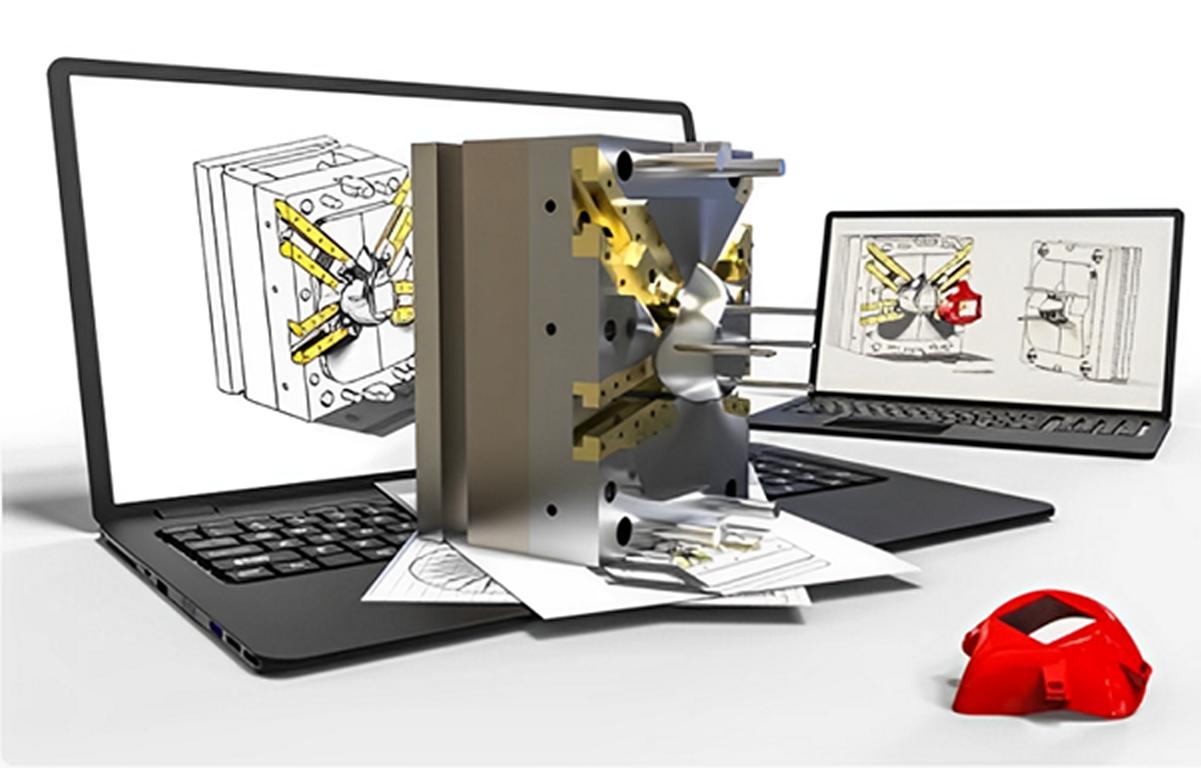
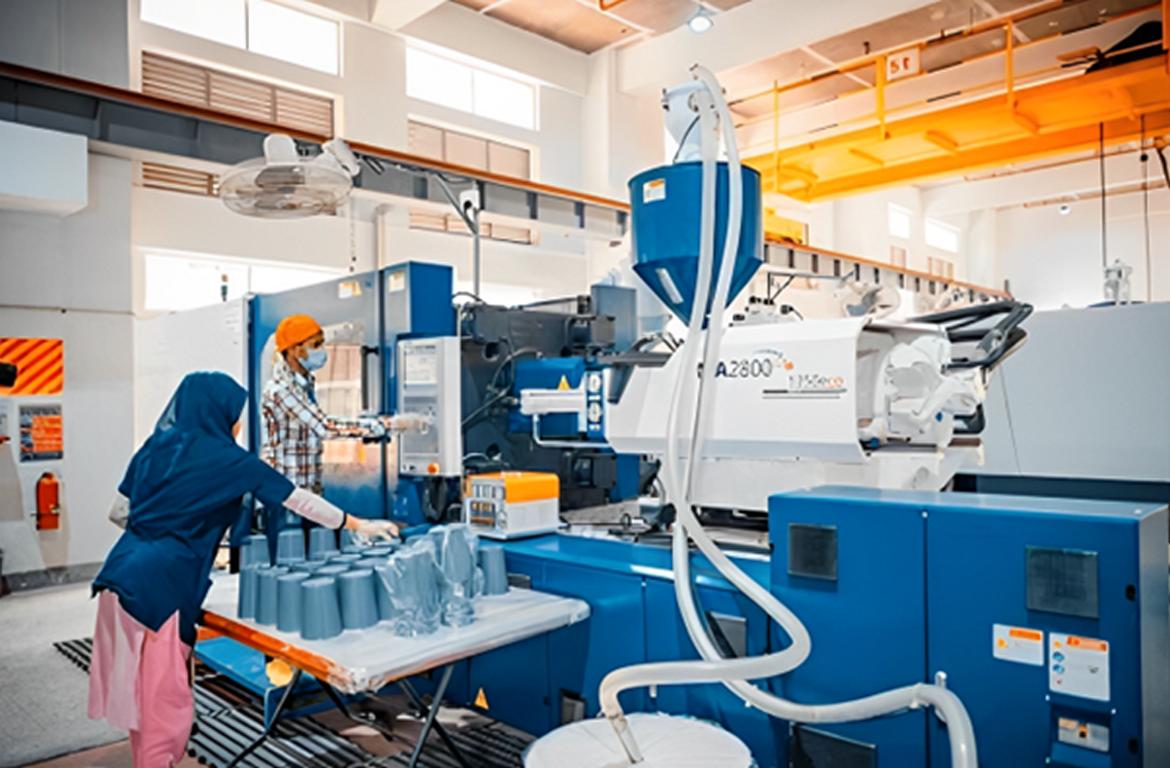
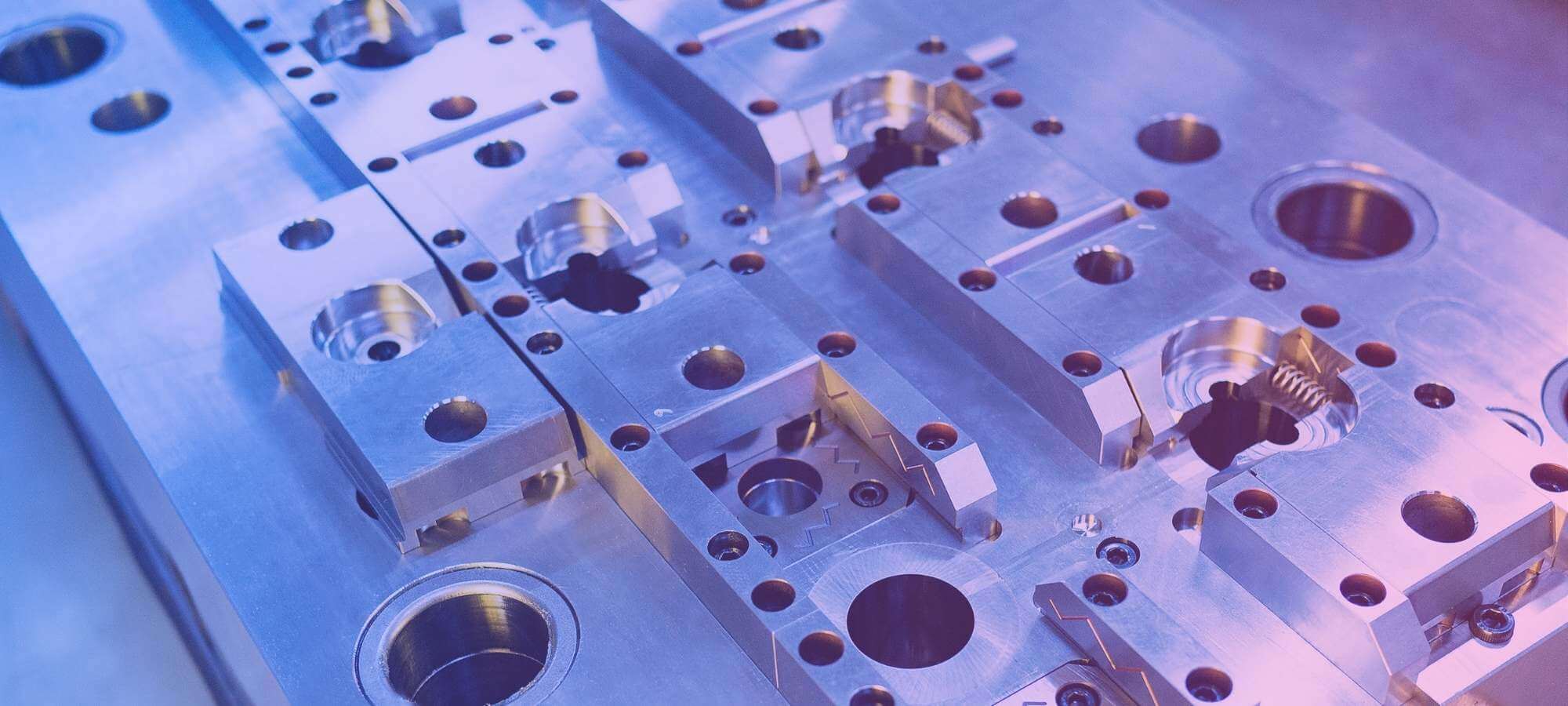
Mold making for plastics are crucial for all types of manufacturing. They help get similar shapes and designs with high accuracy and precision for large-volume productions. Moreover, these molds can be of different shapes and made of numerous materials, i.e. aluminum, steel, iron, plastic, etc. In this article, we will discuss plastic molds. Besides this, we will learn how to make mold for plastic, its applications, and its advantages in different fields.
What are Plastic Molds?
Plastic molds are commonly used in industries to create small products, from utensils to small parts for home appliances and large machines. This is a better approach because it enables the creation of unique molds. Besides, it comes with fewer costs in the long run and creates molds for prototypical commercial or personal projects. This comprehensive article will explain how to make a mold for plastic and consider important factors and tips and tricks that will help you do it without a hitch. Go to plastic mold technology page to know more informatino about plastic molds.
Types of Plastic Molds
Before going towards how to make a mold for plastic, let’s discuss a few types of plastic molds;
1. Injection Molds
Injection molds are applied in industries to create a large number of objects. It’s usually done with the help of injecting a liquid polymer material into a molding cavity. It helps manufacture complicated products such as toys, packaging materials, and detailed auto parts. Moreover, this technique is characterized by high output rates, precision, and negligible time required in post-processing.
2. Compression Molds
Compression molds use thermosetting plastics, are put in a mold cavity, and get exposed to heat and pressure. This method is most suited for applications that require quality and heat-stable components. These may include automobile parts and electronic appliances. Thus, it is economical in low-production runs and ideal for creating thicker parts, especially those big ones.
3. Blow Molds
Blow molds have wide-scope applications for molding hollow parts such as bottles and containers. This works in a way in which the plastic is first turned into a tube referred to as a parison. Then it is allowed to get inflated between two molds to form a final hollow product. One of the major applications of blow molds is, that they’re highly used in PVC for making light and empty parts in a big quantity.
4. Silicone Molds for Resin
Silicone molds are flexible and more common to beginners and they are used in small DIY projects. Besides this, they have many applications even when working with resin. Such molds can retain fine and complex structures. Moreover, they are reusable, making them suitable for crafting, resin work, and prototyping. They are pleasant to deal with and can be used in many ways for other artistic endeavors.
Properties of Materials Used for Plastic Molds
| Material | Purpose | Common Types | Key Properties | Typical Values/Range |
| Mold Material | It helps form the mold structure | Steel, Aluminum, Silicone | Durability, Heat Resistance, Machinability | Tensile Strength: 250-1500 MPa (steel), 90-300 MPa (aluminum) |
| Release Agent | It prevents material from sticking to the mold | Silicone Spray, Wax, PTFE | Non-stick, High Heat Resistance | Max Temp: 120°C-200°C, Friction Coefficient: <0.05 |
| Mold base/Frame | This holds mold material in place | Wood, Plastic, Metal | Strength, Rigidity | Density: 0.9-1.3 g/cm³ (plastic), 2.7 g/cm³ (aluminum) |
| Master Object/CAD Model | It makes shape for the mold | 3D Model, Prototype | Precision, Smoothness, Complexity | CAD Accuracy: ±0.005 mm, Surface Finish: Ra 0.8-1.6 μm |
| Mixing Tools | Mixes mold material components | Stirring Rods, Mechanical Mixers | Even Mixing, No Air Bubbles | RPM: 300-1200 (mechanical mixers), Volume: Variable |
Step-by-Step Guide to Mold Making for Plastics
The following is the complete process for mold making for plastics.
1. Designing the Mold
Get a rough design of the mold and consider the need for the plastic part that you want to generate. When you have complex shapes, use your CAD software to design in a way that will help in the CNC machining of the mold. Some of the features include the geometry of the part, the thickness of the walls of the part, and draft angles. They facilitate the removal of extra material from the mold. The choice of the mold material like aluminum or steel depends on the life span required for the mold. Besides this, the material selection also depends on the quantity of products you want to produce.
2. Creating a Mold Box or Frame
For plastic mold fabrication, create a mold box or frame that will hold the material during the casting. Mold boxes for CNC machined molds are usually made of sturdy materials. They may include Metal / hard plastic etc. So, during manufacturing, confirm that the box has been well closed properly to avoid any leakage in the pouring process. Moreover, ensure that the box has been reinforced to withstand pressure and temperature during the molding process.
3. Preparing CAD Models & CNC Machining the Mold
Usually in CNC machining the master object is a CAD file with accurate dimensions and free of undercuts on the mold cavities. So, if the materials you use have different forms and structures. CNC machining will help you clean and undergo surface treatment. A release agent is used to avoid the plastic sticking to the mold. The CNC machine further proceeds to make an accurate cut of the mold to achieve the right milled and finished walls. This is important to minimize the chances of defects. Moreover, it allows the smooth flow of the plastic and easy ejection of the final part.
4. Mixing and Pouring the Mold Material
After molding the mold with CNC, the molten plastic material into the mold cavity. If you’re using thermoplastic or resin, make sure the material that you are using is up to the right temperature and flows well. If you use injection molding, heat and melt the plastic material, present in the pellets. Moreover, ensure that you take your time when pouring to minimize air bubbles which if they get into the mixture will reduce the strength of the final product.
5. Curing the Mold
So, allow the material to cool and form a solid in the mold prepared from the plastic material. Depending on the type of plastic used, curing may take a few minutes to several hours. In this stage, it is important to observe that there is no formation of bubbles or any other defect in the mold. As regards the curing of CNC-machined molds, curing is generally faster and more accurate because molds are cured under controlled conditions.
6. Mold Filling and Mold Release
When the plastic reaches its curing point, take out the part from the mold. If you put the release agent correctly, the part should pop out and not stick to the mold surface. Besides this, you can trim or finish the material depending on their requirement. Additional finishing may be done on items through the machines if further polishing is needed for volume production.
Design and Build Considerations for Custom Plastic Molds
Some of the important aspects that need to be considered in the design and building of especially custom plastic molds include the following;
- Material Selection: Select the mold material such as steel or aluminum for its durability, cost, and production volume. Steel molds tend to be long solutions for strength and volume production. Whereas, aluminum molds are more inexpensive for less volume productions.
- Part Geometry: The mold design aspect should be informed by all features of the plastic part, particularly, intricate details, undercuts, and draft angles. So, they can facilitate easy removal from the mold.
- Cooling Channels: This reduction of the cycle time has to be done while at the same time, cooling channels are integrated into the mold design.
- Mold Tolerances: Understand that accurate dimensional requirements mean closer control in the mold. So, it can minimize the amount of post-mold finishing required particularly when the design details are intricate.
- Mold Flow Analysis: Make a brief analysis of the appearance of the cavities and how the mold material will flow in the cavity. Check some of the anomalies that are likely to occur such as warping, shrinkage, or formation of air pockets. This is efficient in aiding the mold design of the automobile and also improves production efficiency.
Selection of Resin for Making Plastic Molds
Let’s explore the different types of resin options to make the plastic molds.
- Epoxy Resins: Organic epoxy resins are strong and thus can be used to make molds in industries that require high heat and pressure when molding.
- Polyurethane Resins: These are flexible and durable so they are the best for molds that will be used where a moderate amount of production is to be done. So, we can get that resistance and a certain degree of flexibility.
- Silicone Resins: Silicone is very flexible and can be very convenient when operating on tight molds that are small and complex as well as suitable for DIYs or a few runs.
- Polyester Resins: These are cheaper and preferred for big molds with fewer details. Besides this, they offer fair strength but relatively low elasticity compared to silicone and polyurethane.
- Thermosetting Resins: Sometimes called thermosetting plastics, these resins become permanently solid and rigid when exposed to heat. So, they are suitable for tough applications like the engineering industry.
Finishing and Polishing the Plastic Mold
Always follow the following aspects while finishing and polishing the plastic molds.
1. Drilling the mold and polishing
Smooth edges to start making the actual part. Here the mold first undergoes inspections to see whether it has sharp edges or uneven surfaces. Scour carefully using fine paper or special machinery that provides polish to figure out the body of the mold. This results in a smooth finish of the last plastic product and the reuse of the mold without causing harm to the cast parts.
2. Making Repairs if Necessary
There are defects on the substrate surface beforehand, such as small cracks,
unevenness, or visible bubbles. It is mandatory to eliminate them with the help of appropriate filler materials, i.e. epoxy resins or silicate. Detection and correction of these issues enable a manufacturer to prevent defects in the final molded parts, go to injection molding surface finish page to know more.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Mold making for plastics
Here are some common mistakes we generally make while mold making for plastics.
1. Air Bubbles in the Mold
One of the common problems with mold making for plastics is the entrapment of air bubbles in the mold material. We can avoid it by ensuring the material is added slowly and after pouring escapes the air trapped in it. Another way to remove bubbles is by employing the use of a vacuum chamber, and pressure pot.
2. Inadequate Release Agent Application
An inadequate release agent application is another way to cause damage since the final part may later stick to the mold. It is important to note that the release agent is applied uniformly and in detail with a special focus on the intricate regions.
3. Warping During Curing
Warping is the product deformation that appears as a result of an inaccurate curing process or normal coil cooling procedures. This should be prevented by regulating the curing environment and ensuring the right curing temperature. Besides this, also make sure to allow enough time for the material to cure thoroughly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, how to make a mold for plastic, Mold making has relevance in many creative industries where ideas are hatched and inventions manufactured ranging from industrial manufacturing to home craft. Learning about mold-making, the available materials, and the requirements presented in this article, will assist in manufacturing accurate and long-wearing molds for plastic parts production. In this case, the required finishing and finishing are done to perfection and the custom molds have wide-scope applications in several fields.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What materials are commonly used for plastic molds?
Steel and aluminum are some of the best materials for industrial molds because they are hard-wearing. Silicone rubber is mostly used on a small scale and for do-it-yourself projects.
Q2.How long does a mold last?
The serviceability of steel mold is measured by the fact that it can run for millions of cycles. For instance, aluminum has tens of thousands of cycles, depending on the degree of production intensity.
Q3. How do I prevent air bubbles in my mold?
Choose a slow blending speed for the mold material and pay attention to pouring the material. Afterward, use a vacuum chamber or pressure pot to eliminate trapped air.
Q4. What is the best release agent for plastic molds?
Varnishing or applying silicone sprays also the ones that are composed of PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene. They are best-suited releasing agents for avoiding the adhesion of plastic to molds.
Q5. What type of mold is best for mass production?
Injection molds should be preferred for mass production. They enable the creation of large numbers of similar spare parts with high accuracy.
Q6. Can mold be repaired if damaged?
Yes, simple damages such as cracks on the siding, small holes or even roughening of the surface can be easily repaired using epoxy or filler materials. Where the extent of damage is bad, then the only solution that may be available may be to replace the whole mold.