Custom Plastic Molding
Custom Plastic Molding
Custom Plastic molding is one of the most cost-effective processes for producing large quantities of plastic products. It uses a die or mold in which melted plastic is injected under pressure, cooled, and hardened to produce the final part before being released. This cycle can be repeated very quickly, possibly 1000 times, which distributes the initial cost of the mold over a large number of units, making the cost per part a few dollars or less.
Repeatability and reliability are achieved because a single mold can be used to produce each part. Furthermore, injection molding provides flexibility in terms of a broad range of material options, colors, finishes, and surface treatments that cannot be matched by CNC machining or 3D printing.
Sincere Tech has a highly skilled workforce with years of experience in different sectors, like medical injection molding and LSR molding. New customers are also given a $500 credit on their first mold with Sincere Tech. We have choices for domestic and custom plastic molding company services from a broader prospect.
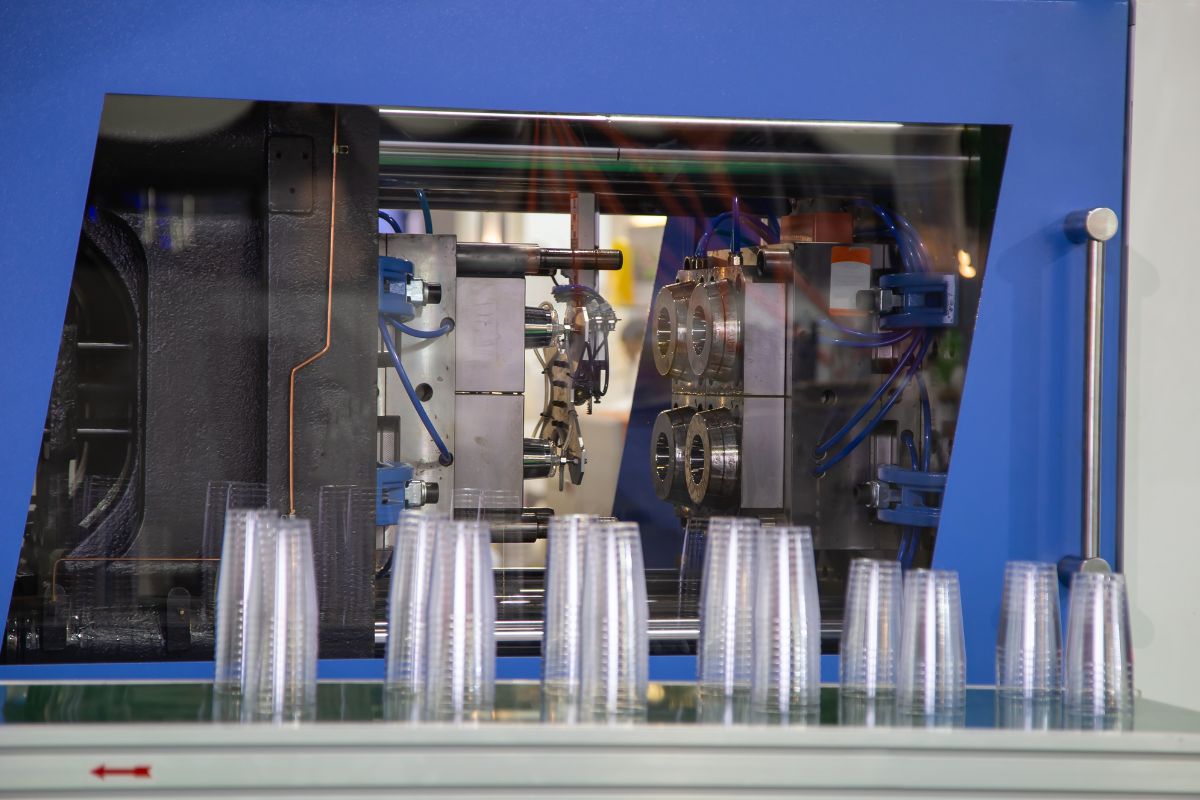
Types of Custom Plastic Molding Techniques
In designing custom molded products and their components, it is critical to choose the correct manufacturing process to obtain a high-quality and durable final plastic product with acceptable costs and production time. Here are the most commonly used techniques of custom plastic molding process;
Thermoforming
Thermoforming involves heating a large sheet of plastic to make it pliable and then forming it over a one-sided mold. The use of vacuum pressure or compressed air to force the thermoplastic closely against the mold to the required shape. The advantages of thermoforming are the low cost of tooling, the short time to market, and the ability to produce large parts such as bathtubs and car dashboards. Also, thermoforming is fast in prototyping and can be customized to a great extent.
Extrusion molding
Extrusion molding is mainly applied to produce long and straight products such as tubes, hoses, or pipes. This method involves the use of pressure to force liquid plastic into a specific shape of a die. Although round shapes are typical, t-shapes, l-shapes, and squares are also possible due to the die’s shape. The advantages of extrusion molding are the low cost of tooling and machinery, little or no need for finishing other than cutting the pieces to the required length, and the possibility of attaining intricate and uniform cross-sectional shapes.
Compression molding
Compression molding is most commonly applied with thermosetting plastics, which, when heated and then cooled, undergo a chemical change to become a rigid solid. In this method, the plastic resin is melted and formed into a putty-like substance and then put into a hot mold. The putty is then compacted by the mold and left to cool. Compression molding is suitable for making plastics that compete with metals, are suitable for rigid lightweight thermosets, and are commonly used in fiberglass reinforced or rubberized plastics.
Blow molding
Blow molding is similar to injection molding, where the plastic is first melted and then injected into the mold. Air is then pumped into the plastic, making it expand and conform to the shape of the mold walls. Blow molding is most suitable for manufacturing items that are thin-walled and have a hollow structure, like water bottles or 2-liter bottles for sodas. This method is fast and is relatively cheaper when large quantities are being produced.
Rotational molding
Rotational molding, or “roto-molding,” is the process of placing a mold into a heated container of liquid polymer and then spinning the mold rapidly. This process covers the plastic uniformly on the walls of the heated metal mold while the interior remains empty. Rotational molding is mainly applied to large, hollow-partitioned containers, storage bins, and even kayaks. The advantages of this method include low setup costs, constant thickness of the walls, and low cost for very small or short runs.
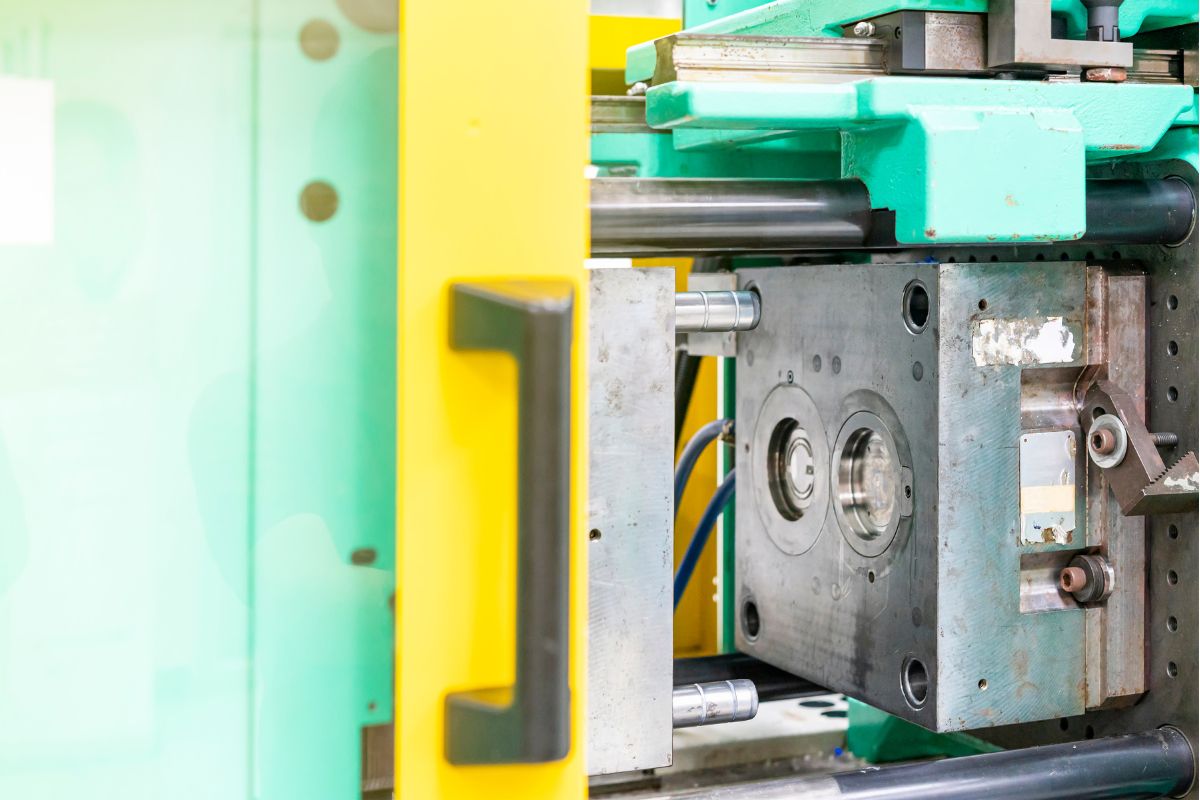
Injection molding
Injection molding is one of the best cost-effective molding technology comparing to rest of above, and this is our mean services, we have offering this service over 18 years, if you have any project that need custom injection molding service, welcome to contact us, and you can go to custom injection molding page to know more about this technology.
The six manufacturing methods of plastics are as follows: By knowing these six manufacturing methods of plastics it will assist manufacturing companies in choosing the best method that will produce the required durability, quality, cost, and efficiency of the products.
Custom Molding Plastic Materials
Custom plastic mold uses engineered grade custom molded plastics to design intricate patterns or part designs. Some common types include;
ABS, or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is a strong plastic that is used in many market goods. A lot of people know this material for how well it resists wear and shock. It is often found in car parts and home items.
ASA stands for acrylonitrile styrene acrylate. It is like ABS, but it is more resistant to UV light, so it can be used outside. It doesn’t fade or wear out quickly. This material is often used in cars and outdoor furniture.
Calcinedioacetate, or CA, is a clear material that can be bent and is used in films and glasses. For uses that come into touch with food, it is safe. It looks shiny and can hold its shape well when pulled apart.
HDPE, which stands for “high-density polyethylene,” is strong for its weight and doesn’t react with chemicals. It’s used for many things, like fuel tanks, food bins, and playground equipment outside. Strong and resistant to the weather.
It has a great mechanical strength even at high temperatures. It is called LCP (liquid crystal polymer). Micromolding and parts with thin walls are both possible. It is used in medical products and electrical connectors.
LDPE, or low-density polyethylene, is a strong material that can be used for many things and doesn’t react with acids, bases, or alcohol. Used in snap lids, trays, and other general-purpose cases. Offers good resistance to force.
PA 6 (polyamide 6, nylon 6) is known for being stiff and strong on a technical level. It resists heat and chemicals well. Used in industry and automotive parts.
PA 6/6, also known as polyamide 6/6 or nylon 6/6, is similar to PA 6 but has better mechanical qualities. Better at keeping heat in. Used a lot in places where there is a lot of stress, like gears and bearings.
Polyarylamide, or PARA, is often backed with glass or mineral fibers to make it hard. You can use it to make structural parts because it doesn’t creep or soak up water. Used for medical and travel purposes.
Polybutylene terephthalate, or PBT, is a type of plastic made from polyester that is used to keep electronics safe. Often used as an alternative to nylon in car parts because it doesn’t wear down as quickly. Offers good stability in terms of size.
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are two materials that work well together to make things stronger and more resistant to chemicals. Used in situations where the ability will be needed for a long time. Seen in the production of car and electronic parts.
PC, or polycarbonate, is a type of polymer that is very light and doesn’t break easily when hit. It is often used in safety gear and glasses. This item has great sharpness and lasts a very long time. Widely used in many fields for tasks that need to be very strong.
PC-ABS, which stands for polycarbonate-acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is a mix of PC, which is stiff, and ABS, which is flexible. Strong enough for technical tasks that need to be done. Used in the electronics and auto businesses.
PC-PBT (polycarbonate-polybutylene terephthalate, Xenoy): Can’t be damaged by chemicals or lubricants used in the housing of electronics. Offers strength and stiffness. Often used in industrial settings.
PC-PET, which stands for polycarbonate-polyethylene terephthalate, is a material that is strong and resistant to poisons. Strong cleaners and chemicals won’t work on it. utilised in the creation of sporting items and medical gear.
Polycyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate (PCT): It absorbs water better and is more stable in the environment than PET. It is often used in switches and links. Suitable for applications that need great performance.
PE (polyethylene): It can be shaped very easily and is resistant to chemicals and wear. Used in tubes, films, bottles, and other packaging products. It has different grades, like UHMW, LDPE, and HDPE.
PEEK, which stands for polyether ether ketone, is very strong when pulled apart and doesn’t melt at high temperatures. In high-stress situations, it is sometimes used instead of metal. It is used in medical and aircraft settings.
Polyetherimide, or PEI, is used a lot because it can handle high temperatures and flames. A cheap material that can be used instead of PEEK in medical settings. Offers good stability in terms of size.
Polyethylene-polypropylene, or PE-PP, is a blend made up of polyethylene and polypropylene that has properties of both. Used in a variety of general-purpose situations. Chemical protection is good.
Polyethylene-polystyrene (PE-PS) is a material that has the qualities of both polyethylene and polystyrene. Suitable for a wide range of uses. combines being flexible and stiff.
Plastic called polyethersulfone (PES) is clear, hard, and doesn’t mix with chemicals or heat. It can also be sterilized. Used in the aerospace and food processing equipment businesses. It is often used in situations where great performance is needed in harsh conditions.
PET (polyethylene terephthalate, Rynite): It’s usually tough, clear, and light, and it’s used to make food wrappers and drink bottles. With a plastic code of 1, it can be recycled. It works well as a shield.
PLA, or polylactic acid, is a plastic that is good for the climate, can be recycled, and has a low glass transition temperature. Often used in short-term situations. Compostable and good for the environment.
PMMA, also known as acrylic or polymethyl methacrylate, is a clear plastic that looks like glass and wears well. Great for using outside. For example, in displays, signs, and glass.
Acetal polyoxymethylene, or POM, is a material that doesn’t absorb water and doesn’t stick to things easily. A great choice for precise parts. Used in bearings, gears, and other industrial parts.
Polypropylene (PP): It’s good at conducting electricity and staying stable in chemicals. Low ability to absorb water. It is used in textiles, car parts, and packaging.
Polyphthalamide, or PPA, is a type of nylon that has a relatively higher melting point and a relatively lower ability to absorb water. It can be used in both cars and factories. Useful for devices that distribute fuel and fluids.
Polyphenylene sulphide, or PPS, is a high-tech thermoplastic that is very resistant to acids. Found in the electronics and auto businesses. It’s very resistant to heat.
PS (polystyrene) is clear, stiff, and easy to break. It is often used to make food wrap and single-use items. It doesn’t cost much and is easy to make. Often found in shopping goods.
Noryl is made of PS-PPE, which is polystyrene-polyphenyl ether. It is also very resistant to heat and flame. Good hardness and tensile strength at high temperatures. Used in the auto and electrical businesses.
Polysulfone (PSU) is stylish, hard, and clear. It’s a better choice than polycarbonate and works better. Used in the production of medical gear and tools for moving food. Chemical protection is good.
Polyvinyl chloride (Shore D) or PVC is a hard, mass-produced plastic that is used to make pipes and things that don’t last long, like food wrap. Long-lasting and useful. Used in the automotive and building industries.
PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride, also known as Kynar): Doesn’t mix with anything and can handle high temperatures. Used to make plumbing parts, electrical insulation, and chemicals. It doesn’t stick to things well and doesn’t last long.
SAN stands for styrene acrylonitrile. It is clear, doesn’t melt in the heat, and is cheap. Kitchen tools, plates, and other things used around the house have it. It makes the gloss and clarity better.
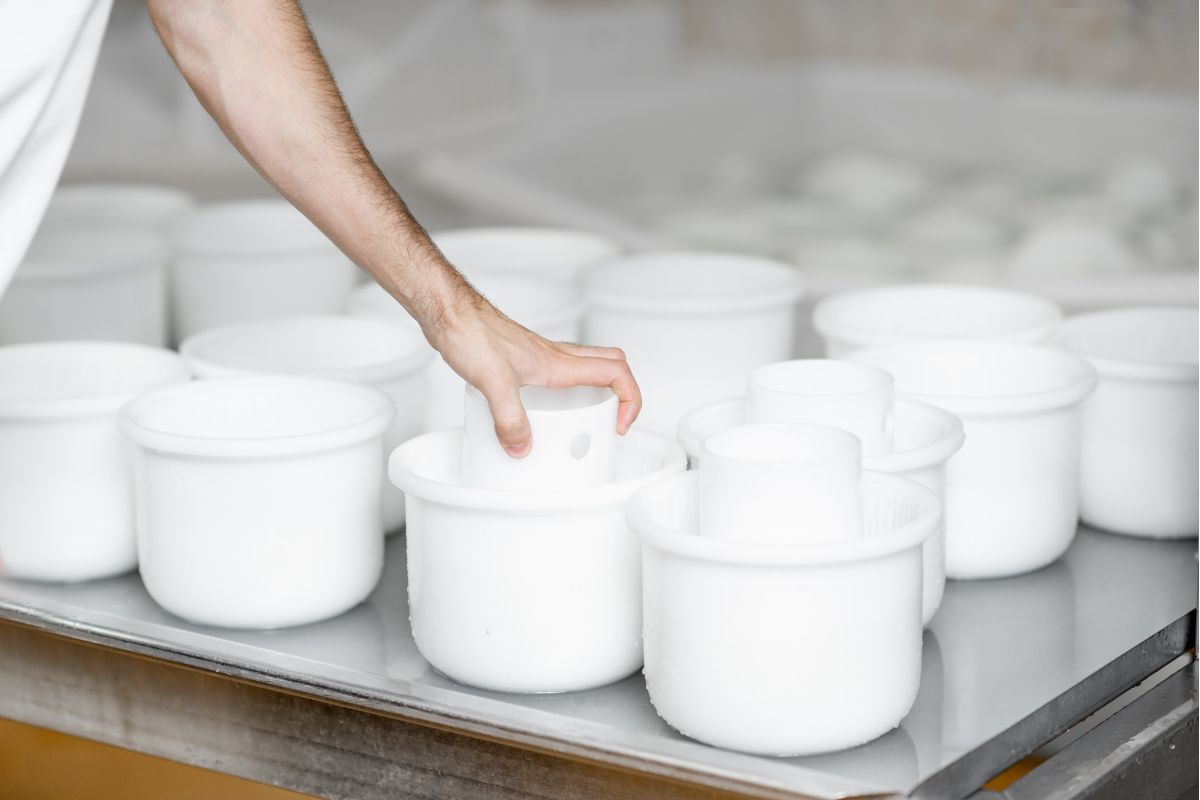

Elastomeric Injection Molded Materials
Elastomeric parts can also be processed through the injection molding process, transfer molding, and compression molding. Some common types include;
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber): EPDM is widely used due to its high heat and chemical resistance. Some common uses include in automotive seals, gaskets, O-rings, and electrical insulators.
PEBA (polyether block amide): PEBA is soft and flexible and widely used in the construction of medical instruments such as catheters. PEBA foams are used for padding, shoe insoles, and sports equipment because of their moisture and UV resistance.
PVC (polyvinyl chloride, Shore A): PVC is an elastic thermoset that is a resilient material, and is often used in products for outdoor use, protective coatings, and mats. It needs plasticizers to make it flexible and is famous for its flame resistance.
TPE (thermoplastic elastomer): TPEs are a group of elastomers that possess the characteristics of thermosets but with the processing ability of thermoplastics. They encompass a broad spectrum of special elastomer categories.
LSR (liquid silicone rubber): These are used in foods and biomedical applications due to their heat, biocompatibility, and flexibility. LSR is applied in medical devices, automotive, aerospace, and consumer products, and it is processed differently from injection molding.
Custom Plastic Molding Surface Finishing Options
Standard Finish: This finish, usually SPI B-2, is selected by the mold maker depending on the part’s shape and the angles of the parting line. It is often applied to non-aesthetic parts, and the parts are left machined for functionality without extra expense or time.
SPI Finishes: These are the standard surface finishes set by the Society of the Plastics Industry that dictate the feel and look of the molded parts. They assist in meeting certain aesthetic and functional objectives, which makes them suitable for many uses.
MoldTech Finishes: These are specialized texturing processes that put patterns or textures on the mold surface to improve the aesthetic and feel of the finished part. MoldTech finishes are applied to achieve specific looks and enhanced tactile feel or to mimic other materials such as wood or leather.
Other Textures – VDI: VDI textures are available in various forms, with varying degrees of roughness and appearance to meet certain design requirements. They are widely applied in industries where the surface finish is a critical factor in the product’s functionality or aesthetics.
Design Tips For Custom Plastic Molding
Undercuts: Reduce undercuts to make the tool ejection mechanisms easier and to avoid complications in manufacturing. The use of pass-through coring can also help achieve this goal while at the same time not compromising on the costs of production.
Wall Thickness: Ensure that the thickness of the wall is constant so that there will not be problems such as wall sinks and voids during molding. Reduced wall thickness is beneficial in the aspect of cycle time and cost of manufacturing.
Drafts: Make sure that the parts have a minimum draft angle of 0. 5° to 5° especially when molding textured faces, to ensure that the faces eject smoothly and free from molding defects.
Ribs/Gussets: Make the ribs to be 40-60% of the outer wall thickness while ensuring that the draft angles are correct for the structure. In this case, it is possible to achieve an increase in strength while maintaining the moldability of the gussets.
Bosses: Design bosses with a depth of 30% of the thickness of the wall and include a 30% edge recess for optimal performance.
Benefits & Applications of Custom Plastic Molding
Injection Molded Part: The tooling is inexpensive, and the company can produce parts quickly, with delivery in as little as 10 business days at low prices.
Rapid Prototyping: Injection molding is a fast method of prototyping and can be used to test various designs within a short span.
Production Parts: Custom plastic molds are ideal for manufacturing a large number of production parts at high efficiency and low cost.
Range of Industries and Certifications: Injection molding is used in different fields and complies with the necessary standards to meet the needs of specific applications.
Stand Afirm With Sincere Tech For Your Custom Plastic Molding Project
In as much as custom plastic injection molding is concerned, Sincere Tech is one of top 10 plastic injection molding compnies in China. With ISO 9001:We have 2015 and ISO 13485 certifications, and this means that we value quality and precision in all the projects that we undertake. The extensive capabilities make it possible for us to work with many industries and provide high-quality injection-molded components with high precision.
Contact us today to find out more about our state-of-the-art plastic injection molding services. Whether it is prototype or production parts, Sincere Tech is dedicated to providing you with the parts you need in the best quality by offering stringent quality custom molded plastic materials and finishing solutions. So, do not wait to get a quote and become our partner in your next successful injection molding project.




