¿Qué es el informe de análisis de flujo de moldes?
Análisis del flujo de moldes (MFA) es una herramienta de simulación que se utiliza para predecir y optimizar el flujo de resina plástica en un molde durante el proceso de moldeo por inyección. La simulación tiene en cuenta las propiedades de la resina y la geometría del molde, y predice el comportamiento del plástico a medida que llena el molde y se enfría.
Informe de análisis del flujo de moldes puede ayudar a identificar y resolver posibles problemas del proceso de moldeo por inyección, como disparos cortos, alabeos, líneas de soldadura, trampas de aire, marcas de hundimiento, etc. Informe de análisis del flujo de moldes también puede utilizarse para optimizar el proceso de moldeo por inyección identificando la mejor ubicación para las compuertas y los canales, determinando la velocidad de inyección óptima y prediciendo el mejor tiempo y temperatura de enfriamiento. Esto puede ayudar a reducir el tiempo de ciclo, mejorar la calidad de las piezas y aumentar la eficiencia de la producción.
Informe de análisis del flujo de moldes
Resumen de los resultados del análisis del flujo de moldes
Una vez que hemos terminado el diseño del molde, antes de comenzar la fabricación del molde, para asegurarnos de que todo está sin problemas, tenemos que hacer el Análisis del flujo del molde para comprobar los posibles problemas, esta es la forma de seguridad para evitar errores, especialmente para los grandes moldes. a continuación se presentan algunos puntos que tenemos que comprobar al hacer el informe de análisis de flujo de molde.
Tiempo de llenado del molde – El tiempo de llenado es el tiempo necesario para llenar la cavidad de la pieza. El gráfico de tiempo de llenado también proporciona una animación del llenado de la cavidad del molde. El tiempo de llenado también puede controlarse durante el análisis para resolver problemas de calidad, como tensiones de cizallamiento elevadas.
Presión de inyección – A standard injection molding machine is capable of pressurizing the melt flow to 20,000 psi (2,000 psi hydraulic gage pressure). A portion of the pressure is used to push the plastic through the runner system, some of the pressure is used to push the plastic into the cavidad del molde, and a portion of the pressure is used to “pack out” the part after it is filled. If the part and runner system require more pressure than the machine is capable, than the part will be a short shot or have deep marcas de hundimiento.
Líneas de soldadura Defectos – Weld lines are formed when two flow fronts meet and “weld” together. Weld lines are usually a visible line on the part and can be an appearance issue. Weld lines may also reduce the part strength by 10% – 20% potentially creating a structural issue depending on their location. If mold flow analysis is not used to fix these problems before the tool is built, the molder will be forced to: increase injection pressure, increase melt temperature, increase mold temperature, enlarge vents, change the gate location and/or alter the thickness of the part. All of these “solutions” take time and money to implement and/or increase the cost of the part.
Trampas de aire Defectos – Air traps are formed when the molten plastic traps air in the part cavity as it fills. If these air traps are not vented, they can lead to quality problems such as burn marks, short shots, pronounced weld lines and incomplete fill. Our air trap plots allow the toolmaker to know exactly where the vents need to be placed when the tool is built. Air traps that are in locations that are difficult to vent can be moved to better locations by moving the gate. Doing this work before the tool is built can save on the amount of debug and mold changes that are required.
Calidad – The definition of a quality molded part is not only that the part filled completely. A quality molded part must also be free of material degradation and low in molded in stress. The quality plot shows the severity and areas that are suffering from quality problems. The problems detected include excessive shear stress and shear rate, and hard to pack areas. Suggestions like thickness adjustments, processing condition changes and fill time adjustments can be tried to eliminate the quality issues.
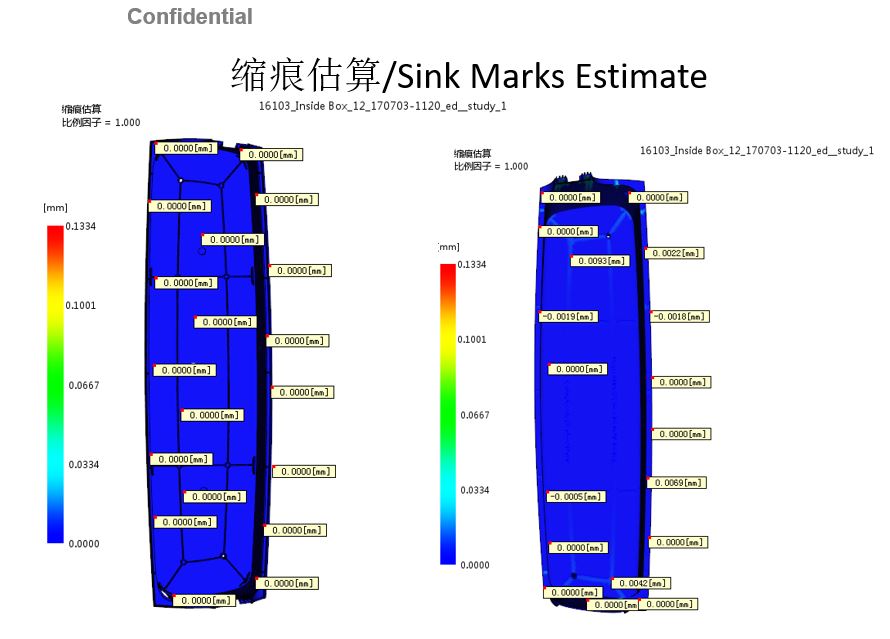
Marcas de fregadero Defectos – Sink marks are localized depressions in the surface of injection molded parts caused by a non uniform shrinking of the plastic during the cooling. In cosmetically critical parts, they can be a serious problem. Sink marks often come as a surprise when the tool is complete. If the sink marks are objectionable to the customer, the molder is often tasked with “eliminating them”. This usually means running the molding machine at the extremes of the process window, which can lengthen cycle times and increase the amount of molded in stresses and material degrade.
Tiempo de enfriamiento – It has been shown that cooling time averages about 50% of the molding cycle. If the material in use is a commodity resin, the molding cost far outweighs the material cost. In this case, a reduction in cooling time has a big reduction in the part cost. Our Cooling Analysis can reduce your cooling cycle and optimize your cooling system eliminate hot spots and warpage.
El AMFE es una potente herramienta que puede ayudar a mejorar la eficacia y la calidad del proceso de moldeo por inyección, simulando el comportamiento de la resina plástica a medida que fluye por el molde y se enfría. Ayuda a identificar posibles problemas y a optimizar el proceso para minimizar los defectos y mejorar la calidad del producto final.
Realizamos análisis de flujo de molde para su proyecto
Si usted tiene un proyecto que tienen muchas preocupaciones, por favor póngase en contacto con nosotros, vamos a comprobar todos los de su dibujo de la pieza y hacer Informe DFM y moldflow análisis para usted, y resumir todos los posibles problemas en la hoja de datos y enviársela de vuelta.

