Czym jest raport z analizy przepływu w formie?
Analiza przepływu formy (MFA) to narzędzie symulacyjne, które służy do przewidywania i optymalizacji przepływu żywicy w formie podczas procesu formowania wtryskowego. Symulacja uwzględnia właściwości żywicy i geometrię formy oraz przewiduje zachowanie się tworzywa sztucznego podczas wypełniania formy i stygnięcia.
Raport z analizy przepływu formy może pomóc zidentyfikować i rozwiązać potencjalne problemy związane z procesem formowania wtryskowego, takie jak niedolewy, odkształcenia, linie spawania, pułapki powietrzne, wgłębienia itp. Raport z analizy przepływu formy może być również używany do optymalizacji procesu formowania wtryskowego poprzez identyfikację najlepszej lokalizacji dla bramek i kanałów, określenie optymalnej prędkości wtrysku i przewidzenie najlepszego czasu i temperatury chłodzenia. Może to pomóc w skróceniu czasu cyklu, poprawie jakości części i zwiększeniu wydajności produkcji.
Raport z analizy przepływu formy
Podsumowanie wyników analizy przepływu formy
Po zakończeniu projektowania formy, przed rozpoczęciem produkcji formy, aby mieć pewność, że wszystko będzie działać prawidłowo, musimy wykonać następujące czynności: analiza przepływu formy aby sprawdzić potencjalne problemy, jest to bezpieczny sposób na uniknięcie błędów, szczególnie w przypadku dużych form. Poniżej przedstawiamy kilka punktów, które należy sprawdzić podczas sporządzania raportu z analizy przepływu w formie.
Czas wypełnienia formy – Czas wypełnienia to czas wymagany do wypełnienia wnęki części. Wykres czasu wypełnienia zapewnia również animację wypełnienia wnęki formy. Czas wypełnienia można również kontrolować podczas analizy, aby rozwiązać problemy jakościowe, takie jak wysokie naprężenia ścinające.
Ciśnienie wtrysku – A standard injection molding machine is capable of pressurizing the melt flow to 20,000 psi (2,000 psi hydraulic gage pressure). A portion of the pressure is used to push the plastic through the runner system, some of the pressure is used to push the plastic into the wnęka formy, and a portion of the pressure is used to “pack out” the part after it is filled. If the part and runner system require more pressure than the machine is capable, than the part will be a short shot or have deep ślady zatonięcia.
Linie spawania Wady – Weld lines are formed when two flow fronts meet and “weld” together. Weld lines are usually a visible line on the part and can be an appearance issue. Weld lines may also reduce the part strength by 10% – 20% potentially creating a structural issue depending on their location. If mold flow analysis is not used to fix these problems before the tool is built, the molder will be forced to: increase injection pressure, increase melt temperature, increase mold temperature, enlarge vents, change the gate location and/or alter the thickness of the part. All of these “solutions” take time and money to implement and/or increase the cost of the part.
Pułapki powietrzne Wady – Air traps are formed when the molten plastic traps air in the part cavity as it fills. If these air traps are not vented, they can lead to quality problems such as burn marks, short shots, pronounced weld lines and incomplete fill. Our air trap plots allow the toolmaker to know exactly where the vents need to be placed when the tool is built. Air traps that are in locations that are difficult to vent can be moved to better locations by moving the gate. Doing this work before the tool is built can save on the amount of debug and mold changes that are required.
Jakość – The definition of a quality molded part is not only that the part filled completely. A quality molded part must also be free of material degradation and low in molded in stress. The quality plot shows the severity and areas that are suffering from quality problems. The problems detected include excessive shear stress and shear rate, and hard to pack areas. Suggestions like thickness adjustments, processing condition changes and fill time adjustments can be tried to eliminate the quality issues.
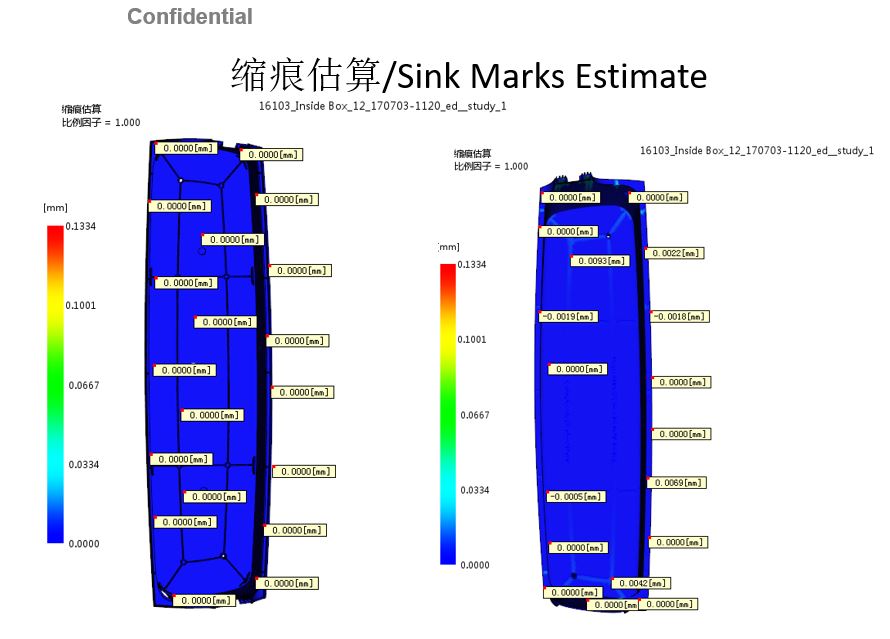
Wady śladów zatopienia – Sink marks are localized depressions in the surface of injection molded parts caused by a non uniform shrinking of the plastic during the cooling. In cosmetically critical parts, they can be a serious problem. Sink marks often come as a surprise when the tool is complete. If the sink marks are objectionable to the customer, the molder is often tasked with “eliminating them”. This usually means running the molding machine at the extremes of the process window, which can lengthen cycle times and increase the amount of molded in stresses and material degrade.
Czas chłodzenia – It has been shown that cooling time averages about 50% of the molding cycle. If the material in use is a commodity resin, the molding cost far outweighs the material cost. In this case, a reduction in cooling time has a big reduction in the part cost. Our Cooling Analysis can reduce your cooling cycle and optimize your cooling system eliminate hot spots and warpage.
MFA to potężne narzędzie, które może pomóc w poprawie wydajności i jakości procesu formowania wtryskowego, symulując zachowanie żywicy plastikowej podczas jej przepływu przez formę i chłodzenia. Pomaga zidentyfikować potencjalne problemy i zoptymalizować proces w celu zminimalizowania wad i poprawy jakości produktu końcowego.
Przeprowadzimy analizę przepływu w formie dla Twojego projektu
Jeśli masz projekt, który budzi wiele obaw, skontaktuj się z nami, sprawdzimy wszystkie rysunki części i wykonamy je. Raport DFM I przepływ formy przeprowadzimy dla Ciebie analizę i podsumujemy wszystkie możliwe problemy w arkuszu danych, który następnie odeślemy do Ciebie.

