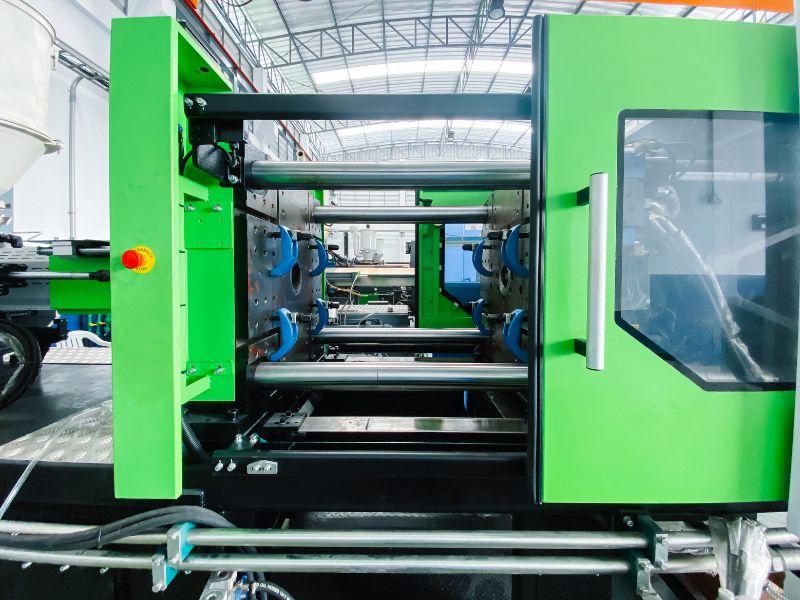
Devi sapere come risolvere il problema dello stampo, manutenzione dello stampo in plastica, riparazione dello stampo in plastica, se gestisci un'azienda di stampaggio a iniezione di plastica, la manutenzione dello stampo è importante.
Lo stampo, indispensabile nello sviluppo dell'industria moderna e nel miglioramento del livello tecnologico, è un tipo di attrezzatura di processo ampiamente utilizzata durante il periodo intermedio della produzione industriale. Secondo le statistiche, lo stampaggio rappresenta 75% di lavorazione grezza di parti industriali e 50% di lavorazione di precisione. Lo stampo può essere classificato come stampo per punzonatura a freddo, stampo a iniezione (o stampo a iniezione di plastica), stampo per pressofusione, stampo per gomma e così via.
1. Introduzione allo stampo a iniezione
1.1 Campo di applicazione:
Lo stampo a iniezione è adatto per materiali termoplastici come ABS, PP, PC, POM, ecc., mentre lo stampo in gomma è adatto per materiali plastici termoindurenti, come la plastica fenolica, la plastica epossidica e così via.
1.1.1 Classificazione dello stampo a iniezione:
Per struttura: stampo a due piastre, stampo a tre piastre
Per tipo di cancello: stampo per cancello a bordo, stampo per cancello a perno, stampo a canale caldo
1.1.2 Struttura dello stampo a iniezione
UN. Parti/componenti di stampaggio: normalmente chiamati cavità e nucleo, che sono le parti più vicine nei prodotti in plastica.
B. Sistema di alimentazione/colata: Canale per il flusso di plastica fusa dall'ugello alla cavità. È classificato come canale principale, canale secondario, canale di colata, pozzo di scorie fredde, ecc.
C. Sistema di guida/principale:Il sistema che determina la posizione relativa della cavità e del nucleo durante il serraggio/chiusura dello stampo è normalmente costituito da perno guida e boccola guida. Anche le piastre di espulsione devono essere posizionate tramite perno guida e boccola guida.
D. Struttura di sformatura: È la struttura che espelle la parte in plastica dallo stampo. Solitamente, è composta da perno di espulsione, piastra di espulsione/piastra di estrazione, manicotto di espulsione, ecc.
E. Sistema di condizionamento della temperatura: L'acqua di raffreddamento deve essere installata sia nella cavità che nel sito del nucleo per soddisfare i requisiti della temperatura dello stampo durante la processo di stampaggio a iniezione.
F. Linea di separazione laterale e azione laterale: Lo scorrimento dovrebbe essere adottato quando c'è una struttura sottosquadro sul design del prodotto, vale a dire la struttura inconsonante con la direzione di sformatura. Di solito è costituito da scorrimento, sollevatore, anima libera, ecc.
G. Sistema di ventilazione: È costituito da due forme: la scanalatura di sfiato e lo spazio tra i componenti dello stampo. Per scaricare l'aria nella cavità e il gas causato nel processo di stampaggio, la scanalatura di sfiato è solitamente impostata sulla linea di separazione, con il principio di progettare la scanalatura di sfiato il più grande possibile in conformità con un traboccamento e una lampeggiatura uniformi. Nel frattempo, il perno di inserimento, il perno di espulsione e l'inserto dello stampo scaricano l'aria attraverso gli spazi tra i componenti dello stampo.
2. Riparazione di stampi in plastica
La riparazione dello stampo è necessaria in caso di abrasione normale o anomala e in caso di vari fenomeni anomali verificatisi durante produzione di stampaggio di plastica.
2.1 Preparativi per il moldmaster (costruttore di stampi)
A. Chiarire in quale misura la muffa è danneggiata;
B. Sviluppare un piano di riparazione in base al campione di modanatura danneggiato.
C. È necessario avere una comprensione precisa del lavoro di riparazione da svolgere: La riparazione dello stampo viene solitamente eseguita senza disegno con il principio di non modificare la struttura e le dimensioni delle parti in plastica. Pertanto, è un prerequisito per il nostro tecnico capire esattamente dove e a quale dimensione la parte deve essere riparata.
2.2 Cosa fare e cosa non fare durante il montaggio e lo smontaggio dello stampo
UN. Segno di segno: Il segno corrispondente nella base dello stampo deve essere ricordato chiaramente quando si rimuove il perno guida, il manicotto di espulsione, il perno di espulsione, l'inserto dello stampo, il blocco di supporto, ecc., per garantire la corretta reinstallazione dello stampo, in particolare per quelli con requisiti di direzione. In questo processo, è necessario prestare attenzione ai due elementi seguenti:
- Il marchio firmato è esclusivo e non duplicabile;
- Il segno di segno deve essere fatto su ogni inserto dello stampo di conseguenza
B. Anti-danno: La protezione anti-danno deve essere eseguita per le parti facili da installare. In altre parole, le parti non possono essere reinstallate con un'installazione non corretta;
C. Posizionamento: Le parti rimosse devono essere riposte in ordine, mentre viti, molle e O-ring devono essere riposti nella scatola di plastica.
D. Protezione: È necessario adottare misure di protezione per le parti di precisione, quali l'anima dello stampo, la cavità e così via, per evitare danni causati da persone incaute.
2.3 Cosa fare e cosa non fare quando si ripara una superficie con texture di muffa
UN. Lucidatura: Misure di protezione per il componente della superficie strutturata devono essere prese prima del lavoro di riparazione quando è necessaria la lucidatura per parti in plastica con aderenze e graffi dello stampo. È vietato lucidare l'area della superficie strutturata. La riparazione dello spegnimento dello stampo deve essere eseguita se non si è certi del risultato della riparazione.
B. Linea di saldatura: Durante la saldatura su superfici strutturate, prestare attenzione ai seguenti elementi:
- Il materiale della bacchetta di saldatura deve essere coerente con quello del nucleo dello stampo;
- La tempra deve essere effettuata dopo la saldatura;
C. Ristrutturare:Quando la riparazione dello stampo è terminata e si è pronti per rimuoverlo per la nuova testurizzazione, fabbricante di stampi dovrebbe creare una buona protezione dell'area di texture coperta con carta, segnare la posizione per creare l'area di texture e attaccare il modello di texture con lo stampo. Dopo la testurizzazione dello stampo, il produttore dello stampo dovrebbe esaminare attentamente la superficie testurizzata per garantire una buona qualità e quindi reinstallare lo stampo.
Se non si è sicuri del risultato della riparazione, si dovrebbe prima effettuare il test della muffa. Se è OK, allora togliere la muffa per creare la consistenza
3. Manutenzione degli stampi in plastica
Manutenzione degli stampi in plastica è più importante della riparazione dello stampo. Più frequentemente viene riparato, più breve sarà la vita dello stampo. E viceversa.
3.1 La necessità della manutenzione degli stampi
- Mantenere il normale movimento dello stampo ed evitare l'abrasione non necessaria delle parti mobili;
- Mantenere lo stampo per una normale durata di servizio;
- Ridurre la contaminazione dell'olio durante la produzione.
3.2 Classificazione della manutenzione delle muffe
- Manutenzione ordinaria dello stampo;
- Manutenzione programmata dello stampo;
- Mantenimento dell'aspetto dello stampo.
3.3 Articoli per la manutenzione degli stampi in plastica
a. Manutenzione ordinaria:
- Riempimento di olio nelle parti mobili come perno di espulsione, slitta, perno guida e manicotto di espulsione;
- Pulizia della superficie dello stampo;

- Dragaggio del canale di raffreddamento;
b. Manutenzione programmata, in base a quanto sopra indicato;
- Pulizia della fessura di sfiato. Aggiungere una fessura di sfiato nei punti di intrappolamento dell'aria e posizionare l'area del segno bruciato;
- Riparazione di parti danneggiate e soggette ad usura;
c. Mantenimento dell'aspetto:
- Verniciare l'esterno della base dello stampo per evitare la ruggine;
- Dopo la caduta/chiusura dello stampo, la cavità deve essere rivestita con olio/grasso antiruggine.
- Per evitare che la polvere penetri nel nucleo dello stampo, è opportuno chiuderlo ermeticamente prima di riporlo.
3.4 Cosa fare e cosa non fare per la manutenzione delle muffe
a. Per le parti mobili, è necessario il rabbocco dell'olio durante la manutenzione di routine;
b. La superficie dello stampo deve essere sufficientemente pulita: la carta per etichette non può essere attaccata sul lato P/L. Non chiudere lo stampo quando la parte di stampaggio è attaccata alla cavità o al lato del nucleo, pulire i residui di plastica nella posizione P/L.
c. Identificazione delle condizioni anomale. È necessario intervenire tempestivamente in caso di anomalie nell'espulsione, forte rumore durante l'apertura e la chiusura dello stampo.
4. Problemi di sicurezza durante la riparazione e la manutenzione dello stampo
La sicurezza dovrebbe essere messa al primo posto sempre e ovunque. La riparazione e la manutenzione degli stampi, con stretto contatto con la macchina per stampi e le attrezzature in acciaio, non fanno eccezione. È necessario prestare molta attenzione alle questioni di sicurezza durante questo processo.
- Esaminare attentamente prima dell'uso per assicurarsi che l'anello di sospensione sia in perfette condizioni.
- Il lavoratore deve indossare occhiali di sicurezza quando utilizza la macchina per stampi per evitare che i trucioli volino negli occhi
- Durante il processo di saldatura il lavoratore deve indossare indumenti protettivi e occhiali di sicurezza.
- È vietato operare sul fondo dello stampo.
- Prima di azionare la macchina, la macchina per stampaggio a iniezione deve essere ferma e su di essa deve essere appesa la targhetta identificativa.