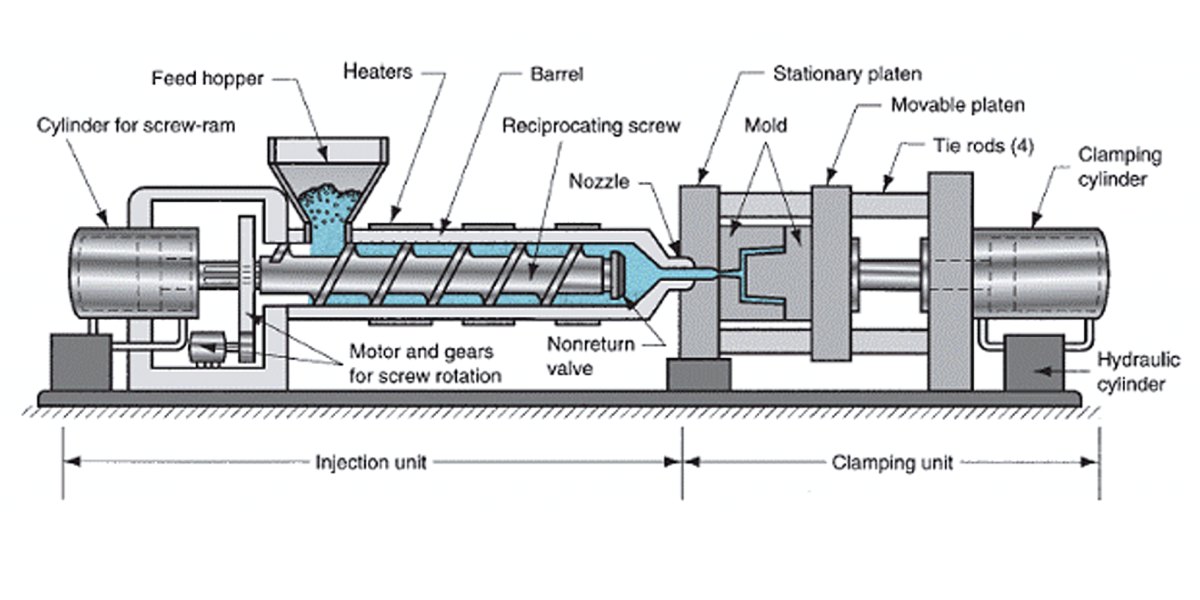
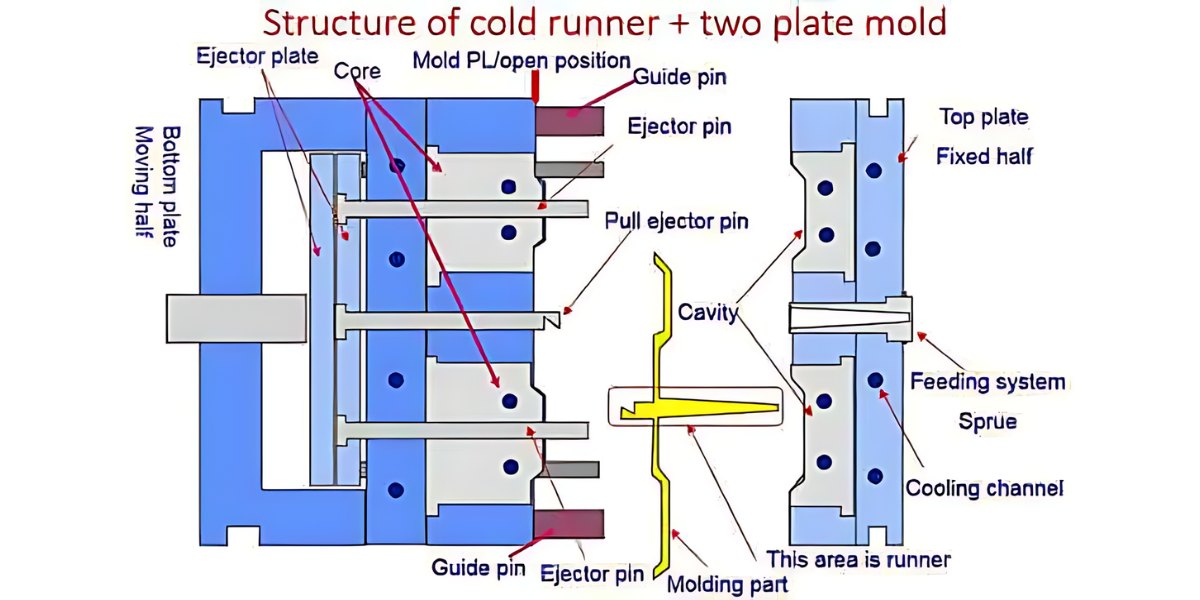
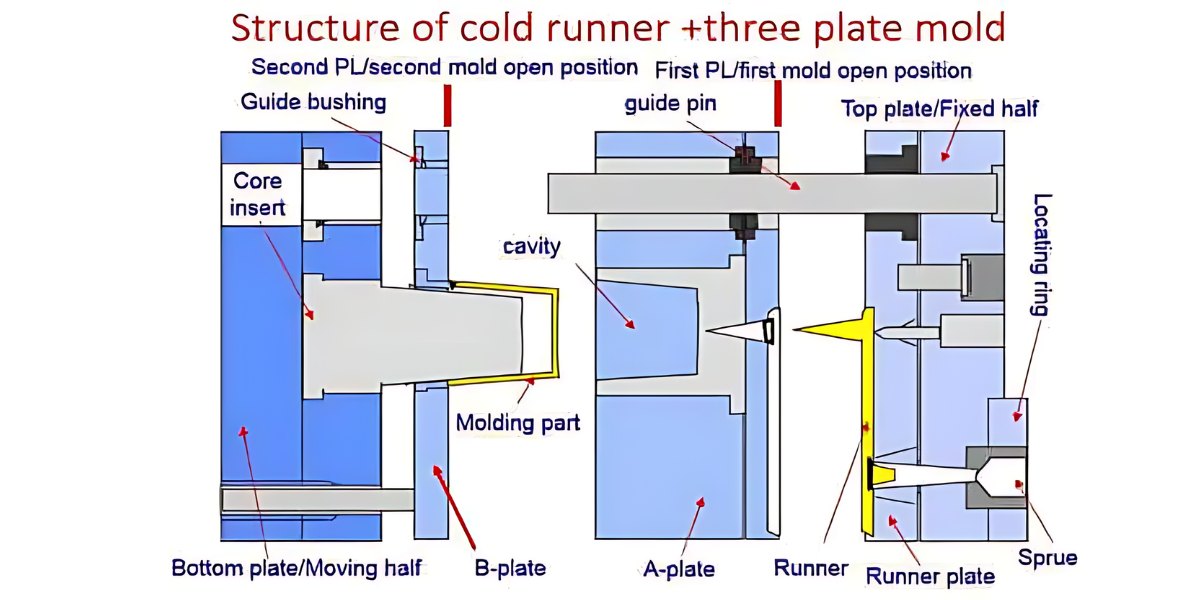
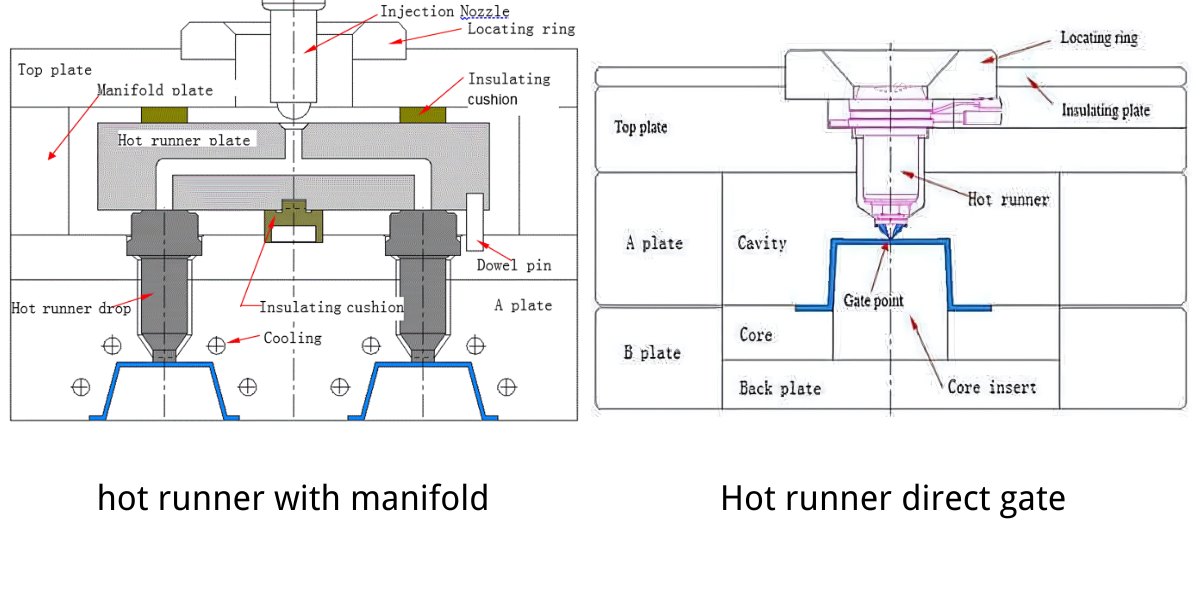
Polypropylene injection molding or PP injection molding, is a molding manufacturing technique using polypropylene, which is a type of thermoplastic polymer material that is exposed to heat until it turns to melt. The process forces the low viscosity molten polymer to flow into specially designed molds. On cooling, the liquid turns into a solid plastic and assumes the mold’s shape. This technique is most effective when used on the polymer in its processed form. This technique enables the creation of geometries that would otherwise be challenging to achieve. Curious about polypropylene itself? Now, let’s explore more about polypropylene and its uses, along with the reasons for its popularity in injection molding.
In this article, we will give you a comprehensive description of injection molding polypropylene and discuss the strengths of PP material as well by considering its applications across manufacturing sectors.

Types of Polypropylene Used In Molding Applications
The most common types of propylene employed in molding applications include;
1. Homopolypropylene (PP-H)
PP-H, or homopolypropylene is the most used type of polypropylene, characterized by high rigidity and strength as a result of crystalline structure. It is commonly employed in uses where the material will be exposed to a lot of force, as it is with containers, auto parts, and more. PP-H has good chemical and heat resistance hence; it is used in products such as buckets and other household utensils. However, it is less flexible and therefore not as effective in more flexible applications.
2. Random Copolymer Polypropylene (PP-R)
PP-R is a random copolymer polypropylene that contains only a small amount of ethylene, which increases its flexibility and impact strength. This makes PP-R suitable for use in piping systems, automotive parts, and any other consumer goods that are expected to have a long life cycle. Due to these properties, it is commonly used in hot and cold water pipes and containers where strength and flexibility are a requirement.
3. Block Copolymer Polypropylene (PP-B)
PP-B is a block copolymer polypropylene that has a block structure with ethylene thus making it have better impact strength and elasticity compared to PP-A. This type is applied in the automobile industry, in the manufacturing of shockproof packaging material and other heavy-duty consumer products. The automotive sector and protective packaging industries are ideal for PP-B because of its flexibility and damping properties in stressed applications.
Polypropylene Injection Molding: How Does it Work?
PP Plastic Injection molding provides an advantage of mass production of identical plastic parts. High volumes- from a thousand to millions of identical parts can be produced at one time. Because the intended mold is reused several times in the part’s manufacturing process. This makes polypropylene injection molding another suitable option to meet the large demand and ensure that the products produced are of equal quality, simultaneously.
Process Conditions For Propylene Injection Molding
Table 1: Operational Parameters for pp plastic injection molding.
| Parameter | Specification |
| Drying Requirement | Dry at 80-90°C (176-194°F) for 2 hours; moisture level must be under 0.1%. |
| Melting Temperature Range | 220-280°C (428-536°F) |
| Mold Temperature Range | 20-80°C (68-176°F) |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | 100°C (212°F) at 0.46 MPa (66 PSI) |
| Injection Temperature | 32-66°C (90-150°F) |
| Tensile Strength | 32 MPa (4700 PSI) |
| Flexural Strength | 41 MPa (6000 PSI) |
| Density | 0.91 g/cm³ |
| Injection Molding Pressure | Up to 180 MPa |
| Shrinkage Rate | 1.5-2.0% |
Comparison of Polypropylene Grades for Injection Molding
Let’s compare, different injection molded polypropylene grades for the molding process.
Table 2: Technical Specifications of different injection molding polypropylene plastic Grades.
| Polypropylene Type | Tensile Strength | Elongation at Break | Flexural Rigidity | Heat Resistance | Notable Features |
| Pro-fax 6323 | 4,930 psi | 11% | 210,000 psi | 199.0 °F | General-purpose, resists stress cracks |
| Pro-fax SG702 | 2,900 psi | 6% | 150,000 psi | 180.0 °F | Impact-resistant, suitable for automotive use |
| Pro-fax 6523 | 4,790 psi | 12% | 200,000 psi | 190.0 °F | Stiffness, ideal for food packaging |
| Pro-fax PD702 | 4,500 psi | 12% | 170,000 psi | 190.0 °F | Maintains dimensions well, easy to process |
| FHR P5M6K-048 | 3,900 psi | 11% | 153,000 psi | 183.0 °F | Clarity-enhanced, visually appealing |
Design Guidelines for Polypropylene Injection Molding Parts
Molding of polypropylene is easy, but to get the best result, one has to follow certain design principles. This section focuses on the practical recommendations that are necessary to produce long-lasting and high-performance polypropylene components.
Living Hinges Key Factors
When designing living hinges in polypropylene, it is good to work at a thickness of between 0.2 mm to 0.51 mm. For optimum performance, the radii should be wide and the hinge should have a flat shoulder. This design approach provides flexibility and strength to withstand the usage of the hinge when used several times.
Guidelines for Wall Thickness
In the case of polypropylene parts, the thickness of the walls of the product must not exceed 0.635 mm to 3.81 mm thickness. Thick parts should also have smooth changes in thickness from one level to another to avoid defects such as sink marks. Moreover, ribs should preferably be less than half the thickness of the adjoining walls to provide strength and prevent the formation of structural voids.
Radii in design
Radii in the mold design also assists in reducing stress concentrations. So, it significantly impacts the life cycle of the part. The suggested radius should be at least twenty-five percent of the wall thickness. The radius of curvature should be 75% of the thickness of the wall which gives both the strength and the fine surface finish.
Draft Angle Recommendations
Polypropylene can take very small angles of drafting, as small as one degree, which is adequate for most parts. But if your part has textured surfaces, it’s recommended to increase the draft angle up to five degrees depending on the depth of the texture. In the case of filled polypropylene materials, it may be necessary to have a draft angle of up to ten degrees to facilitate easy ejection of the part and to improve the quality of the final part.
Setting Part Tolerances
Requirements for tolerance of polypropylene parts can be classified into commercial tolerance or fine tolerance. Commercial tolerances are relatively larger and cheaper as compared to fine tolerances which are precise but expensive. For instance, a commercial tolerance for a 20 mm part will be in the region of ± 0.125 mm, while the fine tolerance for the same part is about 0.075 mm. Thus, it’s crucial to understand that if tighter tolerances are desired they can have a large impact on the production cost.
Polypropylene Material Processing
Polypropylene has a melting point within the range of 160-170°C and this means that correct temperature control is required while processing the material. Additionally, it is crucial to dry the polypropylene pellets for the injection molding process. For optimal outcomes and splay-free parts, the moisture must be kept below 0.02%.
Injection Molding
The PP injection molding temperature is needed around 220°C and 280°C while the mold temperature is between 30°C and 80°C. These conditions are as follows to have proper flow and solidification. Cycle time is another critical consideration. Usually, it refers to the time taken to complete a cycle and it should be reduced to avoid warping, and efficient cooling is important. In addition, cooling channels must be designed in such a manner that allows equal distribution of heat all over the surface.
Extrusion Processing
Extrusion is carried out by melting Polypropylene at a temperature of 210°C to 250°C. Temperature control and cooling rate are two critical factors that need to be well controlled to allow the formation of the desired product properties.
The extrusion die is a critical component in the process. It has to be designed to not allow the die to swell and control the flow of the material that is being extruded to achieve the desired quality of the final product.
Blow Molding
The blow molding process involves heating polypropylene and then forming it into a parison and blowing it in a mold. Temperature and inflation pressure should be strictly maintained to produce the desired shape of the product. Ejection Part cooling is required to retain the part shape and dimensions. The cooling rate should be dependent on the size and complexity of the part in question.

Quality Inspection:
The two areas that are of particular importance include;
- Sanitary and Storage Procedural Measures The Purity of polypropylene depends on handling and storage procedures and clean equipment.
- Quality Control Periodical examination during processing helps to ensure that the material and the final products are of the right quality and standard and meet the requirements.
What are The Benefits of Propylene Injection Molding?
The following are the benefits of polypropylene injection molding:
- Affordability: Polypropylene injection molding is relatively cheap and more so for productions that will require large quantities. The process has a low material cost and little wastage since the material that is in excess can be reused in the system. This efficiency means that large production volumes are offered at cheaper unit prices than would be in the case of smaller production volumes.
- Short Cycle Time: The injection molding process can produce high volumes of parts in the shortest time possible. Polypropylene has good thermal properties and hence the molds can be filled and cooled quickly enhancing the production rates and lead times.
- Superior Chemical Resistant: Polypropylene is highly resistant to a vast number of chemicals such as acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This property makes it suitable for use in applications in extreme conditions including car parts and chemical vesse.
- Least Impact: Polypropylene has less impact strength as compared to HDPE, however, copolymer polypropylene has good impact strength. This makes it a preferred choice for products that require mechanical strength and resistance to impact, for example, automotive and durable consumer goods.
- Dimensional Stability: Once it has been cooled, polypropylene has high dimensional stability. This stability is very essential to guarantee that the molded parts are fitting correctly and performing their intended tasks without requiring further modification.
- Low Moisture Absorption: Polypropylene has little or no capability to absorb moisture and therefore the strength and dimensions of the material do not change when exposed to different humidity levels. This property makes this property suitable for use in applications where the material is exposed to moisture most of the time.
- Flow Characteristics: Due to the favorable flow characteristics it is easier to process polypropylene and this makes the molding process easier. It makes it possible to produce large quantities of molded products and also helps overcome the typical problems with molding, such as warping or lack of filling.
What are the Limitations of Propylene Injection Molding?
Some of the demerits of Polypropylene Injection Molding include the following;
- High Thermal Conductivity: Polypropylene has a low heat resistance and thus it cannot be used in high-temperature areas. Polypropylene has poor thermal stability and the parts made from it may deform or lose their strength at temperatures above 100°C (212°F).
- UV Stability Polypropylene is not very resistant to UV light and when exposed to UV light for long, it undergoes degradation by fading to an undesirable color, becoming brittle, and exhibiting low mechanical properties. This limitation makes it necessary to use UV stabilizers or coatings especially when the product is to be used outside.
- High Shrinkage Rate: As much as 1.5% to 2.0% of polypropylene shrinks, the parts made from this material may warp or undergo dimensional changes if not well controlled. This can also influence the quality of the final product because the performance of the product can be compromised where precision is required.
- Not Suitable for High Stress Application: Although polypropylene has good impact strength it does not offer high strength and stiffness. In applications where high tensile or flexural loads are applied on the part, PP may not offer sufficient strength.
- Limited Ability to Produce Small Features: While polypropylene has many uses, it is not easy to produce very small features and intricate details. The flow characteristics of the material and the cooling properties may reduce the level of detail in very fine designs.
- Less number of colors available: Polypropylene has fewer choices of colors as compared to other plastics in the market. Striking specific or even desired shades may be possible only with the help of colorants or other kinds of treatments.
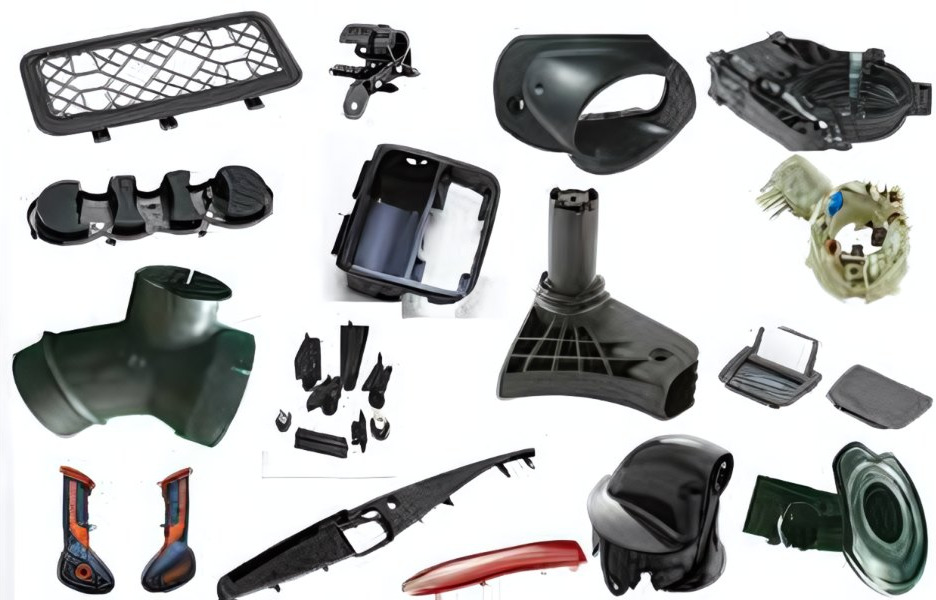
Common Parts Manufactured by Polypropylene Injection Molding
Propylene injection molding commonly produces the following parts:
- Dashboard Panels
- Glove Compartments
- Mirror Housings
- Plastic Containers
- Kitchen Utensils
- Food Containers
- Crates and Pallets
- Medical Device Housings: Lots of medical injection molding parts made from PP material.
- Plumbing Pipes
- Toys: Many of plastic injection molding toys made by ABS and PP materials.
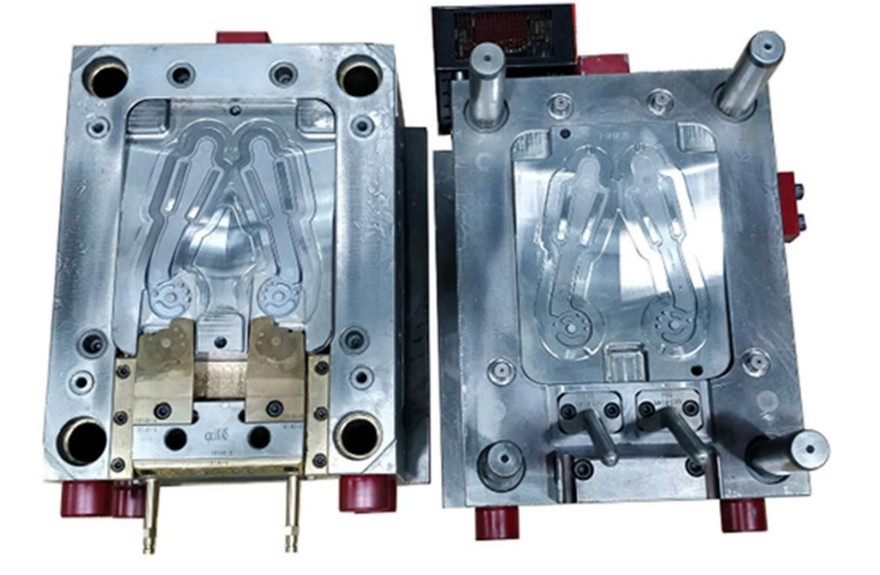
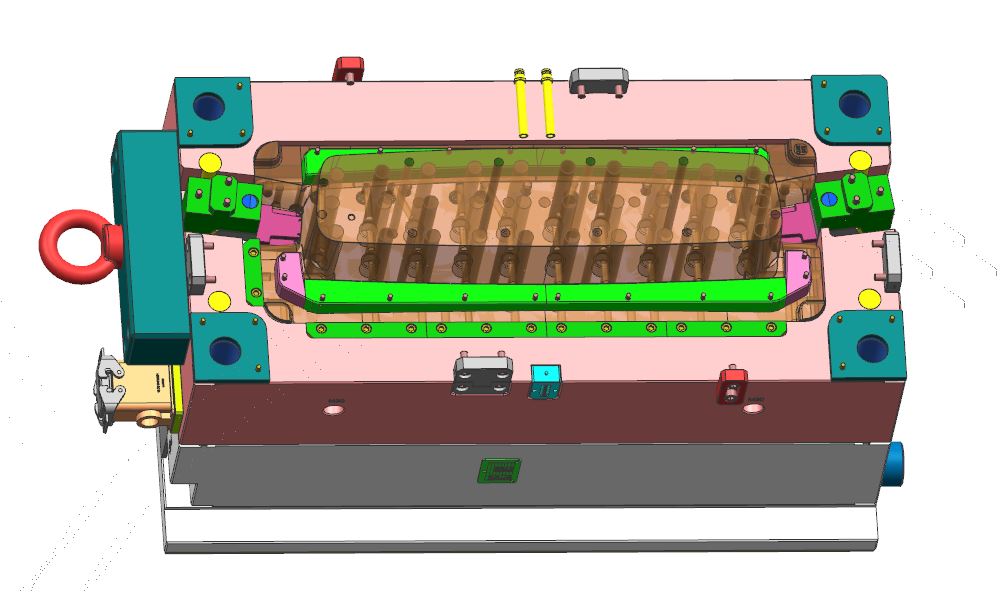
Gates and runners in polypropylene injection molding tool
In polypropylene injection molding, gates and runners constitute some of the most important features that control the flow of the molten material into the mold cavity. The design of these elements should enable proper filling, and the quality of the finished parts should be very high.

Sprue Design
The sprue serves as a conduit for molten polypropylene, connecting the injection molding machine to the mold cavity. This is a cylindrical design with a spherical part at the end that fits properly into the machine nozzle. This is critical to prevent leaks and ensure a smooth flow of materials through the system and equipment.
Runner System
Molten polypropylene travels through runners from the sprue to the mold cavity. Molds with multiple cavities design their runners with branches to evenly distribute the material. We suggest employing cold slugs at junctions to prevent early stiffening and ensure free flow. The runner diameters range from 4 to 7 mm to ensure that there is optimal flow and cooling for the mold.
Gate Functionality
Gates are the last opening through which molten polypropylene is allowed to flow into the mold cavity. The dimensions and the kind of gate determine how the material is transported throughout the manufacturing process and the quality of the last part. They are pin gates and edge gates and they are chosen depending on the type of mold that is to be made. The gate should allow for easy flow of materials into the mold while at the same time reducing the formation of surface defects.
Gate Sizing and Placement
Small gates are normally used to minimize friction and prevent the wear out of the material. The thickness of the gate land is the part of the gate that joins the cavity should be as thin as possible so that it can be easily filled. Gate location is important, usually located at the thickest section of the mold to achieve an even spread of material and minimize defects.
Design Considerations
Some of the common problems such as sink marks and poor filling can be solved through proper gating and runner systems. To improve production efficiency and part quality, updating the designs at some intervals based on the best practices and feedback on the process is effective.
Industry Applications of Propylene Injection Molding
PP injection molding often finds its applications across various manufacturing sectors;
Food Packaging
Polypropylene is widely used in food packaging since it is safe and has a longer lifespan. Take-out containers and food storage products such as cups and containers are made from PP foam for thermal insulation and protection. PP material is used in making plastic cups and bottles for beverages and food products since the material does not react with moisture or chemical substances.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods industry, polypropylene is preferred for its strength and the ability to be molded. PP is used in small appliances like blenders and hairdryers because it offers impact strength and ease of molding. Polypropylene is safe and durable and it is used often in injection molding toys. Furthermore, polypropylene’s durability is also used in household products such as bins for storage and utensils in the kitchen.
Automotive
The automotive industry is one of the major users of polypropylene as the material is light in weight and has a high degree of strength. PP is utilized in interior trim parts such as dash and panels due to the material’s versatility in terms of appearance and durability. There are also polypropylene glove compartments and mirror housings to give the needed strength and impact protection.
Textiles
It is common knowledge that polypropylene fibers are essential in different textile areas because of their strength and resistance to stains. PP fiber carpets are capable of withstanding wear and stain. PP is used for furniture and automotive interiors since it does not wear out easily and is easy to clean. Due to its excellent characteristics, polypropylene fibers are used in the production of clothing that wicks moisture, providing comfort and performance.
Packaging Films
One of the most important types of packaging films is polypropylene films because of the strength and flexibility that they offer. The applications of BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene) films are in packaging due to their high clarity, excellent mechanical properties, and moisture and oxygen barrier properties. CPP (Cast Polypropylene) films are used for heat sealability in flexible packaging applications for a variety of products.
Pipes and Fittings
Polypropylene pipes are used in plumbing and industrial practices since they are chemically inert and can be easily installed. PP plumbing pipes are used for both hot and cold water because of their strength and resistance to corrosion. In industrial applications, the use of polypropylene pipes is in chemical and waste handling systems, and the material is well endowed with the strength and capability of withstanding aggressive conditions.
Summary
This article gives more information about polypropylene (PP) as an engineering plastic, including the different types available, the properties of the PP, and the complexities of the injection molding process. It also examines the challenges associated with selecting the right equipment, addressing issues related to product design, and discussing the fundamentals of mold design. In the same vein, the article discusses some of the major defects that are likely to occur during production and how to correct them.

To ensure the best PP material and injection molding production, it is wise to seek advice from an experienced supplier. An experienced provider can provide recommendations on the most suitable PP plastic injection moldings for your product’s functional requirements and the final product’s appearance, ensuring a successful project.
FAQs – Polypropylene Injection Molding
Q1. What are the major categories of polypropylene Pallets for injection molding?
They include Homopolypropylene (PP-H) for rigidity, Random Copolymer Polypropylene (PP-R) for flexibility, and Block Copolymer Polypropylene (PP-B) for impact resistance.
Q2. What should be done to polypropylene before molding?
Polypropylene has to be dried at 80-90°C for not less than 2 hours to bring the moisture content to below 0.1% reduction in molding quality is achieved to avoid the formation of poor-quality products.
Q3. What are some of the problems that may occur in polypropylene injection molding?
Some of the most common imperfections are sink marks, flowlines, venting issues, warping, and incomplete filling. These problems can be solved by adjusting the thickness of the wall, increasing venting groove, the temperature of the mold, and the pressure of injection.