Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a copolymer composed of three different monomers:, – Acrylonitrile; – Butadiene; and – Styrene. Well-established for its good impact strength, dimensional stability in processing, and fantastic wearing resistance. ABS is used in autos and truck parts and modules, home appliances, toys, and 3D printing. The ABS is technically synthesized from three monomers; acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene rendering it highly strengthened, rigid, and heat resistant than other thermoplastics. So, it is ideal for all general use as well as industrial products. In this article, you will learn what this ABS is and how exactly is it created. So, let’s get some additional information about the properties, manufacturing process, and uses of ABS plastic.
What is ABS Material?
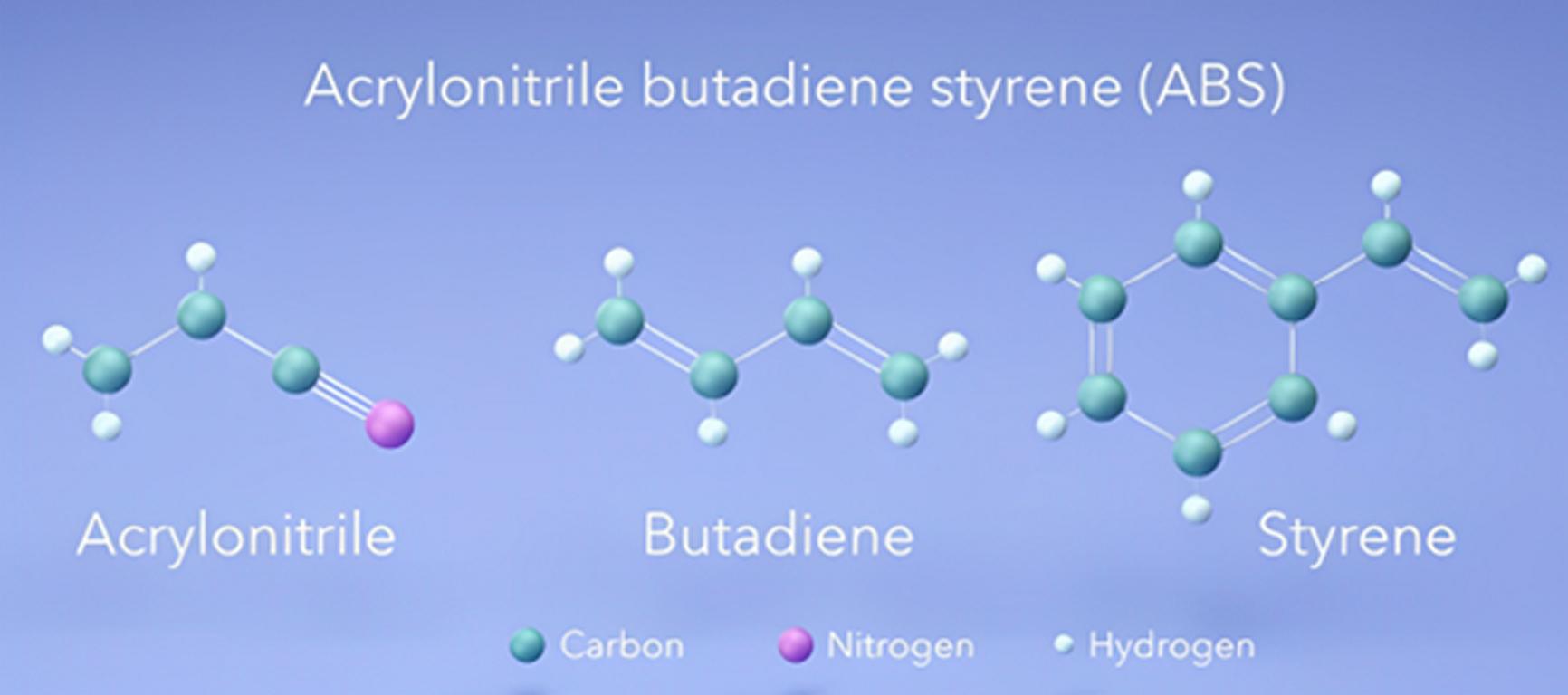
ABS is a Thermoplastic alkyloidal polymer with formula (C3H3NO) – based on acrylonitrile, butadiene, styrene &. This material is highly valued for its high impact strength and its aptitude. So, it can resist a large number of temperatures. ABS is a blend of the rigidity of acrylonitrile, toughness of butadiene, and processability of styrene so it has a variety of uses for every product.
What is ABS Made Of
ABS is made from three monomers:
- Acrylonitrile: It offers chemical resistance and Heat Stability Both chemicals and heat resistance. These are essential features as the product is used in industries with high temperatures and chemical exposure.
- Butadiene: Helps to provide strength and shock strength.
- Styrene: Increases the stiffness and smoothness and increases the flow ability.
These two characteristics combine to produce a well-balanced plastic material. So, it can have various applications for different uses according to the ratio of monomers involved.

What are the Properties of ABS?
ABS possesses several notable properties that make it a preferred material in numerous industries;
- High impact resistance: Because of the butadiene component, the product is capable of absorbing energy. Thus, it can resist shocks without cracking or breaking.
- Rigidity: Styrene offers the ABS structural strength required for additional application adhesion.
- Thermal stability: It is relatively insensitive to temperature effects and stays constant over a pretty large range of temperatures.
- Chemical resistance: Such properties impact resistance Chemical and oil resistance Acrylonitrile contributes to ABS in this way.
- Good electrical insulation: ABS is a very good insulator; therefore, it can be used for electrical appliances.
The following table will help you describe the properties of ABS material
| Property | Typical Values |
| Density | 1.03 – 1.12 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 20 – 40 MPa |
| Tensile Modulus | 1,500 – 3,000 MPa |
| Impact Strength (Notched Izod) | 80 – 130 kJ/m² |
| Flexural Strength | 60 – 100 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 2,000 – 3,500 MPa |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 85 – 105 °C |
| Vicat Softening Point | 95 – 105 °C |
| Flammability | UL94 HB or V-2 |
| Water Absorption | 0.2 – 0.5 % (by weight) |
| Surface Hardness (Rockwell) | M60 – R118 |
What Consequences Follow When ABS Blends with Thermoplastic?
ABS can improve its properties by blending with other thermoplastics commonly polycarbonate (PC) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). For example:
- The material with PC enhances the heat resistance and strength of ABS. So, it works in accord with the plasticity and flexibility of a polycarbonate (PC). Please go to PC vs ABS Plastic and polycarbonate injection molding page to know more about PC material,
- When it is combined with PVC, it has better chemical resistance as well as flame resistance.
These blends are employed where specific modifications in properties of the polymer are desired to meet high-performance criteria.

How do Additives Improve the Properties of ABS Material?
Additives such as stabilizers, plasticizers, and colorants can be added to ABS to improve or modify its properties;
- Stabilizers: Improve the heat and UV stability of ABS.
- Plasticizers: Strengthen the element of flexibility and softness in your clothing.
- Colorants: Permit modification of the look of ABS without having an impact on the functionality of the car.
Other additives for example flame retardants also enhance the fire resistance of the products made from ABS.
Is ABS Toxic?
European Union’s stand on ACS is that it is non-toxic and thus suitable for use in consumable products. There are no toxic compounds such as phthalates, bisphenol-A (BPA), etc in it and it neither emits a foul smell. But when it is undergoing the process of manufacturing or when exposed to high heat/ flames (burning), the ABS derivative puts off toxic fumes. This helps prevent exposure to the chemicals during the processing and disposal of these products.
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process of ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Here is the complete process of manufacturing of ABS Material;
1. Preparation of Raw Materials
The three monomers, i.e. acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene are synthesized individually with the required ratio. Each monomer contributes unique properties to the final ABS polymer. Here, styrene gives rigidity and ease of processing acrylonitrile contributes to heat and chemical resistance and butadiene contributes to impact strength.
2. Polymerization Process
ABS is created using two main polymerization methods, such as;
A. Emulsion Polymerization
In emulsion polymerization, the monomers are rather insoluble in water and are thus dispersed with the help of surfactants. Butadiene creates initially the formation of rubber particles, and then acrylonitrile and styrene polymerize and surround the rubber particles to form an interlocking structure of a polymer matrix. This method enables the control of the final polymer structure and its properties to a larger extent.

B. Mass (Bulk) Polymerization
In mass polymerization, there is no use of water in the mixing of monomers. Catalysts lead to the polymerization process and the commercial process occurs in very large reactor vessels. This is followed by melting and extruding the polymer, cooling, and then pelletizing. This process is also quicker and more efficient in large-scale production than batch processing.
3. Addition of Stabilizers and Additives
Stabilizers and additives are mostly added to the food. So, they help retain certain properties of the food like color and texture. After polymerization is done some other ingredients which include UV stabilizers, pigments, and plasticizers are added to the ABS. Such additives serve to improve the properties of the material, including strengthening resistance against weather conditions, and color or to increase flexibility.
4. Cooling and Pelletizing
Then the polymer melt is extruded through a die and comes out in the form of long strands. These strands are then cooled with water or air to set the polymer into a solid material. After this process is complete the strand is reduced to small, equal-sized pellets after it cools down. These are ABS pellets which are easy to transport and are used as basic material to be used in product manufacturing.
5. Final Processing
These ABS pellets have various applications in many manufacturing processes, i.e. injection molding, extrusion and blow molding. It involves the abs injection molding of products such as automotive parts, electronics casings, and abs molding toys among others through the process of melting the pellets and then injecting them into molds. Extrusion blow molding is applied to products like pipes and bottles and the other one is injection blow molding which is applied to products like toys and containers. All the above techniques maximize the use of ABS’s properties to develop strong and quality finished products.
Is ABS Recyclable?
Yes, ABS is recyclable. It does not degrade in properties much when it has been reprocessed and reused. Recycling of the ABS procedure involves the breaking of the material into pellets so that they can be remelted into required products. However, recycling of ABS is not so much as compared to other plastics like PET or HDPE because of some reasons such as contamination and sorting.
Commercially Available ABS Grades
The following table gives a deep understanding of the different ABS grades available in the market.
| ABS Grade Type | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| General Purpose ABS | Good impact resistance, moderate heat resistance | Consumer products, household appliances |
| High Impact ABS | Enhanced toughness and impact strength | Automotive components, industrial parts |
| High Heat ABS | Higher heat deflection temperature | Automotive dashboards, electrical enclosures |
| Plating Grade ABS | Suitable for electroplating and high surface quality | Automotive trim, decorative products |
| Flame Retardant ABS | Contains flame retardant additives | Electrical housings, appliances, electronics |
| Extrusion Grade ABS | Good melt strength for extrusion processes | Pipes, profiles, sheets |
| Transparent ABS | Clear or tinted, good impact strength | Lenses, medical devices, cosmetic packaging |
Advantages of ABS Material
Here are some advantages of ABS material;
- High impact resistance: Used best for protection purposes.
- Durable: Very hard and brittle thus is used where stiffness is required such as in structural members.
- Easily machinable: These can be easily molded, drilled as well as shaped.
- Cost-effective: Is more cost-effective as compared to other engineered plastics.
- Wide temperature range: Good high-temperature performance coupled with satisfactory low-temperature performance.
Disadvantages of ABS Material
Besides several advantages, ABS also offers some challenges. These may include;
- Poor weather resistance: Sufficiently fragile to their light sensitivity they degrade under ultraviolet exposure.
- Low chemical resistance: They can resist only weak acids or solvents.
- Limited heat resistance: This is an important consideration when using ABS products because the higher temperatures can cause deformation of the products.
- Non-biodegradable: ABS is one of the materials that cause the accumulation of plastic waste in the landfill.
- Harmful fumes emission: It should be effectively managed in terms of the ways it is processed and how its wastes are disposed of. Because, when we burn it, it emits hazardous fumes.
Uses of the ABS Material
The following are the applications of ABS material in various fields;
- Automotive parts: The possible flashpoints include the dashboard, wheel covers, or the bumpers and their components.
- Consumer electronics: Notebook protectors, computer keys, and telephone body shields.
- Toys: Used in products such as the LEGO bricks since it is beyond stiffness.
- Household appliances: Vacuum cleaners, kettles, forks and cutleries, and food processors.
- 3D printing: Frequently used as the building material in 3D printing, filaments utilize dow ABS.
- Medical Devices: Medical device housing as well as other subassemblies and components require a material that is difficult to break, scratch, or wear as well as easy to sterilize, that is why ABS is widely used with parts such as inhalers and surgical instruments.
- Construction Materials: ABS is used cin construction products such as plumbing pipes and fittings. It is generally because of the material’s impact and chemical corrosive resistance characteristics.
- Automotive Interiors: In addition to the use in the dashboard and bumpers, it is also used for those parts of the vehicle that have to both be strong and give an elegant look. These may include interior trim, center console, and door panels.
- Office Equipment: ABS is used in the production of office equipment such as printers photocopying machines, and fax machines since it is rigid as well as has a good impact strength.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ABS is one of those well-known varieties of thermoplastic materials that demonstrate high levels of abrasion, impact, and heat resistance as well as ease of processing. Although it has very poor UV sensitivity and very low heat resistance, it is a better material owing to the many advantages it possesses in most uses. ABS is a reusable material that is used in various applications. These may include car parts, electronic gadgets, toys, and other products. As sustainability aspects getting much needed importance the recycling of ABS is getting attention for reducing the waste plastics.
Frequently Asked Questions
Whether it is safe to use ABS for food Contact?
It should be noted that, as a rule, ABS is not used for direct contact with foodstuffs. Although it finds several applications in indirect food-contact settings. please go to is ABS material safe page to know more.
How does ABS stand with high levels of heat?
ABS is heat resistant and it has the disadvantage of warping when exposed to heat for a long period.
How long does ABS Plastic last?
While very lightweight, ABS is also very tough and has high impact strength, so it’s good for unforgiving usage.
What are the uses of ABS in 3D printing?
ABS materials are commonly used in 3D printing that provide rigid and tear-resistant components such as prototypes, models, and part products.
Is ABS flame retardant?
There are ABS grades that are flame retardant, but the unalloyed ABS may not contain this property.


