Every business, regardless of its type, has to be innovative to survive in the market. It may apply to any kind of product, including electronic gadgets. So, whether you are a local supplier or run a factory, you must be familiar with it. Your electronic product design should be more unique and creative than other competitors in the market. For this, you must follow the formalities of electronic product design and development.
As you know, people always prefer accurate and efficient products. To meet this demand, you must develop a strategic approach. A product design and development guide can greatly assist you in this endeavor. This article primarily focuses on the manufacturing process of an electronic product in a factory. How do engineers approve of the quality? What factors matter the most? If you are looking for an electronic product design and development service, you are welcome to contact us. We have been offering electronic product design and manufacturing services for over 18 years.
The article typically focuses on explaining electronic products. It explains everything from the design phase to production, certificate, assembly, and packing. However, you may also use this guide for other types of products. But you must be familiar with the technical parameters.

What is Electronic Product Design And Development?
Electronic products comprise three key elements: PCBs, plastic, and metal parts. PCBs play the most crucial role in this case. They are typically the heart of the device, which is why we call them electronic products. However, their main job is to control the electronic flow. On the other hand, structures primarily rely on plastic and metal parts for support. Typical examples are smartphones, laptops, hair dryers, trimmers, and many more.
Electronic product design is the first step in manufacturing. It is not a one-time task; instead, it is an iterative process. It begins with a rough idea. Then, the engineer or designer reforms it several times to achieve the best result. The engineer or designer may take into account several factors during this process. The product’s shape and various survival factors are the most crucial ones, and from the part design until the product can meet the production stage, we call all of these jobs product design and development.
Electronic product design is a complex task that requires knowledge from various areas. The three most essential areas are electronic engineering, industrial design, and UX design. These diverse perspectives are crucial in ensuring the product’s safety and reliability.
Electronic engineering product design is the key to a company’s success in today’s market. A good design always ensures high product performance and customer satisfaction. Therefore, when designing your electronic products, you must remember these points.
As you know, technology changes too quickly, and people’s tastes constantly change. Therefore, you must come up with a unique and valuable solution. In this case, a reputable manufacturer or product assembly service company can help you. Dong Guan Sincere Tech is a leading OEM contract manufacturer in China. You can choose this company as your trusted partner. The company has been in this industry for many years.
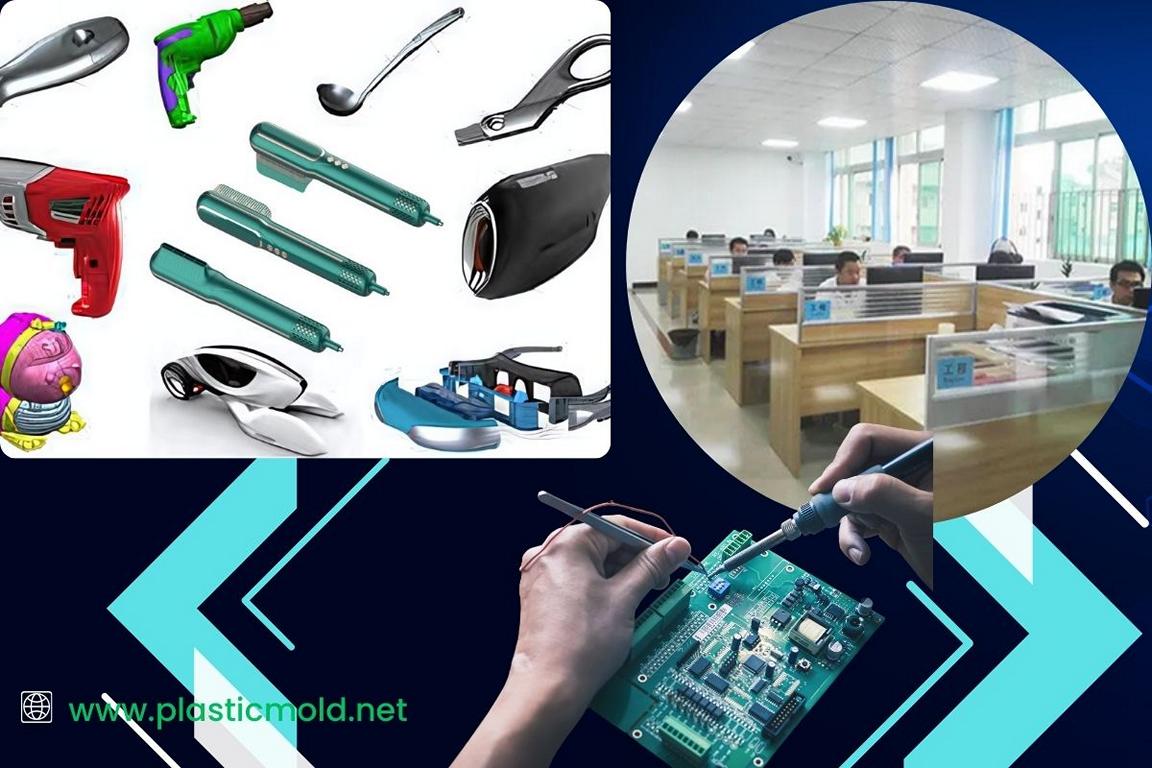

Phases of Electronic Product Design
Electronic product design has five different phases. The number of phases may differ depending on the other products. However, each phase is critical to ensuring a successful product. Let’s explore each phase in detail:
Phase #1. Research customer input
This phase is the foundation of the whole process. It entails conducting research and gathering customer feedback. However, the main goal of this phase is to understand the market needs, user expectations, and possible problems in the future.
- Market Research: You will analyze different market trends in this part. You will need to scrutinize various competitor products and identify their weaknesses. If you are familiar with the SWOT analysis in business, you can quickly grasp this part. S means strength, W means weaknesses, O means opportunity, and T means threats.
- Customer Input: After assessing the SWOT, you can collect customer input. Who are your potential users, and how do they react to other brands? You can also check the online reviews of the existing products.
Phase #2. Gather Design Requirements
Once the initial research phase is complete, the next step is to gather design needs. In this stage, you will mainly collect the product’s technical and functional specifications.
- Technical Specifications: You will need your electronic product’s technical data. Electronic products typically need PCB, component data, and power needs. You will also need to know the material types, components, and technologies used in the product.
- Regulatory requirements: This part involves dealing with national and international standards. Various testing requirements, such as RoHS and EMC, will also be needed. As a result, you must thoroughly research the regulatory requirements of your product.
- Design Constraints: This part typically defines the boundaries of your electronic product design. Consider a scenario where your product operates in high-temperature environments, necessitating the use of materials that can endure this level of heat.
Phase #3: Wireframe Design
Once your design requirements are ready, you can create the sketch or digital models. This phase generally has three main stages: sketch, digital model, and prototype. Wireframe design typically allows you to identify possible issues. You can make the necessary changes based on the test results, saving time and cost.
- Sketches: These are simple and may be hand-drawn or digitally drawn. They mainly visualize your product’s layout, including size, shape, and components.
- Digital Model: Using various CAD software, you can create your product’s digital model. 3D models give a more accurate picture of your product’s structure. They primarily depict the internal and external shapes and components, as well as their arrangement in the final products.
- Prototype: To test certain designs, prototypes are usually required. This case is notable for heat, weather, and UV testing.
Phase #4. Review and Approval
We will send your prototype for review and approval once it’s ready. This phase typically has three main stages.
#1. The reviewer examines the prototype’s interior. He collects data and compares it with technical specifications. He also checks the layout and component placement of the product.
#2. The reviewer then checks the prototype’s outside condition. In this case, he checks the edges, size, and aesthetics.
#3. If the reviewer is unsatisfied with the design, you must iterate the whole process again. You cannot send your prototype to the next level until you achieve the desired result. You must ensure that your design is feasible for the development stage.
Phase #5. Product Development Phase
Once the design is ready, the product moves to the development phase, where the actual building begins. The development phase has several stages, which you will learn about in the next section.
It is crucial to mention here that if the reviewer needs a change in the design, even in the development phase, the process above iterates again. It may happen several times until you get the best outcome.
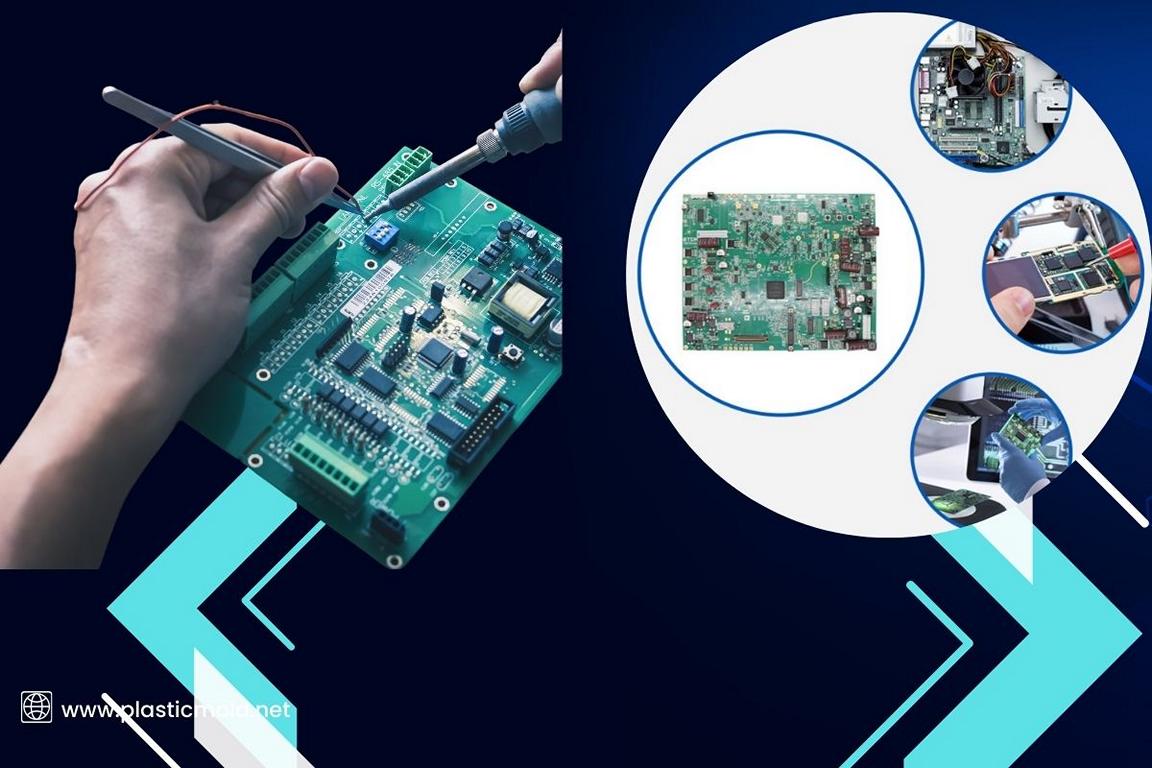
What is electronic product development and manufacturing?
Product development typically prepares a ready-to-market product design. You can also observe similar situations with electronic products.
Following the phases sequentially is essential for various reasons. It mainly ensures that your product meets the safety and quality standards.
#1. It helps identify the problems ahead. This way, you can ensure that your products are safe to use. You can also take the necessary steps to avoid sudden accidents.
#2. You can closely monitor the quality of your product at each stage. This way, you can reduce the chances of defects in your electronic product.
#3. It also assists you in identifying design flaws. During these phases, you can quickly identify functional and material issues.
#4. You can also test your product before each review and approval stage. This will ensure that your product performs well and meets your exact needs.
#5. Following each phase allows you to manage your project better. This way, you can efficiently schedule and allocate resources.
Product development vs. product management in electronic engineering
Most people mistakenly describe product management as product development. In reality, these two terms are entirely different.
Product development typically focuses on creating the product. Conversely, product management involves monitoring your product from a business perspective.
Product development has several stages. Designing, prototyping, testing, and manufacturing are the most critical phases. Product management checks your product’s performance in the market. It evaluates the end user’s feedback. Overall, it finds a better solution to be more competitive in the market.
Apple Technology is the best example. You may have wondered why Apple launches new models and features in its devices every year. This is a crucial part of their business strategy. Similar activities can be observed for other electronic gadgets.
Furthermore, the product management team plays a critical role in ensuring that your product meets market demands. They also guarantee that your product remains within the allocated budget and arrives punctually.
Overall, product development mainly focuses on the technical side. On the other hand, product management takes into account the market’s success.
Product development phases
Once again, electronic product development and manufacturing play a crucial role in turning your design into market-ready products. This process generally has various phases. You must follow these phases sequentially. You already know the importance of the sequential manufacturing process.
Phase #1. Creating Mockups
When the design is ready, it’s time for you to create mockups. You may wonder why mockups are necessary when you can directly create prototypes. Before I explain it, let’s check what mockups are.
Mockups are generally a physical model of the final product. Typically, they cannot replicate the functionality of the final product exactly. Their main job is to show your product’s size. This may include the height, length, inside shapes, intricate details, and more.
Let’s come to the point: why do you need it? Creating mockups is generally easier than creating prototypes. On the other hand, building prototypes is also far more expensive. Therefore, engineers prefer creating mockups to decide on the visual specifications.
Phase #2. Review & Approval
Once you have your mockups ready, send them for review. The reviewer checks whether they meet all necessary design standards. Most of the time, you will need approval from more than one reviewer. The factory may sometimes ask you to check if you are a buyer.
This review phase generally has three main stages.
#1. Design Integrity Check: The reviewer confirms the size and other visual specs. In this part, he mostly looks for design defects.
#2. Functionality Check: You know mockups are non-functional. But you can still understand how the final product may behave.
#3. Approval: The reviewer ultimately assesses the outcomes from the previous two stages. He draws a conclusion and makes a decision. If they approve the mockup, we will proceed to the prototype creation stage. If not, you should iterate the electronic product design again.
Phase #3: Creating a Prototype
When the mockup passes review, you can safely create the first prototype. This phase may generally iterate several times until you achieve the desired result.
What is a prototype? It is typically a working model of the final product. You may also call it a mockup, but with all functional capabilities. Please keep in mind that all prototypes are mockups, not prototypes.
You will need a prototype because you can test it several times to ensure the product’s safety. Testing the prototype also tells you whether you can proceed to the final production.
Although creating prototypes might be expensive, they guarantee reliability. They ensure that your final product meets your requirements and performs as expected. Prototypes also reduce production costs if any problems are found later.
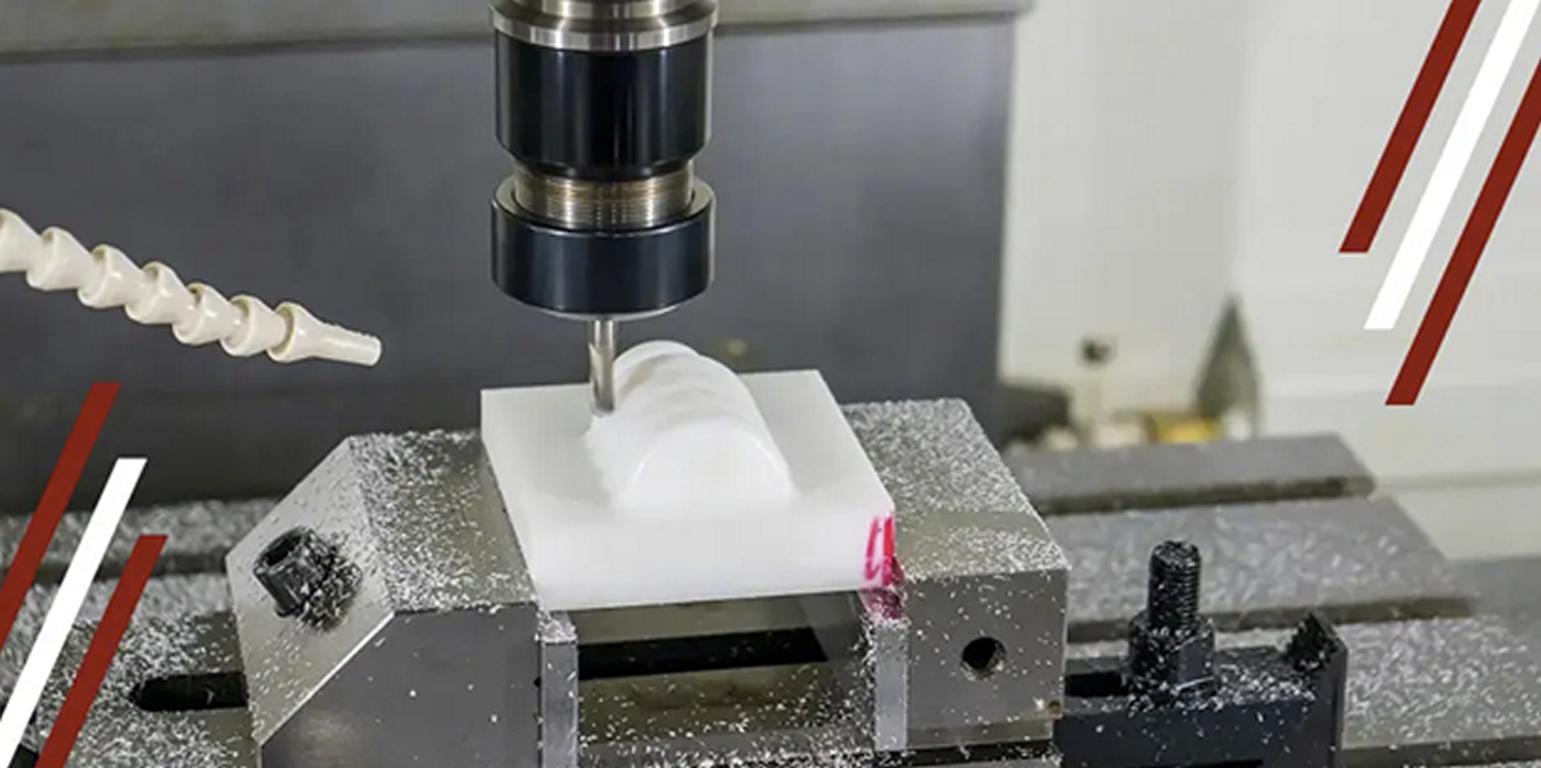

Phase #4. Testing
The testing lab receives the built prototype. Why do you need multiple tests? It generally ensures that your product is safe and reliable. As a result, it is one of the most critical phases in electronic product development. However, factories typically conduct three significant tests for electronic products. Still, the number of tests may vary based on the type of products you are making.
Work Testing
In this test, the engineer typically checks how well your product performs. He simulates a virtual environment that is identical to your project. He primarily tests electronic circuits, components, and software for electronic products. If they find any problems, they note them for later review and approval.
Safety Testing
Electronic products must meet strict safety standards. These safety tests are necessary to avoid electric shock, overheating, or short circuits. Safety tests may include proper insulation, grounding, and thermal tests.
Regulatory Testing
Every country follows specific standards. The manufacturer must follow these standards during manufacturing to meet your requirements.
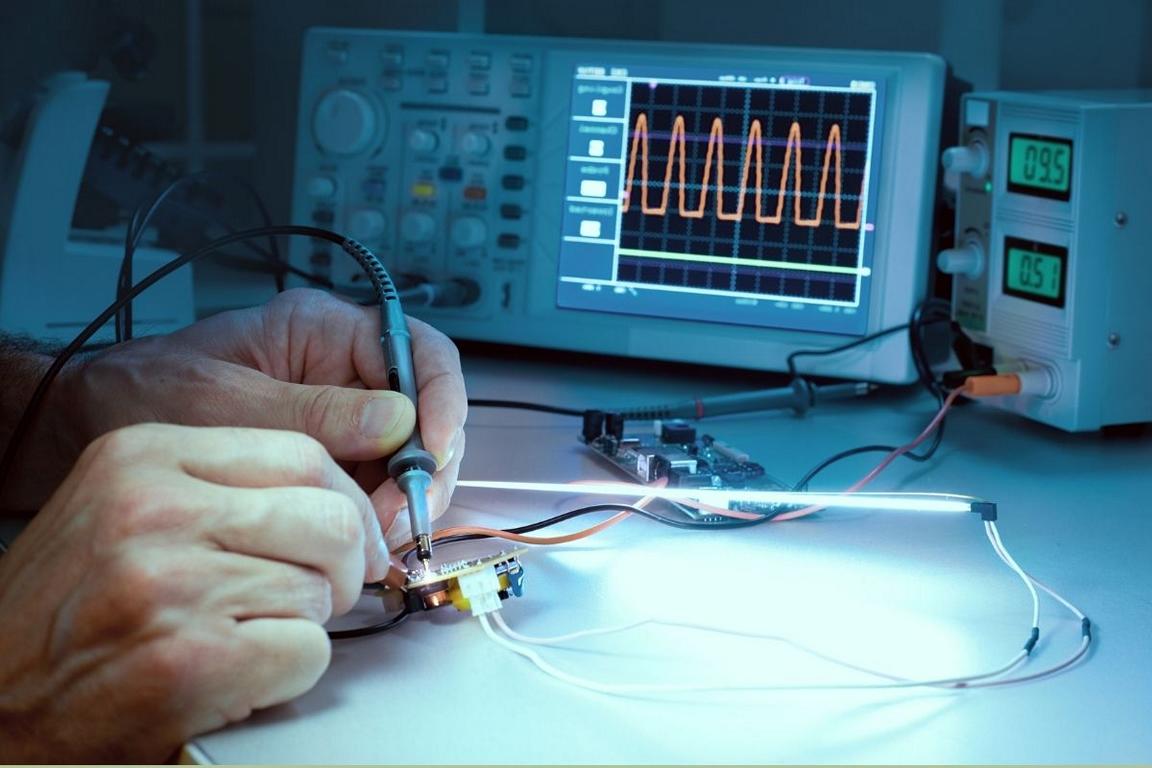
Phase #5. Review and Approval
Typically, the test result undergoes a review and approval process after completion. This part is typically reviewed by engineers, product managers, and quality specialists. Sometimes, you can also use this result to participate in the approval process. They check whether the test result meets the functional, safety, and compliance standards.
If the results meet the standard, the product is ready for mass production. However, if it doesn’t, the electronic product development phase iterates until you achieve the desired result.
Phase #6. Assessing Mass Production
This phase is one of the most critical parts of the electronic product development process. Here, the engineer typically decides how to manufacture the product cheaply. He must also consider your product’s consistent quality.
However, two parameters are mainly important here: scalability and cost analysis.
The scalability review mainly checks the factory’s capabilities. The electronic product development team checks whether they have sufficient tools to make your product. In this case, they consider your product’s design, materials, and assembly processes. It ensures that the components are available in large quantities.
The cost analysis primarily determines the optimal cost for the entire production process. It is a crucial step for every business. In this case, it considers materials, labor, and production time. However, the main goal is to find the best way to optimize the manufacturing process.
Phase #7. Final Production
Once everything is ready, the electronic product development and manufacturing team decides on final production. This phase primarily ensures the product’s consistent quality throughout production. Maintaining proper logistics and delivery is also a prime concern here.
Differences between Electronic Product Design and Development
In general, there is a close relationship between product design and development. Without others, one cannot process. However, they are both different approaches. To complete successful product cycles, you must understand these distinct approaches.
To understand their differences, you can divide them into five main points. Each of these points is critical in manufacturing.
#1. Objective
Electronic product design aims to create precise digital drawings. It mainly defines how the end product will look and function. This process is all about translating your concept into detailed blueprints.
Conversely, electronic product development aims to create functional prototypes. Rapid prototyping, also known as multiple prototyping, is a key component. This process mainly transforms the product design into a functional product.
#2. Stages or phases
Electronic product design has five main phases. First, the process collects necessary information from the customers. Second, it creates a variety of design requirements. Third, the wireframe design is established. Fourth, the digital drawing is sent for review and approval. Fifth, the design is ready for the development process.
Electronic product development and manufacturing have seven main phases. First, they create mockups. Second, they review the mockup and approve it for the next level. Third, they create a prototype. Fourth, they test the prototype. Fifth, they review the test results and approve them for final production. In the sixth step, the process typically involves researching factory capabilities and optimizing costs. Finally, the product moves on to the final manufacturing stage.
#3. Focus Area
Electronic product design typically focuses on creating an accurate digital drawing. It includes everything from circuit schematics to component placement.
On the other hand, electric product development focuses on creating functional prototypes. It mainly ensures the prototype is manufacturable and functional for all types of testing.
#4. Team or Expertise
Electronic product design requires a team of designers and engineers. It mainly involves expertise in drawings and specifications.
Electronic product development requires a team of engineers, specialists, and technicians. It mainly involves mechanical & electronic engineering, testing, and quality engineering expertise.
#5. Tools Used
Electronic product design mainly requires software. Typical design software includes AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Cadence, Proteus, Keil, and other simulation software.
On the other hand, for electronic product development, you will need hardware. Typical instruments are molding machines, 3D printers, and testing kits. You can use injection molding machines for plastic parts, while die-casting machines are used for metal parts. Sometimes, you can also use 3D printers to create prototypes.
Electronic Product Design and Development: An Example
One notable example could be a smart home thermostat. A thermostat is an automated device that controls temperatures. Its sensing mechanism automatically turns the heating or cooling systems on or off. You may find it commonly used in homes and buildings.
In 1830, inventors created the first thermostat. Although it was a manual version, the first automatic thermostat appeared in 1906. The journey began with proper market research. Subsequently, the above design and development processes were followed. You will find many thermostat types with unique designs and features in today’s world.
Similar procedures can also be observed for other electronic gadgets. Therefore, you can see that the proper use of electronic product design and development is indispensable in the electronic industry.
OEM Contract Product Design, Development, and Manufacturing at DG Sincere Tech
Dong Guan Sincere Tech is one of China’s top 10 plastic injection molding companies, having offered plastic molds, die casting, and machining services for over 18 years. Its significant areas of expertise are designing, developing, and manufacturing products.
Sincere 2019, The company bought a new product assembly company that is professional in creating new electronic products. Since then, Sincere Tech has provided all-in-one services for electronic products, including part design and development, prototypes, testing, certificates, mold manufacturing, die and metal parts, surface finishing, assembly, and packing. This implies that our services encompass the entire process from design to final production. We will ensure quality and make your brand more competitive in the market.
DG Sincere Tech has more than 60 large pieces of machinery for manufacturing and assembly. Specifically, they have 60+ assembly workers and 40+ injection and die-casting machinery. This company always tries to keep up with the latest technology so that its products can achieve the highest tolerances.
In addition, the company offers CNC machining, 3D printing, and other large-scale productions. You can also get secondary services like painting, chrome coating, and anodizing.
One of the best reasons for choosing this company is that Sincere Tech is a one-stop shop for everything. Here, you can get all types of services, from designing to making custom parts. This manufacturer also offers a wide range of product assembly services for your outsourced components.
If you are looking for electronic product design services, you are welcome to contact Sincere Tech. Their customer service is swift and reliable.

