اللدائن المرنة بالحرارة أو مادة TPE هي نوع خاص من المواد البلاستيكية الحرارية متعددة الأطوار شبه البلورية متعددة الأطوار التي تتميز بخصائص؛ مرونة البوليمرات المطاطية وقابلية معالجة المواد البلاستيكية الحرارية. كما هو الحال مع معظم اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية أو TPEs، تُستخدم هذه المواد على نطاق واسع في العديد من الصناعات بما في ذلك صناعة السيارات والمعدات الطبية. في هذه المقالة، سنناقش مادة TPE من حيث التركيب الكيميائي، وتقنيات التصنيع، أي القولبة بالحقن، والمكانة في التسلسل الهرمي البوليمرية. كما نلقي نظرة على إمكانات وعيوب بلاستيك TPE بالإضافة إلى بعض أحدث التطورات.
ما هي قوالب حقن TPE (اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية)؟
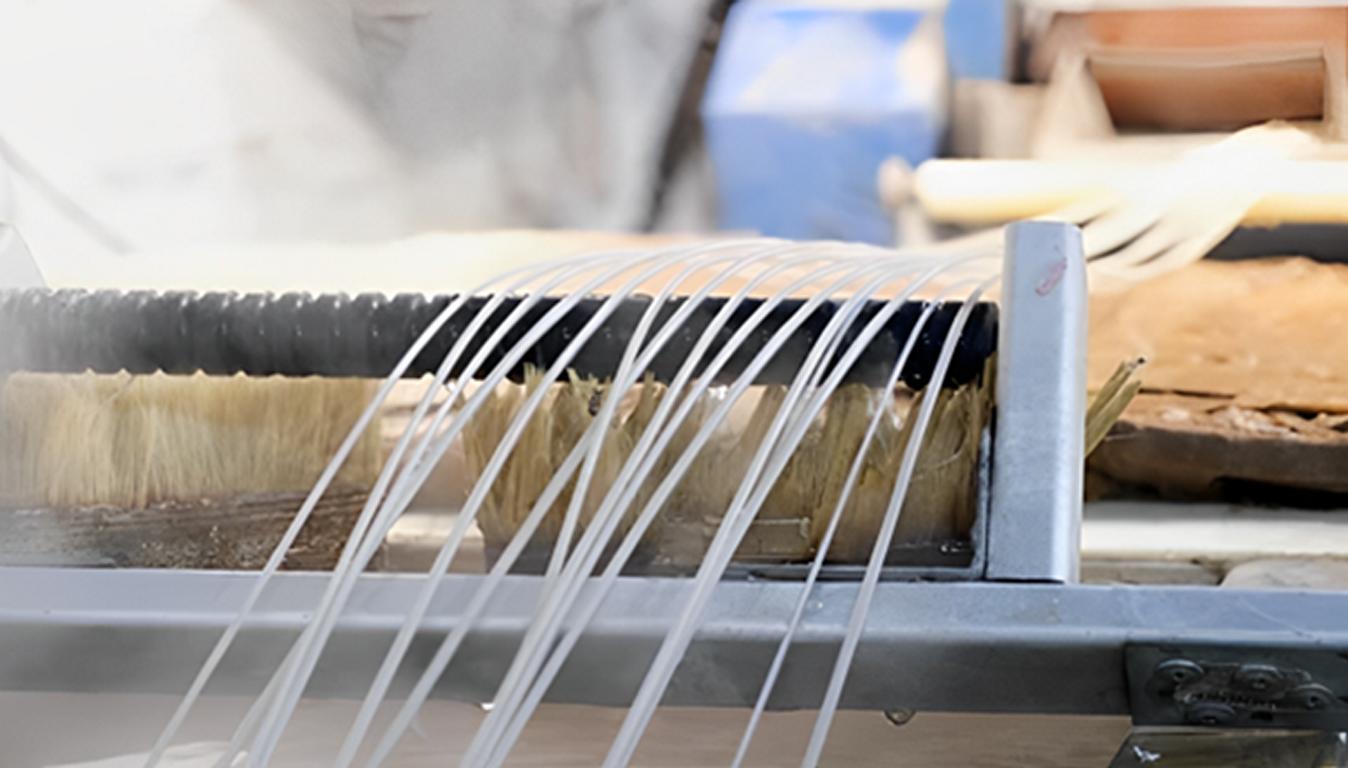
صب حقن TPE هي إحدى تقنيات التشكيل التي تستلزم تشكيل الأجزاء باستخدام TPE عن طريق قولبة المادة من خلال تقنية الحقن بالذوبان. هذه العملية شائعة لأنها سريعة وصديقة للبيئة ويمكنها تصنيع أجزاء رقيقة وقوية. حقن TPE يوفر مرونة في تصميم التحمل وهو مثالي للتصنيع الآلي على نطاق واسع. لذا، فهي شائعة في صناعات السيارات والإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية.
ما هي اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية (TPE) البلاستيكية؟
تعدّ البولي إثيلين متعدد الألياف عائلة من اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية التي توفر مرونة شبيهة بالمطاط في التطبيق وقابلية المعالجة البلاستيكية. وعند تسخينها، يمكن تليين هذه اللدائن عدة مرات، كما يمكن تقويتها عدة مرات من خلال التسخين متبوعًا بعملية تبريد معاكسة دون حدوث تغييرات ضارة. ويشيرون إلى أن هذا الجانب بالتحديد هو ما يميز مادة TPE عن المطاط الحراري. لذا، فإن هذا يجعل من السهل إعادة تدويرها وتشكيلها.
عملية تشكيل TPE (اللدائن الحرارية البلاستيكية)
دعونا نستعرض العملية الكاملة التي ينطوي عليها تكوين بلاستيك TPE
1. تحضير المواد الخام:
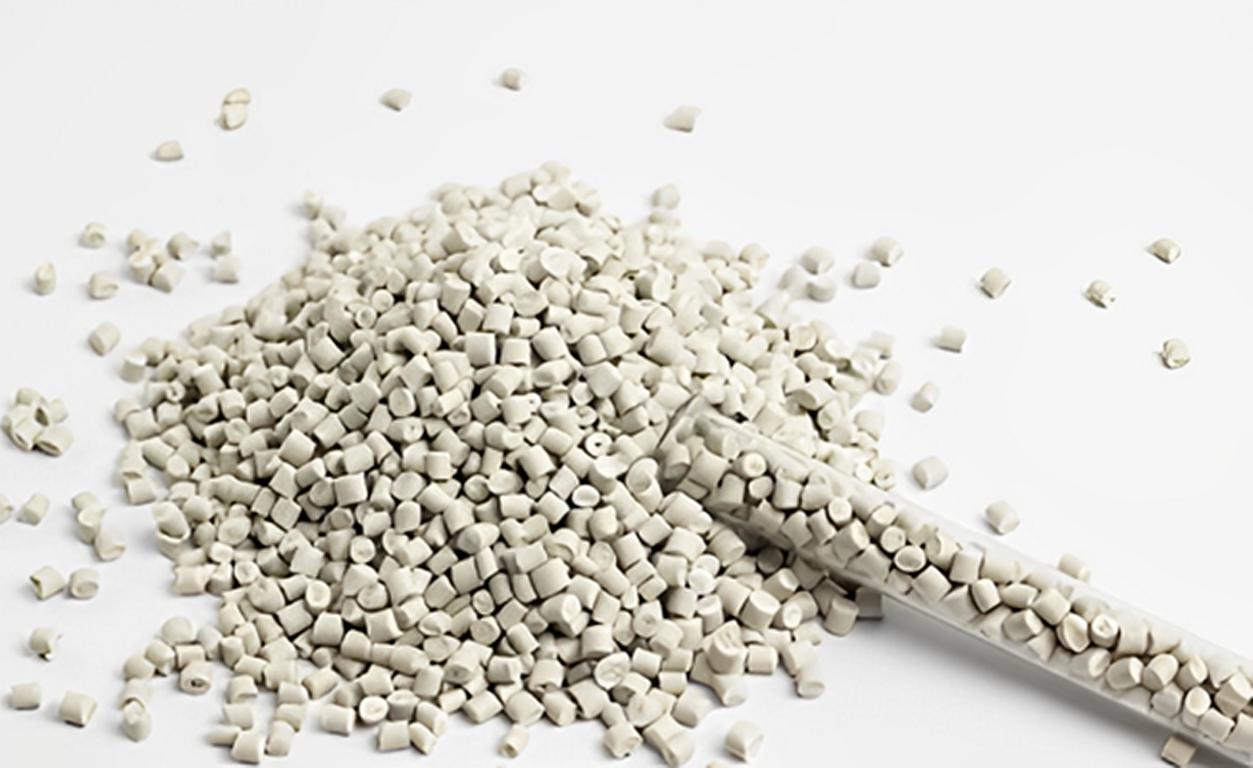
يتم تجميع مواد TPE في شكل كريات وتغذيتها في قادوس، عادةً فوق ماكينة التشكيل بالحقن. يتم دمج المكونات في كريات واحدة، مما يعني أنها متساوية الكفاءة في كل مرحلة من مراحل التشكيل والتسخين. وهذا يجعل النتائج متوقعة للغاية ويقلل من مشاكل مناولة المواد طوال العملية.

2. مرحلة الذوبان
ثم تُنقل كريات TPE هذه من القادوس إلى غرفة التسخين حيث يتم تسخين الكريات (عادةً عند درجة حرارة تتراوح بين 200 و250 درجة مئوية تقريبًا). يعتمد نطاق درجة الحرارة هذا على نوع مادة TPE المراد استخدامها). تعمل الحرارة على تليين الكريات إلى كتلة تشبه السائل ويمكن تشكيلها بسهولة في الشكل المطلوب. يجب مراقبة جانب درجة الحرارة بشكل خاص في هذه العملية بشكل جيد لأن درجة الحرارة المرتفعة للغاية يمكن أن تتلف المادة وتؤثر على جودة المنتج.
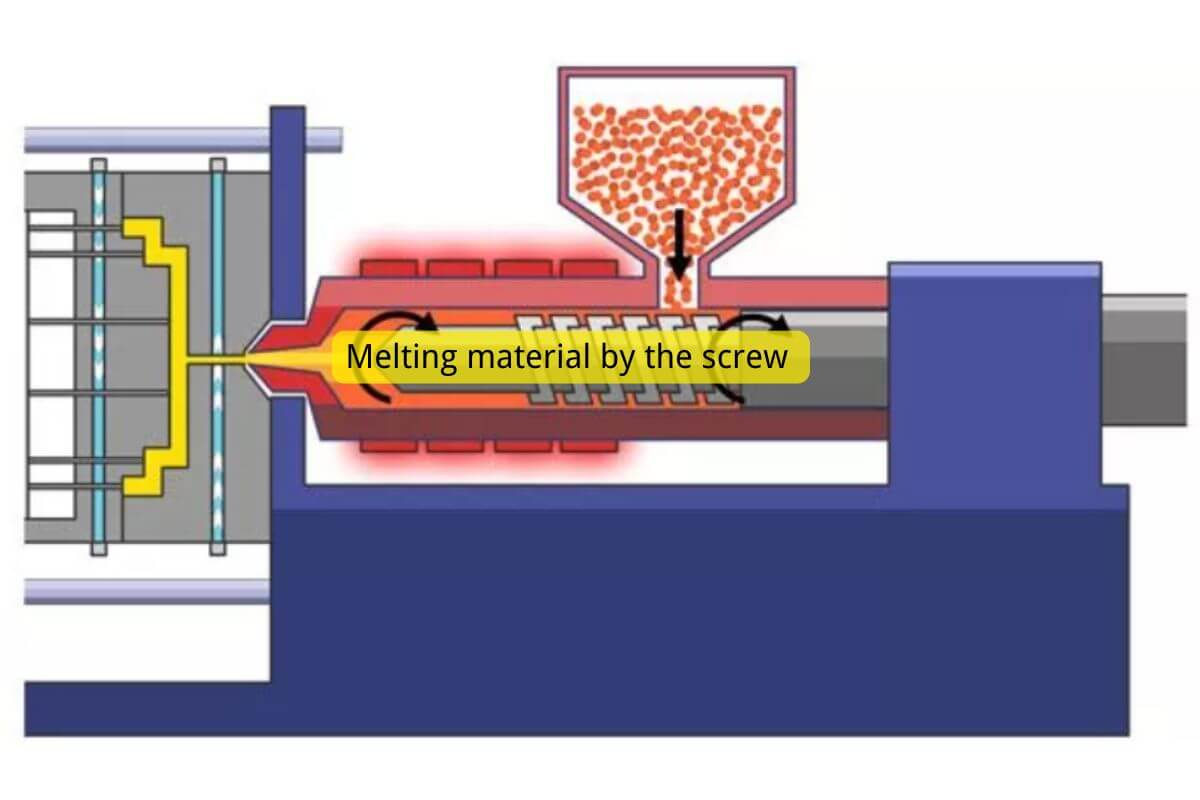
3. مرحلة الحقن
يدفع البرغي أو المكبس مادة TPE تحت ضغط عالٍ إلى شكل تجويف القالب. يأخذ شكل القالب للجزء المطلوب وقد يحتوي على شكل معقد فيما يتعلق بسمات المنتج النهائي. يجب مراقبة هذه المرحلة عن كثب لضمان انسكاب الجزء العلوي من الجانب العلوي بالمئات، دون انكماش أو فراغات أو فقاعات هواء في الجزء النهائي.
4. التبريد والتصلب
أثناء ملء تجويف القالب، يبرد TPE المصهور، ويشكل قالبًا للتجويف، ويتصلب في هذه العملية. لتنظيم معدل تبريد المنتج وتقليل التوزيع غير المتساوي لدرجة الحرارة الذي يؤثر على تشويه الجزء. وهنا يمكن تزويد القالب بنظام تبريد مثل الممرات المائية. ومن المزايا الأخرى للتبريد المتحكم فيه أنه يزيل الالتواء ويقلل من احتمالية الانكماش أيضًا، كما أن الحجم النهائي سيكون دقيقًا.
5. مرحلة الطرد
بعد أن يتصلب جزء TPE، يتم دفع تجويف القالب إلى الخارج باستخدام دبابيس القاذف أو ما شابه ذلك. وبعد ذلك يتم نزعه وتجهيزه لأي عملية أخرى مطلوبة له. تنطوي هذه المرحلة على عامل توقيت حرج حيث قد يؤدي الطرد قبل الوقت المطلوب إلى تشويه الجزء بينما قد يؤثر الطرد بعد ذلك على معدل الإنتاج الكلي.
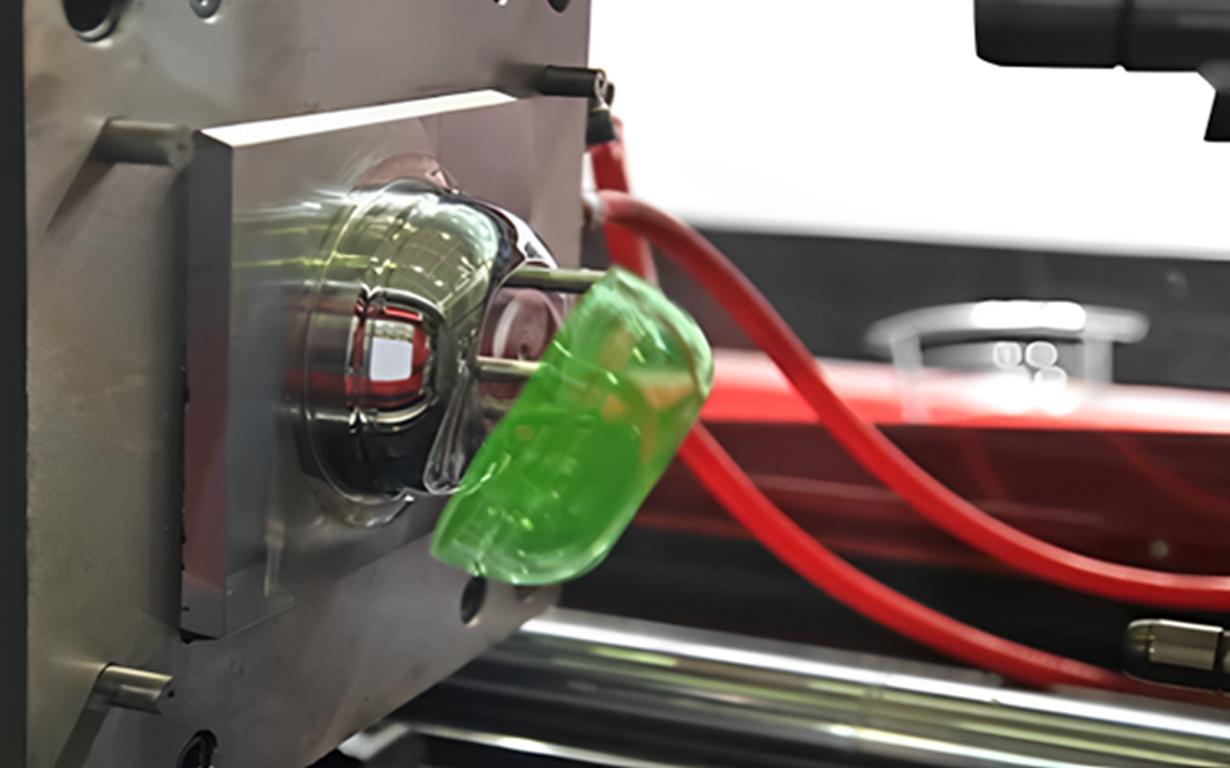

ما الفرق بين مادة TPE ومادة TPR
يقدم الجدول التالي مقارنة مفصلة بين TPE و TPR؛ يمكنك الانتقال إلى مادة tpr صفحة لمعرفة المزيد عن ماهية بلاستيك TPR.
| ميزة | TPE (إلاستومرات حرارية بلاستيكية) | TPR (المطاط الحراري البلاستيكي) |
| تعبير | مزيج من البلاستيك والبوليمرات الشبيهة بالمطاط (مثل البوليمرات الشبيهة بالمطاط، وبوليمرات البولي يوريثان ثلاثي الفينيل متعدد الكلور) | المطاط الصناعي القائم على الستايرينيك، عادةً SEBS |
| الصلابة (الشاطئ أ) | 20-90 | 10-80 |
| مرونة | مرتفع، يشبه المطاط | أنعم قليلاً، ومرونة عالية |
| درجة الحرارة القصوى. درجة الحرارة القصوى | حتى 120 درجة مئوية | حتى 100 درجة مئوية |
| التطبيقات | السيارات، والطبية، والإلكترونيات | الأحذية والمقابض والأدوات المنزلية |
| المقاومة الكيميائية | معتدلة إلى عالية | معتدل |
| قابلية إعادة التدوير | عالي | معتدل |
فئات مختلفة من اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية (TPE)
تنقسم اللدائن البلاستيكية الحرارية (TPE) إلى عدة فئات بناءً على تركيبها الكيميائي وخصائصها:

- بوليمرات كتل الستايرينيك المشتركة (SBCs)
تعد بوليمرات كتل الستايرينيك المشتركة (SBCs) واحدة من أكثر أنواع البوليمرات متعددة الكثافة استخدامًا على نطاق واسع نظرًا لتركيبها الفريد من كتل الستايرين والمطاط، مما يسمح لها بالجمع بين المرونة وقوة البلاستيك. يمكن معالجة SBCs من خلال طرق مختلفة مثل البثق والقولبة بالحقن والقولبة بالنفخ، مما يجعلها قابلة للتكيف مع مجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات.
وتتميز هذه البولي إثيلين متعدد الألياف بمرونة وشفافية ومرونة ممتازة، كما أنها قابلة للتلوين بسهولة. وهي تُستخدم عادةً في التطبيقات التي تتطلب مواد ناعمة الملمس ومرنة، مثل المقابض والمقابض والأجهزة الطبية ومواد التغليف والأدوات المنزلية. كما توفر SBCs أيضًا مقاومة ممتازة للرطوبة ووضوحًا جيدًا، مما يجعلها خيارًا مثاليًا لمواد التغليف الشفافة والاستخدامات المتخصصة في منتجات العناية الشخصية.
- البولي يوريثان بالحرارة (TPU)
تشتهر مواد البولي يوريثان بالحرارة (TPU) بمتانتها ومرونتها الفائقة، مما يجعلها خيارًا شائعًا للتطبيقات التي تتطلب الكثير من المتطلبات. تتميز مواد TPU بمقاومة ممتازة للتآكل، مما يساهم في طول عمرها في التطبيقات عالية التآكل، كما أنها توفر مرونة كبيرة ومرونة في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة ومقاومة للزيوت والشحوم والمذيبات.
هذه الخصائص تجعل من البولي يوريثان ثلاثي الفينيل متعدد البروم مناسبًا بشكل خاص لتطبيقات السيارات والأحذية والتطبيقات الطبية. في صناعة السيارات، تُستخدم البولي يوريثان ثلاثي الفينيل متعدد الكلور بشكل شائع في البطانات المعلقة وموانع التسرب والمكونات الداخلية. وفي الأحذية، تُستخدم في الأحذية في النعال التي تتطلب المرونة والمتانة على حد سواء. في الأوساط الطبية، تُستخدم البولي يوريثان ثلاثي البولي يوريثان في الأنابيب والقسطرة وغيرها من الأجهزة التي تتطلب مرونة وتوافقًا مع جسم الإنسان. ونظرًا لتعدد استخداماتها، يمكن تخصيص وحدات البولي يوريثان ثلاثي الفينيل متعدد البروم لمختلف مستويات الصلابة ودرجات الشفافية. انتقل إلى صب حقن TPU الصفحة لمعرفة المزيد.
- الأوليفينات البلاستيكية الحرارية (TPO)
الأوليفينات البلاستيكية الحرارية (TPO) عبارة عن مزيج من البولي بروبيلين (PP) واللدائن المرنة، مما يوفر مادة تجمع بين خصائص كل من المطاط والبلاستيك. تتميز هذه المواد بمقاومة فائقة للمواد الكيميائية وقوة الصدمات ومقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية مقارنةً بالبولي بروبيلين القياسي، مما يجعلها مناسبة تمامًا للتطبيقات الخارجية والاستخدامات عالية الإجهاد.
وهي تُستخدم عادةً في تطبيقات السيارات، خاصةً في أغطية المصدات والديكورات الداخلية ومكونات لوحة القيادة، بالإضافة إلى أغشية الأسقف في البناء، حيث تكون المتانة ومقاومة الطقس أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. وفي الأجهزة المنزلية، تساهم البولي بروبيلين تيريفثاليتات البوليسترين المشبع في المكونات التي تتطلب مقاومة الصدمات والقوة. ويتم تقدير هذه المواد لقدرتها على إعادة التدوير، مما يعزز جاذبيتها في تصميم المنتجات المستدامة.
- الفلكنة بالحرارة (TPV)
تعتبر اللدائن الحرارية المفلكنة بالحرارة (TPV) مزيجًا فريدًا من اللدائن الحرارية والمطاط، حيث يتم ربط مرحلة المطاط بشكل ديناميكي متقاطع. تعمل عملية الربط المتقاطع هذه على تعزيز مرونة المادة ومقاومتها للحرارة ومتانتها بشكل عام، مما يسمح للبلاستيك الحراري بمحاكاة العديد من خصائص أداء المطاط المفلكن التقليدي مع الاستمرار في تقديم مزايا المعالجة التي توفرها اللدائن الحرارية.
تُستخدم عادةً في التطبيقات التي تتطلب مقاومة للحرارة والمواد الكيميائية، مثل مانعات تسرب الطقس والخراطيم والحشيات الخاصة بالسيارات. توفر البطانات البلاستيكية TPV مرونة ممتازة ويمكنها تحمل الضغط والانثناء المتكرر، مما يجعلها خيارًا مفضلًا في التطبيقات الديناميكية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فهي خفيفة الوزن، مما يساهم في تحسين كفاءة استهلاك الوقود عند استخدامها في قطع غيار السيارات.
- إيلاستومرات البوليستر المشترك (COPE)
تُقدَّر استومرات البوليستر المشترك (COPE) لتوازنها بين المرونة والقوة، مما يسمح لها بأداء جيد في ظل ظروف الضغط العالي. وغالبًا ما تُستخدم في التطبيقات التي تتطلب مقاومة لدرجات الحرارة العالية والوقود والزيوت، مما يجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات الهندسية، خاصةً في قطاعي السيارات والصناعة.
على سبيل المثال، تُستخدم مركبات ثاني أكسيد الكربون COPEs في إنتاج التروس والأحزمة والمخمدات، حيث تحتفظ بمرونتها وسلامتها الهيكلية حتى عند تعرضها للعوامل البيئية الصعبة. وبالإضافة إلى استخدامات السيارات، تُستخدم مركبات COPEs في السلع الرياضية والإلكترونيات حيثما كانت المرونة والمرونة مطلوبة. وتتميز هذه اللدائن بمقاومة عالية للإجهاد المرن، مما يعني أنها يمكن أن تتحمل الانحناء والالتواء المتكرر دون تآكل كبير.
- أميدات كتلة البولي إيثر (PEBA)
توفر أميدات كتلة البولي إيثر (PEBA) مزيجًا رائعًا من المرونة والمقاومة الكيميائية والخصائص خفيفة الوزن. يشيع استخدام أميدات البولي إيثر متعدد الأثيرات (PEBA) المعروفة بعمرها المرن الممتاز وكثافتها المنخفضة في التطبيقات التي يكون فيها توفير الوزن والمتانة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية. في المجال الطبي، تُستخدم مادة PEBA في مكونات مثل أنابيب القسطرة ورأب الأوعية الدموية بالبالون، حيث توفر المرونة اللازمة والتوافق الحيوي ومقاومة السوائل الجسدية.
في المعدات الرياضية، يساهم في صناعة منتجات خفيفة الوزن وعالية الأداء، مثل الأحذية الرياضية وأحذية التزلج، حيث تعتبر المرونة والمرونة في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة ومقاومة الصدمات من الأمور الأساسية. وبالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتميز البولي إيثيلين بايثيلين بيثينول بيبا بمقاومة عالية للزيوت والشحوم والمواد الكيميائية المختلفة، مما يسمح له بالحفاظ على الأداء حتى في البيئات القاسية.
- بوليمرات الأوليفين الحلقية المشتركة (COC)
تنفرد بوليمرات الأوليفين الحلقية المشتركة (COC) بأنها فريدة من نوعها بين بوليمرات البوليمرات متعددة الكلور (TPE) نظرًا لوضوحها البصري العالي وانخفاض امتصاصها للرطوبة وثبات أبعادها. وتمتلك هذه المواد بنية بوليمر عشوائية، مما يمنحها شفافية استثنائية تشبه الزجاج. وغالبًا ما تُستخدم بوليمرات البوليمرات متعددة الكلور في التطبيقات الطبية والبصرية حيث يكون الوضوح والمقاومة الكيميائية والنقاء ضروريين، مثل أجهزة التشخيص والتغليف الدوائي والعدسات البصرية.
وانخفاض امتصاصها للرطوبة يجعلها مناسبة للغاية للتغليف الطبي، حيث تساعد على حماية المحتويات الطبية والصيدلانية الحساسة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن درجة حرارة التحول الزجاجي العالية لمركبات الكربون الكلورية فلورية تجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات التي تتطلب مقاومة للحرارة، في حين أن انخفاض انكسار انكسارها مفيد في الأجهزة البصرية. غالبًا ما يتم اختيار مركبات ثاني أكسيد الكربون COCs لمواد التغليف المتقدمة والعدسات التي تتطلب الشفافية والقوة في آن واحد.
وتوفر كل فئة من فئات البولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات ثلاثي البولي إيثيلين خصائص فريدة تجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات المتخصصة في مختلف الصناعات، بما في ذلك السيارات والمنتجات الطبية والاستهلاكية والهندسة الصناعية. من خلال اختيار النوع المناسب من بولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات الألياف، يمكن للمصنعين تحسين أداء المنتج والمتانة والفعالية من حيث التكلفة في مختلف التطبيقات.
الخصائص المهمة لمادة TPE
دعنا نستكشف الخصائص المختلفة لـ TPE;

1. المرونة
يتميز TPE بخصائص المطاط المرن الذي يمكن تمديده وإعادة تمدده بسبب خصائص المرونة المطاطية نسبياً. وهذا يجعلها مناسبة حيثما كانت المرونة والمرونة لها تطبيقات، أي الأختام والحشيات وغيرها من التطبيقات الناعمة الملمس.
2. اللدونة الحرارية
يتميز TPE بخصائص مماثلة للمطاط ولكنه فريد من نوعه لأنه يمكن صهره وإعادة استخدامه في درجات حرارة عالية. وهو من اللدائن الحرارية، مما يعني أنه يمكن صهره واستخدامه لتشكيل المنتجات، ثم إعادة تشكيله، وهو أمر مناسب للتصنيع وإعادة التدوير.
3. المتانة
يوفر TPE خصائص ممتازة في التآكل والتآكل والصدمات مع تطبيقات مختلفة. خاصةً عند الحاجة إلى أجزاء متينة مثل قطع غيار السيارات والإلكترونيات.
قابلية إعادة التدوير
مثل أي بلاستيك حراري آخر، فإن مادة TPE قابلة لإعادة التدوير وتقلل من تأثير التصنيع على البيئة. هذه القابلية لإعادة التدوير مفيدة في الصناعات التي تحاول تقليل النفايات أو التخلص منها بشكل أكبر عند محاولة أن تكون منتجة في استخدام مواد التغليف.
ما الفرق بين TPE مقابل TPE السيليكون أو المطاط TPR؟
يقدم الجدول التالي مقارنة مفصلة بين مطاط TPE و TPR السيليكون والمطاط الطبيعي؛ انتقل إلى TPE مقابل السيليكون صفحة لمعرفة المزيد عن الفرق بين TPE والسيليكون. إذا كنت تريد معرفة المزيد عن السيليكون، يرجى الانتقال إلى هل السيليكون آمن صفحة.
| ميزة | TPE (إلاستومرات حرارية بلاستيكية) | سيليكون | المطاط (طبيعي/اصطناعي) |
| تعبير | مزيج من اللدائن الحرارية واللدائن المرنة | بوليمر اصطناعي، قائم على السيليكا | طبيعية (لاتكس) أو اصطناعية (مثل SBR) |
| الصلابة (الشاطئ أ) | 20-90 | 10-80 | 30-90 |
| مرونة | مرتفع، يشبه المطاط | عالية جداً ومرنة في درجات الحرارة المنخفضة | عالية جدا |
| درجة الحرارة القصوى. درجة الحرارة القصوى | حتى 120 درجة مئوية | حتى 200 درجة مئوية | تصل إلى 100 درجة مئوية (طبيعية)، 150 درجة مئوية (اصطناعية) |
| المقاومة الكيميائية | معتدلة إلى عالية | ممتاز | جيد (اصطناعي)، معتدل (طبيعي) |
| يعالج | قولبة الحقن، البثق | القولبة بالضغط، البثق | الفلكنة، والضغط، والبثق |
| قابلية إعادة التدوير | عالي | قليل | منخفض إلى متوسط |
| التطبيقات | السيارات، والطبية، والسلع الاستهلاكية | الطبية، والمواد الملامسة للأغذية، والإلكترونيات | الإطارات والحشوات وموانع التسرب والأحذية |
| يكلف | $6T$ (فعالة من حيث التكلفة وقابلة لإعادة التدوير) | $6T1T1T6T1T$ (أعلى تكلفة، متين) | $6T$ (تختلف حسب النوع، قابلية إعادة التدوير محدودة) |
الاعتبارات الرئيسية عند اختيار مادة TPE
فيما يلي بعض النقاط الرئيسية المهمة عند اختيار مادة TPE;
1. متطلبات التقديم
تحديد الخواص الميكانيكية المحددة اللازمة للتطبيق مثل قوة الشد والمرونة والصلابة. وتختلف الخصائص النموذجية لـ TPE اعتمادًا على تركيبة P و E-PO ويتغير أداء تركيبات TPE المتشابهة اعتمادًا على البيئة التي يتم استخدامها فيها.
2. نطاق درجة الحرارة
ضع في الاعتبار ظروف درجة الحرارة التي سيتم استخدام TPE في ظلها. كما أن لـ TPEs حد أقصى لدرجات الحرارة، واختيار الدرجة المناسبة لتوفير خاصية الأداء اللازمة في ظروف التشغيل في درجات الحرارة العالية أو المنخفضة.
3. التوافق الكيميائي
التقييم الذاتي لمدى التعرض الكيميائي الذي ستواجهه مادة TPE. تتفوق بعض أنواع البولي إثيلين متعدد الألياف على غيرها من المواد الكيميائية؛ وتساعد معرفة البيئة التي ستستخدم فيها المادة والظروف والمواقف التي ستستخدم فيها المادة على الكشف عن مادة لا يمكن أن تتدهور أو تفقد خصائصها.
4. طريقة المعالجة
تحديد طريقة المعالجة المخطط لها (القولبة بالحقن/البثق وما إلى ذلك). قد تكون بعض معدات TPEs مصممة خصيصًا لتعمل بشكل جيد في عمليات معينة وتحدث فرقًا كبيرًا في نتائج التصنيع والتكاليف.
5. الامتثال التنظيمي
يتوافق TPE مع الكود المعمول به في الصناعات. وقد يشمل ذلك الصناعات الطبية أو المتعلقة بالأغذية. ويجب أن تتوافق منتجاتها وموادها مع متطلبات السلامة والمتطلبات البيئية.
العوامل البيئية وعوامل إعادة التدوير ل TPE
دعونا نناقش بعض المصانع البيئية الهامة ومصانع إعادة التدوير الخاصة بـ TPE;
- قابلية إعادة التدوير: غالبًا ما تكون TPEs قابلة لإعادة التدوير وهذه واحدة من أكبر الفوائد مقارنةً ببعض أنواع المطاط الأخرى. حدد ما إذا كان مفهوم TPEs قابلاً لإعادة التدوير ويمكن إعادة استخدامه بعد استخدامه، ويمكن إعادة استخدامه.
- التأثير البيئي: قم بتحليل مدى ملاءمة مادة TPE من حيث تأثيرها البيئي في الاستخدام والإنتاج والتخلص منها. قم أيضًا بتقييم المشتريات والمصدر الذي تحصل منه على مادة المنتج أو المصنعة من أجل التجديد.
- اعتبارات نهاية العمر الافتراضي: تحديد خطة للتعامل مع المنتج في نهاية دورة الحياة. معرفة بعض خيارات إعادة تدوير معدن TPE أو إعادة استخدامه أو تصريفه.
- قابلية التحلل البيولوجي: مركبات البولي إثيلين متعدد الكلور غير قابلة للتحلل الحيوي وصديقة للبيئة في السوق.
- ممارسات الاستدامة:
تقييم استهلاك الطاقة والانبعاثات والتخلص من الشركة المصنعة لمواد TPEs وغيرها من القضايا ذات الصلة. يجب أن يتم ذلك مع الموردين الراغبين في ممارسة عمليات الإنتاج المستدامة.
تطبيقات TPE
فيما يلي بعض التطبيقات المهمة لـ TPE;
- مكونات السيارات: يُستخدم البولي إثيلين ثلاثي البولي إيثيلين في الأختام والحشيات وأجزاء السيارات الداخلية بسبب قوته ومرونته العالية.
- الأجهزة الطبية: تتمثل التطبيقات الرئيسية ل TPE في الأنابيب والقسطرة ومانع تسرب الحقن بسبب توافقه الحيوي.
- الأجهزة الإلكترونية الاستهلاكية: وهي معروفة جيداً في تطبيقات الكابلات والمقابس والقبضة الناعمة الملمس.
- الأحذية: يتميز TPE بخفة وزنه وخصائصه الممتازة ومرونته، وبالتالي يُستخدم على نطاق واسع في نعال الأحذية.
- التعبئة والتغليف: ونظرًا لقوة وقابلية تشكيل البولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات الألمنيوم TPE، فإنه يُستخدم في الأغشية المرنة والأغطية والأختام.
إيجابيات مادة TPE وسلبياتها
فيما يلي بعض فوائد وقيود معدن TPE
الايجابيات:
- قابلة لإعادة التدوير وفعالة من حيث التكلفة
- من السهل معالجتها عن طريق القولبة بالحقن
- المادة التي توفر أيضاً بعض المرونة والقابلية للتمدد هي مادة مرنة ومطاطية حرارية.
- يوفر مرونة في التصميم
- نطاق واسع من مستويات الصلابة
السلبيات:
- كما أن مقاومتها للحرارة ضعيفة مقارنةً بمثبطات اللهب الأخرى.
- ومع ذلك، فإن المقاومة الكيميائية لهذه الشرائح متواضعة إلى حد ما في بعض الدرجات.
- تكلفة المواد مرتفعة مقارنةً بالمواد البلاستيكية التقليدية الأخرى.
- كما أنه غير مناسب للاستخدام في المناطق ذات درجات الحرارة العالية.
متى يجب استخدام TPEs
فيما يلي بعض النقاط التي يمكن أن تكون فيها TPEs خيارًا مناسبًا;
- تطبيقات مرنة: أكثر فائدة عندما تكون مرونة المادة مطلوبة كما هو الحال مع الأختام والحشيات بسبب الطبيعة الشبيهة بالمطاط لهذه الفئة من المواد.
- الأجزاء المصبوبة: تستخدم في المقام الأول في تصنيع كميات كبيرة من الأشكال المختلفة. وهي معقدة عن طريق كل من تقنيات القولبة بالحقن والبثق.
- الاعتبارات البيئية: سيكون مناسبًا للمنتجات التي تستخدم البولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات ثلاثي البولي إيثيلين لأنها تلبي متطلبات كونها صديقة للبيئة لأنها قابلة لإعادة التدوير.
- الامتثال التنظيمي: الأفضل للاستخدام في الصناعات والأعمال التي تتطلب الامتثال للمعايير الصحية مثل الصناعات الطبية والصناعات الملامسة للأغذية.
متى لا تستخدم TPEs
فيما يلي بعض النقاط التي يجب أن تتجنب فيها استخدام TPES;
- تطبيقات درجات الحرارة العالية: لا يصلح للاستخدام في البيئات التي تزيد درجة حرارتها عن 120 درجة مئوية حيث من المعروف أن البوليمرات TPE تتحلل أو تفقد خصائصها في مثل هذه البيئات المحيطة.
- التعرض الشديد للمواد الكيميائية: من المستحسن عدم استخدام منتج حيث يجب أن تصادف مواد كيميائية أو مذيبات قوية قد تؤثر على المادة.
- التطبيقات كثيفة التكلفة: إذا كانت التكلفة المنخفضة أكثر ملاءمة لمتطلبات الأداء (المطاط أو البلاستيك)، فينبغي النظر إليها.
خاتمة
وختامًا، نظرًا لخصائصه المرنة ومتانته العالية، إلى جانب إمكانية معالجته بسهولة، يمكن أن يلبي البولي إثيلين تيرفثالات ثلاثي البولي إيثيلين متطلبات التطبيقات المتعددة مثل صناعة السيارات والإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية. ونظرًا لأن الاستدامة تكتسب أهمية كبيرة مع مرور الوقت، فإن إمكانية إعادة تدوير البولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات الألياف وإمكانية استخدام المواد الحيوية تجعلها أكثر جاذبية. ومع حدوث الابتكارات، من المتوقع أن تتبنى مادة البولي إيثيلين تيرفثالات الألياف البوليمرية المزيد من الوظائف في تصميمات المنتجات المختلفة في مختلف الصناعات.
الأسئلة الشائعة
Q1. ما هي مادة TPE؟
بلاستيك TPE هو عبارة عن بوليمر ومن سماته المرونة المطاطية واللدونة الحرارية ويمكن معالجته ليتم تشكيله.
Q2. ما هي الفروق بين TPE والمطاط؟
على عكس المطاط، ومع ذلك, مادة تي بي إي يمكن صهر المواد البلاستيكية وإعادة تشكيلها ويمكن تكرار هذه العملية عدة مرات.
Q3. ما هي الصناعات التي تستخدم المواد البلاستيكية TPE؟
تُستخدم المواد البلاستيكية المصنوعة من بلاستيك TPE في صناعات السيارات والطب والإلكترونيات والسلع الاستهلاكية.
Q4. هل يمكن إعادة تدوير مادة TPE البلاستيكية؟
وبالفعل، يمكن إعادة تدوير مادة TPE وإعادة معالجتها مع حدوث تغيرات متواضعة أو ضئيلة في الخصائص.
Q5. هل بلاستيك TPE مقاوم للحرارة؟
وهو أكثر مرونة من معظم اللدائن الحرارية الهندسية الأخرى ولكنه يتميز بمقاومة منخفضة للحرارة. وإلى جانب ذلك، فهي غير مناسبة في ظروف درجات الحرارة العالية.
Q6. ما هي الأنواع المختلفة من معدات الحماية الشخصية؟
تشمل بعض أنواع اللدائن المرنة البوليمرات المشتركة كتلة الستايرينيك (SBC)، والبولي يوريثان بالحرارة (TPU)، والأوليفينات الحرارية البلاستيكية (TPO).












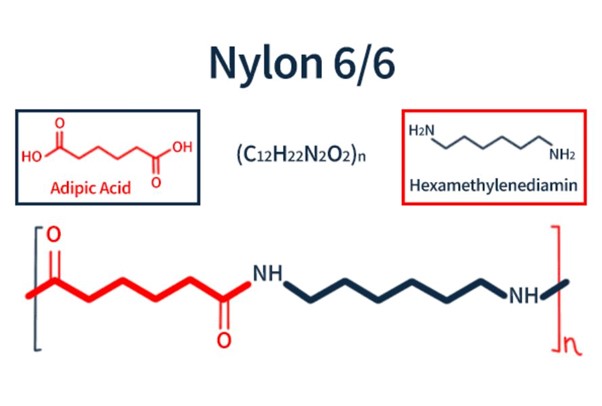
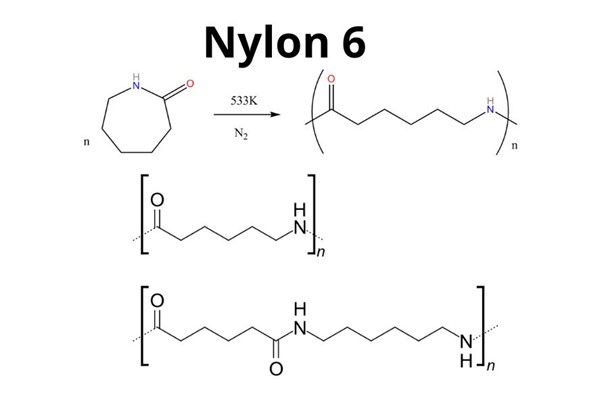
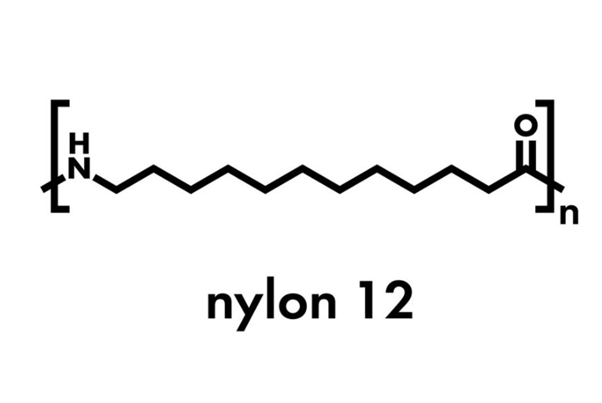




 PA6 GF30 مقابل PA6.6-GF30: ما الفرق؟
PA6 GF30 مقابل PA6.6-GF30: ما الفرق؟