PC VS ABS Plastic is a comparative guide with helpful info. It shows the suitability of each material for different uses. This guide lets you get the information you might need to improve your business strategies.
Plastic is handy, but it also poses environmental issues. However, if you are aware, you can reduce these risks and create a better world.
The first synthetic plastic was discovered in 1907. Since then, people have used plastics instead of metals or wood. Plastics are everywhere, from household items to car parts. We need plastics in electronics items, packaging, and even consumable items. So, you have many product options to create for your customers. However, the issue is choosing the suitable plastic material for them. ABS and PC are two popular plastics used in our modern world.

What is ABS Polycarbonate?
ABS and Polycarbonate, or PC, are two different plastics. They can be combined or used as separate materials but are most commonly found in individual forms.
When you compare these materials (ABS VS PC), you must thoroughly know their properties. Also, you must know how to use them in various products. Once you have ideas for all these, you can choose the best option for your project. If you still have questions, feel free to contact us.
What is PC Plastic?
PC stands for Polycarbonate. People mainly like PC plastics because they are impact-resistant and easy to mold. It’s a type of thermoplastic.
PC plastic was first discovered in 1953, and now, it is one of the most used plastic materials in the industry. Most of the industries prefer PC plastic over ABS plastic.
Polycarbonate has a combination of BPA and phosgene. The process of making PC plastic is known as condensation polymerization.
In the factory, an operator first prepares raw materials. Then, he mixes the BPA in a solvent. During the mixing, the machine introduces the phosgene gas into the mixture. The process is fully automated, so the amount required for the reaction remains stable. Finally, this process will end by creating the polycarbonate resin.
Next, the operator melts the polycarbonate resin and puts it in an extruder. The machine then produces long strands of PC profiles through the extrusion process. The operator cools the strands and cuts them into small pallets. These pallets are the raw PC plastics you need to create various PC injection molding plastic products.
Properties of PC Plastics
The combination of BPA and phosgene improves the behavior of PC plastic. Because of this, polycarbonate pallets are trendy for many plastic products.
(1) The most important benefit that we can get from PC plastic is its toughness. It is almost unbreakable. It can smoothly work in temperatures between -20°C and 140°C.
(2) PC plastic has high impact strength. Note that its density is between 1.2 and 1.22. Because of this, this polymer can resist high impact and fracture. For safety and comfort, PC plastic is an excellent choice.
(3) PC plastic is transparent. According to various scientists, it can transmit light more than 90% of the time. Various manufacturers customize this transparency based on customer needs.
(4) PC plastic is exceptionally lightweight, not lighter than ABS. It typically weighs only 1.19 grams per cubic centimeter. Since it offers excellent transparency, you can use it to create many OEM products, saving significant costs.
(5) PC plastic is entirely UV resistant. This means it can block ultraviolet radiation up to 100%.
(6) This thermoplastic is also chemically resistant. It is excellent against many hydrocarbons, alcohols, and mild acids. However, it shows fair resistance to petroleum. Also, for alkalis and HH, PC plastic breaks easily.
(7) Finally, PC plastic works great under high heat. It remains 100% stable even at 135°C. if you wan to know more high heat materials, please go to high temperature plastic material page to know more.
Business Opportunities of PC Plastics
Because of the above seven benefits, PC plastics are prevalent in various applications. There are great opportunities for businesses to enter this vast market.
PC plastic is better than other plastic materials in many ways. It is resistant to impact and high heat. It also offers transparency up to 94%. Due to these benefits, PC plastic is in high demand in the plastic products market.
The following table showcases the trendy PC plastic products in the niche market. You can also get a similar product made of different alternative materials. Alternative materials might be cheap for specific parts. Therefore, knowing the properties of the materials for plastic parts is crucial when choosing them.
| Category | Popular Products/Opportunities | Alternative Materials |
| Electronic Devices | Power system parts, telecom hardware, high-stable capacitors | ABS, PET, and PVC |
| Building Materials | Dome lights, glazing, roofing sheets, and sound walls | Glass, acrylic, and PVC |
| 3D printing | Prototypes, OEM parts, plastic tools | PLA, ABS, and Nylon |
| Data Storage Kits | Discs, signage sheets, or films | ABS, Acrylic, and PET |
| Vehicle Parts | Headlamp lenses, bezels, reflectors, and bullet-proof window glass | Glass, Acrylic, and ABS |
| Aerospace & Military | Cockpit canopies, riot shields, safety goggles | Glass, Acrylic |
| Optical Devices | Eyewear lenses, camera lenses, sunglass lenses | Glass, Acrylic |
| Mobile Devices | Smartphone cases, coves, screen protectors | Glass, Metal, ABS |
| Medical tools | Sterilize equipment, biocompatible materials | ABS, PEEK, SS |
| Niche Use | Luggage, MP3 player cases, toys, hobby parts, UV-resistant outdoor items | ABS, Nylon, and metal |

What is ABS Plastic?
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. People prefer ABS plastic due to its durability, impact resistance, and ease of molding. It is also a type of thermoplastic.
ABS Plastic was first discovered in 1948 before PC plastic. It is mainly prevalent due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture.
ABS plastic comprises three raw materials: Acrylonitrile, Butadiene, and Styrene. In the factory, an operator prepares these monomers and then moves them to the polymerization chamber.
In the polymerization chamber, the operator mixes the monomers in water with surfactants. This mixing gradually creates tiny droplets. Finally, the reactor produces ABS copolymer.
Later, he mixes the monomers in the reactor again, but he won’t add water this time. This process is fully controlled so the operator can ensure a uniform distribution of the monomers. The result of this process is molten ABS.
After cooling the molten ABS, the operator cuts it into pallets. The plastic product factory mainly uses these pallets to shape them into various ABS products. Go to ABS injection molding page and is ABS plastic safe page to know more about ABS.
Properties of ABS Plastic
The polymer chain of ABS plastic offers many unique benefits. Although ABS is not superior to PC, it is still trendy in the plastic market due to its cost-effective nature and ease of processing.
(1) ABS plastic is also excellent for impact resistance. It can absorb any physical shock.
(2) ABS plastic is strong and long-lasting. Its hardness ranges from 68 to 118. Also, its tensile strength ranges from 22.1 – 74.0 MPa, a significant amount.
(3) This plastic material can remain stable under fair loads. For high loads, it may not be as suitable as PC plastic. However, ABS plastic is still prevalent in many structural applications.
(4) ABS plastic can typically withstand temperatures from -20 to 80 degrees Celsius (-20 to 176 F). However, you can improve its heat resistance ability during molding.
(5) ABS plastic is resistant to mild acids, alkalis, and oils. Unlike PC plastic, it can withstand alkalis and oils. However, it swallows when it comes in contact with some other chemicals. Glacial acetic acid, carbon tetrachloride, and aromatic HC easily break ABS plastic.
(6) ABS plastic is highly flammable at high temperatures. It has a fire resistance of up to 31%. However, heating it above the range may produce hot flames. However, it is good that it doesn’t make any pollutants.
(7) You can 100% recycle ABS plastic. Various factories or small workshops accept old ABS to create toys, appliances, or casings.
Business Opportunities of ABS Plastic
ABS plastic is also in high demand in the plastic market. It is durable and cost-effective. You can use it to create various gadgets, car parts, and household items.
According to Grand View Research, the ABS market will grow at a CAGR rate of 4.6% from 2022 to 2030. So, investing in ABS plastic is undoubtedly profitable. All you need is to know the proper way of investing.
The following table showcases the most popular ABS plastic products in the market. This table can give you some ideas on various ABS products and show the alternative materials used. Note that alternative materials may be cheaper and have lower standards.
| Category | Popular Products/Opportunities | Alternative Materials |
| Gardening Tools | Mini shovels, plastic rakes, plastic hoes, plastic claws, and hand equipment | PP, PE, metal |
| Toys | Varieties of plastic toys, colorful toys | PE, PVC |
| Musical Instruments | Recorders, harmonicas, flutes, bugles, drums and rhythms | Wood, metal, PC |
| Electronic Devices | PC keyboards, enclosures for various gadgets, printer parts, phone case | PC, PP |
| Car Parts | Car dashboard components, door liners, pillar trim, panels for various equipment, mirror housings, seat backs, and belts | PP, PC plastic |
| Medical Devices | Nebulizers, disposable syringes, housings for various medical equipment | PC, PE |
| Household items | Vacuum cleaners, kitchen items, coffee makers, toasters, and more | PC, stainless steel |
| Pipes and fittings | Tools for liquid and gas delivery systems, outdoor and underground use | Metal, PVC, PE |
| 3D printing | OEM parts, additive manufacturing, molds | PLA, Nylon, PC |

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene vs Polycarbonate (ABS VS PC): What’s the Difference?
The above two sections explain what ABS and Polycarbonate are. You have already learned about their making process, popular products, and properties. Now the question is, which one is better? ABS or Polycarbonate? Suddenly, you can not make the decision. However, you will need some comparison to get the best option from PC VS ABS.
First, thoroughly research your project needs. What specific application will the plastic part be used for? Does it need high-impact resistance? Is transparency necessary? You can also determine parameters like mechanical stress, temperature, and moisture.
Second, consider the environment in which your plastic part will be used. Is there any exposure to UV radiation? Does the material need to be fire-resistant? Is there any chemical or solvent exposure?
Third, consider the cost of your whole project. In this case, you should balance the price with the product’s overall performance. You can use cheaper plastics, but the material properties must meet the project’s needs.
For example, your project may involve both impact resistance and temperature. You might be making a mistake if you choose ABS instead of PC. ABS’s max temperature rating is only 80, while PC plastic offers up to 140. So, for the temperature-involved job, PC plastic is suitable. Always take safety factors into account.
After thoroughly researching the project needs, compare the materials (ABS VS PC) and choose the best option. Here, we will use six primary factors to compare these two plastics.
PC VS ABS Plastic: Material Properties
When you compare both plastics (PC VS ABS), the material properties come first. Both plastics have unique advantages and limitations.
When you think of strength, PC offers more impact resistance. The values are in the table below. As you can see, PC has more density and less elongation to break. This means the PC is more rigid and suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Moreover, PC plastic offers high-temperature resistance. It remains stable and does not deform even in high heat. PC also prevents water absorption and has excellent transparency. You can use this transparency feature to create a wide range of plastic products, like lenses, phone screens, and more.
On the other hand, ABS is one step ahead of PC plastic in terms of UV resistance and electric insulation. It also has an excellent capability, up to 31% of flame retardancy. For other materials, ABS shows average standards.
PC VS ABS Plastic: Material Properties Summary Table
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 | 1.01 to 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 114 – 124 Rockwell R | 68 to 118 Rockwell R |
| Tensile Strength | 28.0 – 75.0 MPa | 22.1 – 74.0 MPa |
| Impact Strength | 10 – 90 Kj/m² | 8.00 – 48.0 kJ/m² |
| Elongation to break | 6.10% to 138% | 3.00 – 150 % |
| Temperature Rating | −40 °C to 130 °C (−40 °F to –266 °F) | (-20° C to 80° C (-20° F to 176° F) |
| Melting Point | 220 – 320 °C | 180 – 240 °C |
| Transparency | 0.000 – 94.0 % | 0.000 – 91.0 % |
| UV Resistance | Excellent, but you must add a UV stabilizer | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, except for alkalis and HH | Excellent, except for Glacial acetic acid, carbon tetrachloride, and aromatic HC |
| Electric Insulation | 1000 to 1017 ohm-cm | 109 to 1017 ohm-cm |
| Fire resistance | 25% ( can add fire resistant element) | 0.5% to 31.2% ( can add fire resistant element) |
| Water absorption | 0.0200 – 0.350 % | 0.0500 – 1.00 % |
| Weather resistance | Good with UV stabilizers | Poor; more prone to degradation without protection |
| Surface Finish | Glossy and Smooth | Matte, slightly rougher texture |
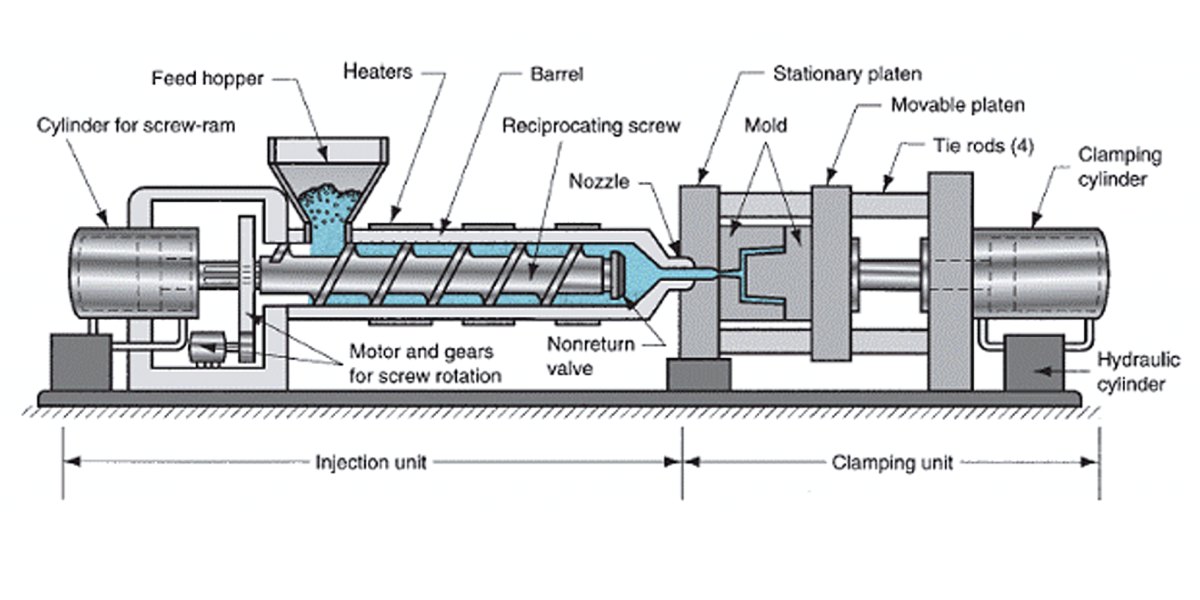
PC VS ABS Plastic: Ways of Processing
There are various ways of processing plastics. Some standard processing techniques are injection plastic mold, extrusion, thermoforming, blow molding, and machining.
ABS plastic is easy to process because it has a low melting point. In injection molding, the process temperature for ABS is 210 to 260 degrees Celsius. On the other hand, the process temperature for PC plastic is 260 to 320 degrees Celsius.
ABS is also easy to process in extrusion. Since it has a lower viscosity, you can create smooth plastic profiles. On the other hand, PC plastic is more rigid, and your extruder will need more pressure to make the profiles.
When you compare them (PC VS ABS), the ease of processing only matters regarding production cost. However, if you consider the product’s outcome, PC plastic will give you the best service.

PC VS ABS Plastic: Filament for 3D Printing
3D printing is trendy in our modern world. You can create 3D objects with a 3D printer. The working principle is the same as the typical printer but on a 3D surface. The printer typically builds the object layer by layer. Various types of materials are used to do this. ABS and polycarbonate plastics are two popular ones.
Each plays a crucial role in 3D printing, comparing both (PC VS ABS) plastics. Each type has its unique benefits and limitations.
ABS filament is typically a durable and flexible plastic. It is mainly used for its strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for various functional parts and household items. ABS filament is easy to print and a cost-effective method. However, it produces fumes that may make you feel uncomfortable. Besides, it may warp if you don’t print on a heated bed.
On the other hand, PC plastic is also strong, transparent, and highly temperature-resistant. These two benefits can be used to create a wide range of 3D objects. However, what makes PC plastic less familiar is its high melting point. It is also more expensive than ABS plastic.
PC VS ABS Plastic: Recyclability
ABS and polycarbonate plastics are both recyclable, but their process may differ. For ABS plastic, people often use the shredding method, sometimes chemically. On the other hand, you can recycle PC plastic in two ways: shredding and melting.
Recycling polycarbonate is more complex than recycling ABS plastics. One reason for this is its composition.
PC VS ABS Plastic: Costs
The manufacturing cost of ABS plastic is lower than that of PC plastic. Also, the melting point of ABS is lower than that of PC plastic. Also, the viscosity of molten ABS is lower than PC. Combining all these properties, you will find that processing ABS plastic is also cost-effective.
You can decide on the right option based on just costs. However, you must also compare performance. PC plastic offers more performance quality than ABS plastic. It even comes with a smooth and glossy finish.
PC VS ABS Plastic: Applications
ABS plastic is widely used in car parts, consumer goods, and electric casings. It is strong and easy to process, so ABS plastic is preferred in these three industries.
Polycarbonate, on the other hand, is favored for safety equipment. Safety gear, optics discs, and medical gadgets are all popular items. You can check the respective tables described above for each item.
Make Your Decision: Which is Better?
When to choose ABS plastic?
If you need a cost-effective material, ABS is the best option. It’s ideal for products that don’t need high-temperature resistance. ABS is generally easy to process. Moreover, ABS plastics are lighter than PC plastic. Therefore, you can use this material to create toys and many weight-sensitive products, and lots of PC materials used in over mold or insert molding process as substrate.
When to choose PC plastic?
Polycarbonate thermoplastic gives you everything you need. It is strong, durable, and high-temperature resistant. Although it is not as cheap as ABS plastic, PC products are stable for a long time. A PC plastic is the right choice if your project demands improved performance and toughness.
You can also create a hybrid version, combining ABS and PC. ABS/PC typically combines the properties of both ABS and PC.
Compared to PC (PC VS PC/ABS ), PC/ABS provides better impact resistance and lower shrinkage. Unlike PC, PC/ABS is easy to process. On the other hand, compared to ABS (ABS/PC VS ABS), ABS/PC provides more heat resistance.
The choice mainly depends on your specific use, budget, and requirements. Therefore, always assess your target before choosing the right material. It not only saves your time but also your valuable investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is PC lighter than ABS?
No, ABS is typically lighter than PC or Polycarbonate. Its density generally starts at 1 gram per cubic centimeter, while PC is up to 1.20. Therefore, ABS plastics are lighter than PC plastic. If weight is a critical factor in your project, ABS may be the better choice over a PC.
Is PC filament stronger than ABS?
Yes, the PC filament is stronger than ABS. The hardness level of PC plastic is 114 to 124 Rockwell. It also has higher impact resistance so that it can withstand greater force. Polycarbonate offers high heat resistance.
What is the ratio of ABS to PC?
The ratio of ABS to PC in a blend typically is 60:40. The custom ratio may also include 50:50 or 70:30. The ratio may differ based on specific project needs.
Which is better, ABS or PC or PP luggage?
PC or Polycarbonate is typically the more robust plastic. This plastic is also durable, making it the most suitable material for luggage. However, people also use PP or polypropylene for luggage manufacturing. Note that PP also offers high strength and durability, if you want to know more plastic materials, you could go to how to choose the best plastic injection molding materials page to know more material selection tips.
Is PC-ABS expensive?
The PC/ABS is more expensive than the typical ABS. The combination of PC and ABS typically increases this price. Although the cost is higher, you can get added benefits.

















