. These instruments must be precise, to facilitate the successful effective of the intended functions during the critical procedures.
4. IV Components
Components used in intravenous operations such as drip chambers, connectors, and valves for IV mixtures are made through injection molding. These parts should also produce very high levels of cleanliness since they are directly connected to the human body, and accuracy in terms of their functionality, and durability so that they can deliver fluids or medication to patients without breaking down.
5. Implants and Prosthetics
Other products that require precise accuracy, and flexibility, such as medical implants or prosthetics like hip replacements or dentures benefit from injection molding. This approach enables the fabrication of intricate designs and forms to be designed and made to the requirements of each patient making for enhanced efficacy and patient satisfaction.

Comparison of Medical Injection Molding with Other Manufacturing Technologies
As said earlier, different manufacturing technologies are utilized in the medical device industry to manufacture components and devices. Every technique is the best in its strengths and weaknesses. Besides this, the method used for a certain object will depend on such factors as accuracy, material type, scale, and cost. This section provides a detailed comparison of medical injection molding with other prominent manufacturing technologies;
So, in comparison to other technologies:
- 3D Printing: It has high design flexibility and short turnaround time. However, the use of this process is most appropriate in the development of prototypes or short production runs. So, it can be costly to use in large-scale production.
- CNC Machining: Allows high accuracy and variability, yet expensive than simpler designs and not optimal for mass use.
- Blow Molding: General purpose, ideal for high-volume production. However, it has a high degree of product standardization, is low on material variety and design freedom, and a time than injection molding.
Besides these, the following table will help you understand the comparison of injection molding and other techniques.
| Feature | Medical Injection Molding | 3D Printing | CNC Machining | Blow Molding |
| Precision & Consistency | High | Moderate to High | High | Moderate |
| Material Variety | Wide (Medical-grade plastics) | Broad (Polymers, Metals) | Broad (Metals, Plastics) | Limited (Mostly Plastics) |
| Scalability | Excellent for high volumes | Limited (Best for prototyping/small runs) | Moderate (Best for low-medium volumes) | Good for high volumes |
| Lead Time | Long (due to tooling) | Short (No tooling required) | Moderate | Long (due to tooling) |
| Cost Efficiency | High for large production runs | High for prototyping, costly for volumes | Costly for complex designs | High for large volumes |
| Surface Finish | Smooth (Minimal post-processing) | Rougher (Requires post-processing) | Smooth (Can be polished) | Moderate (Varies with design) |
| Design Complexity | Moderate to High | High | High | Limited |
| Biocompatibility | High (Medical-grade materials) | Depends on material | High with appropriate materials | Limited |
The Significance of Medical Injection Molding
The importance of medical injection molding therefore centres around its capacity to produce products that can cope with the high standards required in the medical field. Several factors underscore its importance: Several factors underscore its importance:
1. Precision and Accuracy
Tolerances and geometry of medical devices usually have strict and complicated dimensions. Injection molding offers the accuracy required to manufacture components with as few discrepancies as feasible so that individual elements work as envisaged. This is especially the case in items that need accurate tolerances such as medical instruments, measuring tools or any other instruments to be used in surgery or diagnosis.
2. Consistency and Reliability
Repeatability is an important aspect needed in the manufacturing of medical devices to get reliable products in every batch. Injection molding repeatability and dimensional stability are crucial when it comes to matters concerning the quality and safety of medical products. This consistency reduces the formation of defects and also increases the assurance that all the devices produced conform to the required standards.
3. Cost Efficiency
Injection molding is one of the most efficient manufacturing processes, especially for large-scale production. The process minimizes the consumption of material and increases efficiency in the cost of production. In the overall health care sector, this efficiency can translate to lower costs of the associated devices thus improving the availability of the devices.
4. Material Versatility
It can be noted that the major types of material offered for medical injection molding include the following: This versatility of biodegradable polymers enables the manufacturers to choose the materials according to the necessity of the medical device, for instance, biocompatibility, mechanical strength, or flexibility.
5. Design Flexibility
The injection molding is suitable in the creation of designs with high complexity that might be difficult to achieve through other techniques. It also fosters flexibility in creating new medical devices that can improve people’s lives and the efficiency of healthcare equipment.

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Medical Injection Molding
As we know, every rose comes with its throne. Similarly, medical injection molding has its benefits. But still, it has certain limitations. So, let’s discuss both of its merits and demerits concisely;
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High precision and consistency | High initial tooling costs |
| Wide material variety | Long lead times for tooling |
| Scalable for high-volume production | Design limitations on geometry |
| Cleanroom compatibility for sterility | Material waste during production |
| Strong and durable parts | Environmental impact due to energy use |
| Minimal post-processing required | Quality depends on mold design |
| Biocompatibility | Limited material choices for specific uses |
Conclusion
Medical injection molding is highly implemented in the manufacturing of medical devices owing to its accuracy, reliability, and speed. It can create multi-face and high-accuracy components with a high production rate. So, it is vital for developing a vast array of medical devices. The mechanism fosters creativity, and compliance with the state standards, and contributes to efficiency, security, and economical processes that affect the clients’ health conditions. With the increasing development of technology, medical injection molding will continue to be an important technique.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it possible to use Medical Injection Molding to produce implantable devices?
An: Absolutely yes, devices like PEEK and many medical-grade thermoplastics are appropriate for the fabrication of implantable devices. These are biocompatible and fulfill the requirements of permanent implantation of the materials into human body tissues.
Q: In its Medical Injection Molding service guarantee the sterility of molded products?
An: Medical Injection Molding can be done with the equipment being situated in injection molding cleanroom. So, they help improve the cleanliness of the equipment. Moreover, it must be noted that used materials may be suitable for sterilization by autoclaving, irradiation, or ethylene oxide.
Q:What are the factors that affect the Medical Injection Molding cost?
An: These factors may include;
- Some of them are the complexity of the mold design.
- The type of material used in the manufacturing of the mold.
- The volume of production required and additional requirements such as manufacturing in clean rooms.
- Fixed costs are high when developing the actual tooling to create the mold.
- The variable costs of producing each product are very low during the subsequent mass production.
Q: What are the Medical Injection Molding project’s lead times?
An: Lead times can be fixed or flexible depending on the type of mold, type of material, and or quantity to be produced. First-time tooling may consume several weeks. However, it is easy to get into mass production after tooling once a mold is designed.
Q: What is Medical Injection Molding’s approach to design complexity?
An: Medical Injection Molding to intricate designs, as well as complex shapes, can easily be molded. The process has a high level of accuracy. However, some constraints are present associated with aspects of the thickness and geometry of the walls. Mold design is performed using innovative tools and complex simulations. So, it can help improve the mold designs for manufacturing purposes.
Q: What measures are implemented in quality control of Medical Injection Molding?
An: Strict regulatory practices are adopted for quality assurance. These may include in-process checking, dimension checks, and biocompatibility test checks. Medical components too are sometimes subjected to regulatory bodies and quality checks with some of the facilities supporting ISO 13485.

