Plastic Injection Molding Tools
Plastic injection molding tool making is delicate and intricate, so even a single cavity plastic injection mold can cost up to $5000. This manufacturing process involves using sophisticated tools, modern technology, and skilled mold fabricators. Plastic injection molding tools are mainly applied in the mass production of plastic products. This process uses injection mold and molten plastic to form exact specification parts with varying shapes and sizes. In addition to the process, it starts with heating the plastic, often in the form of beads, and supplies it to the factory.
This molten plastic is transferred to an injection molding machine and injected into the mold cavity. In plastic injection molds, channels allow coolants to flow around the hot plastic in the cavity. This circulation also aids in cooling the plastic, which is vital for increasing the solidification rate and improving production.
To understand how the injection molding process works, you need a basic knowledge of injection mold tools: what they are, how they work, where to get them, and which ones are most effective for specific applications. This article provides all the essential information a reader may need before using an injection molding tool.
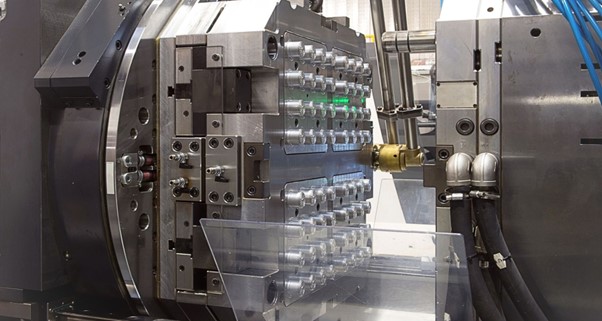
A Brief Overview of Plastic Injection Molding Tools
Plastic Injection mold tools are crucial parts of molding machines. They help produce several parts simultaneously. These simple or complex molds have long lives and can create 1000s of parts during service time.
Moreover, these molds are usually made from high-strength materials like steel or aluminum and have runners that link the injection point to the mold to enable the flow of the molten liquid plastic. Furthermore, coolant holes help cool and solidify the plastic material. Each mold comprises two main central plates: Plate A, which tightly holds the parts in place during the injection molding process, and Plate B, which is usually, used to open and close the mold and eject the final parts or products.
Different Functionalities of Injection Molding Tools
As discussed earlier, the mold tools are a crucial component in plastic injection molding, serving several fundamental functions:
Guiding molten plastic: A channel through which molten plastic can flow from the injection cylinder (barrel) to the mold cavity.
Cooling: It cools the molded part until it sets and solidifies to the desired shape and size. Temperature control of the mold is vital to allow the molding to cool at the right rate to avoid distortion and stress. Usually, water flows through channels made in the mold, as in the case of an automobile engine cooling system.
Ventilation: When the mold is closed, ventilation provides an escape route for the trapped air. If the molded part were not vented, it would have voids (air bubbles or cavities), resulting in a poor surface finish.
Part ejection: Ejector pins help expel the finished molding out of the mold. These functions show the mold tool’s importance in achieving high quality and zero defects or maintaining plastic parts.
Compatible Materials Used for Manufacturing Injection Molding Moulds
Tool steel injection molding mold
The ultimate choice of material for plastic injection molding tools depends on the number of parts to be produced, the type of plastic to be molded, and the tool’s life expectancy. Every material incorporated into these tools has its characteristics. Here are some commonest materials include;
Steel: Steel tools are widely used in plastic injection molding because of their hardness and ability to withstand wear and tear. They are relatively cheap and easy to machine, thus suitable for many uses. From simple features parts to complex shaped components, these tools are invaluable. Their use is indispensable across automotive, aircraft, interior, and exterior parts. However, steel molds may be prone to corrosion, wear under harsh conditions, and require frequent maintenance.
Aluminum: These tools are preferred because they are lightweight and can withstand corrosion. They are easy to machine and produce various medical, electronics, and automobile parts products. Nonetheless, aluminum molds are not as durable as steel molds and may not be suitable for high-thermal and high-pressure applications.
Copper: As many know, copper is solid and electrically conductive. It is used to make molds for electrical parts and other precise products. Copper is also relatively resistant to corrosion, wear, and tear. However, it’s expensive and challenging to use copper in massive sections compared to other metals.
Brass: Brass is a complex, rigid metal made of high traces or % of copper, nearly around 70%. It is widely used to shape molds to produce mechanical parts and other accurate-dimension products. It can withstand high corrosion and wear resistance but is generally more expensive than other materials.
Bronze: Like brass, bronze is rigid and resistant. It’s notably suitable for molds that create mechanical parts requiring high precision and dimensional accuracies. It’s also highly resistant to corrosion and wear but is relatively expensive compared to other molding metals.
Plastic: Plastic molds are used for small, simple parts or prototype designs, and are made of high-strength, heat-resistant materials such as P20 steel or aluminum. They are typically cheaper than metal molds but are not as strong as metals, and thus cannot be employed in large-scale production. Each of these high-quality materials has its advantages and is used based on the requirements of the injection molding process.
Why Is Material Selection Crucial In Mold Manufacturing?
Material selection is vital because it determines the type of material to be used to construct a particular product. It is crucial to select a suitable material for your injection molding tools. The chosen materials determine the quality of your final products, the reliability of your parts, the strength of your tools, and your overall expenses.
Sincere Tech is one of the leading mold manufacturers in China that has been in the technical field for more than a decade. With a team of skilled engineers and technical experts, we employ the best 3D CAD and Moldflow simulation technologies to enhance your part designs to the optimum level. We are proud to work with the most popular polymer and elastomer producers, additives experts, and chemists to rely on their vast experience. This allows us to recommend suitable materials for your application to ensure you get the best performance at the lowest price possible.
Whether you need to do initial design analysis or large-volume parts, our facility provides best-in-class services to meet your requirements. You can send us your drawing,; our engineers will help you analyze and give you the best possible solutions (DFM report) to bring your virtual concepts to reality in minimal time leads.
Relationship Between Tight Tolerance & Tight Tooling Complexity
Precision in plastic injection molding tooling is a delicate balancing act that generally depends upon the intended tool, cavity design, and materials used. Less complicated shape parts can provide better tolerance control than complex parts. Adding more parameters, such as the number of cavities, may decrease the tolerance.
Creating thin-walled symmetrical or cylindrical parts with fine details like threads and undercuts requires sophisticated plastic injection molding tools. In such cases, other mechanical parts, such as rotating gears, may be necessary to deal with the complexities of these geometries. The tooling complexity, precision, and accuracy level needed for plastic injection molding is a delicate balance that will yield optimal outcomes. Plastic injection mold tools are significant in achieving tolerances down to +/- 0.0005x.
Central Parts of Plastic Injection Mold Tooling
Let us explain the significant parts of injection molding tools and their roles.
Guide Pins: These pins are screwed on one mold half and fit into the other half’s holes to ensure proper alignment of the molds during injection.
Runner: Channels in the mold help to convey the molten plastic from the sprue bush to the various cavities, to ensure that they are equally supplied for proper molding.
Tooling gates: The point where the plastic gets into the mold cavity is called a gate and is created as a mold parting line. Injection molds typically feature two primary gate types: 1. In the first place,
Automatic Trim Gates: These gates open autonomously, so there is little or no contact with the walls and consequently fewer damages or scratches. Some examples of these gates include; the hot runner gate, the valve gate, and the ejector pin gate.
Manual Trim Gates: These gates must be operated manually to block the parts from the runners once the cycle is over. Some examples are the sprue, spider, overlap gate, and so on.
Sprue Bush: This is a larger entrance to the mold for the injection of molten plastic, gradually reduced in size to direct the flow of the plastic into the runner system.
Locating Ring: Ensure that the mold is adequately locked on the fixed platen so that the injection nozzle is in the correct position to the sprue bush.
Mold Cavity: The section of the mold that is used defines the final product’s size, shape, and other features.
Ejector Pins: After cooling and solidification, the molded part and the solidified runner should be removed from the mold.
The Shot: The amount of molten plastic injected into the mold at each cycle to form a layer on the cavities, runners, and the sprue.
Sprue: Sprue bar is the solidified plastic left in the sprue bush after molding has taken place. It connects the injection point to the runner system and is usually either removed or recycled.
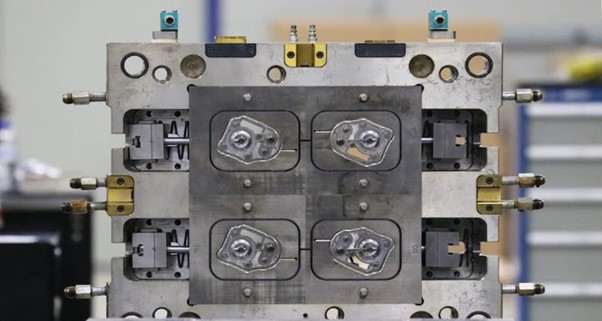
Two Central Phases In Tooling Fabrication
There are typically two phases involved in manufacturing tools for plastic injection molding.
Production Tooling
Firstly, production and development tools are central to plastic injection molding tooling fabrication. The production tooling used in injection molding is made of fully hardened steel with a standard shot life of one million shots. It is ideal for mass production of hundreds and millions of plastic parts. Sincere Tech often uses highly durable stainless steel in construction-related applications, such as high-performance steels in medical injection molding tools.
The integration of conformal cooling technology with metal additive manufacturing optimizes cycle time. The medical mold and the hot runner system are also essential and durable, and engineering-grade medical mold tools are also necessary. As for the class, and strict quality assurance, we adhere to the SPI class 101 standards and implement them in our mold manufacturing. Further, our professionals employ pre-production to in-process and final inspections during mold-making operations.
Mold Tooling Development Phase
Sincere Tech’s recommendation for the development phase is to create a one- or two-cavity ‘development tool’ before a fully hardened multi-cavity production tool. Aluminum is unsuitable for development tools because it is easily damaged on the surface, expensive, hard to machine, and not readily available like P20 steel. P20 steel is a kind of steel that contains carbon, chromium, manganese, and molybdenum and it is ideal for machining, polishing, and plastic injection molding of prototypes.
On the other hand, H13 steel with nickel and silicon has higher heat resistance, strength, and toughness, making it suitable for mass production with constant cooling and heating processes and the production of abrasive plastic parts.
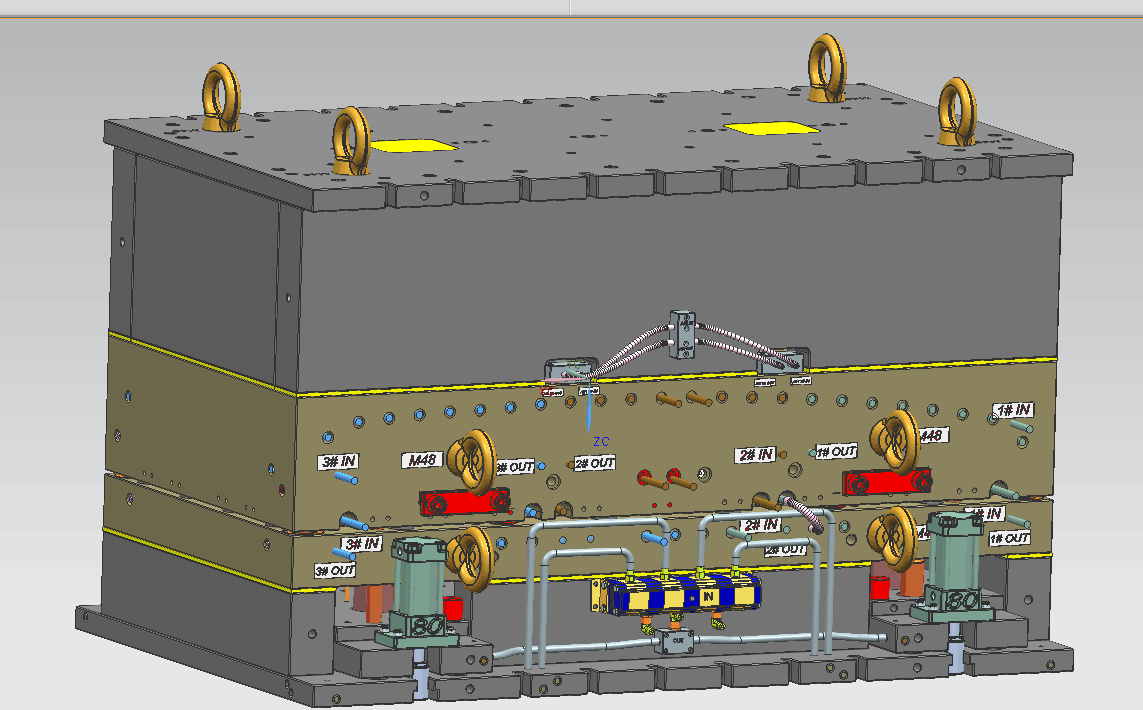
Sincere Tech Engineered Tooling Building Approach
When it comes to building plastic injection molding tools, our in-house production department diligently ensures that your mold tooling is produced according to your specifications using quality control measures.
Design and Prototyping
Customers provide us with their mold designs and other details of the product they wish to be manufactured. Then, our experienced engineers carefully study the client designs and employ the mold-making software to create a model. This prototype is then subjected to simulation to assess the plastic flow and defects and validate the final product.
Material Procurement
Once the design and prototype have been finalized, our mold makers utilize materials based on your constrained budget and the expected lifespan of the mold. In contrast, hardened steel is more durable and lasts longer than aluminum. Typically, it’s very costly compared to aluminum, which is not very hard but cheaper.
Machining
These designs are then presented to the project manager, who oversees CNC and EDM programmers and machinists. CNC machines cut the metal into the desired shape and size and drilling machines are used to make passages for coolant and holes for screws. EDM then further refines more complicated patterns like runners and gates to a more detailed level. Benchwork also plays a vital role in achieving a good finish.
Visual Inspection
The final metal parts products are inspected to ensure the plates are correctly aligned. When approved, the mold goes to the next phase.
Assembly
All mold parts are assembled, and the mold is ready for use and can be installed in an injection molding machine.
Testing
This assembled mold is then taken to an injection molding machine to check whether it produces the right products. Once the mold has been run and confirmed to perform its function as expected, it is sent to the buyer.
Choose Us For Your Manufacturing Precision Injection Mold Tools
When you partner with Sincere Tech, a professional mold maker in China, you can benefit from our advanced manufacturing capabilities, and commitment to detail to provide the best products that meet your expectations.
If you are planning a plastic mold project and looking for reliable injection molding tool suppliers to boost your business, please contact us now. Take advantage of our flexible pricing that suits your needs and budget. Send us your design, and get an instant no-obligatory engineering quote.
Allow Sincere Tech to take your vision to the next level and be your partner in attaining the best injection molding tool!
Key Takeaways
In summary, the time needed to manufacture plastic injection molding tooling depends on its design simplicity and complexity. Fabricating a single mold can take a few weeks to several months. The mold-making process is divided into several steps: design, manufacturing, and tryout. Every process is very delicate and needs to be done appropriately by designing molds to the best of one’s ability because any mistake cannot be made in plastic mold making. Nonetheless, it is efficient to invest in this process because it is cheap and time-saving, thus enabling the production of quality pieces.


