Zinc Nickel Plating
Zinc Nickel Plating, A Complete Overview
Nickel zinc plating is among the several widely used plating methods in automotive, electronics, and other industries. Besides this, it is highly effective in providing high anti-corrosive properties and higher durability. In light of increasing requirements towards protection for metals in rather aggressive conditions, zinc-nickel coatings are highly appreciated for their valuable characteristics. In this article, we will explain what zinc nickel plating is, how it can be done, the advantages of using this type of plating, and what makes it different from zinc plating.
What is Zinc Nickel Plating?
Zinc nickel plating is a surface finishing process in which a layer of zinc-nickel alloy is deposited on a particular surface. It usually has 85 – 93% zinc and 7 – 15 % nickel. Moreover, it outperforms regular zinc plating in terms of corrosion protection, therefore, the product is useful for numerous applications. These may include aerospace, automotive, and heavy equipment production. Zinc-nickel plating is used when an object functions in a harsh environment that can subject it to severe corrosion or severe variations in temperature.
What is the major difference between Zinc-Nickel Plating vs. Zinc Plating
Zinc plating and Zinc-Nickel plating, are different because of their compositions. So, they also have different processes and applications in numerous industries. Let’s explore the major differences between them; check to know more about nickel plating.
| Feature | Zinc-Nickel Plating | Zinc Plating |
| Composition | 85-93% Zinc, 7-15% Nickel | 100% Zinc |
| Corrosion Resistance | Up to 1000 hours (ASTM B117) | 72-200 hours (ASTM B117) |
| Coating Thickness | 8-20 microns | 5-12 microns |
| Temp. Resistance | Up to 120°C (248°F) | Up to 70°C (158°F) |
| Hardness | 350-400 HV (Vickers) | 70-120 HV (Vickers) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Appearance | Bright, matte, various colors | Silver, yellow, blue |
| Environmental Resistance | High (saltwater, chemicals) | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, marine | Fasteners, bolts, general hardware |
Different Types of Zinc-Nickel Plating Techniques
So, here are different types of techniques we can use for zinc-nickel plating;
1. Electroplating
Here we submerge the substrate in a zinc-nickel electrolyte solution and pass an electric current into the solution. So, it can deposit the zinc-nickel alloy onto the metal surface to give precise control over coating thickness. You can go to plastic chrome plating page to know more about electroplating process for plastic products.

2. Barrel Plating
This technique is ideal for small parts and involves placing components in a rotating barrel filled with plating solution. The tumbling action ensures uniform coverage of the zinc-nickel coating on all surfaces. So, this makes it efficient for high-volume production.
3. Rack Plating
Used for larger or complex parts, items are securely mounted on racks submerged in the plating solution. This method allows for better control and thicker coatings. Besides this, it is highly suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.

4. Pulse Plating
An advanced technique that uses alternating current pulses during electroplating. This improves coating quality and surface finish by allowing more precise control over the deposition rate. So, it becomes ideal for intricate designs.
5. Continuous Plating
A high-volume production method where parts are continuously fed through a plating line. This approach maximizes efficiency and ensures consistent coating, used in automotive manufacturing.
6. Immersion Plating
It involves submerging parts in a zinc-nickel solution without an electrical current. This less common method relies on the chemical properties of the solution to deposit the alloy, often used as a pre-treatment step.
Complete Process of Zinc-Nickel Plating
The following are crucial steps towards achieving a uniform and strong deposit of zinc-nickel plating, good adhesion, and corrosion as well as a wear-resistant surface.

1. Surface Preparation
The first process in the zinc-nickel plating process is the careful preparation of the metal surface for the treatment to produce a proper adhesion of the surface finish. Contaminants like dirt, oil, grease, and rust are removed using techniques such as:
- Degreasing: It uses either solvents or alkaline cleaners to wash away the oils and greases.
- Acid Cleaning: This assists in the removal of rust or oxides from the surface, i.e. from the metal.
- Abrasive Blasting: For persistent contaminants, a rough surface is applied using abrasive blasting to eliminate corrosion or scaling.
2. Activation
The metal is given an acid dip, which helps clean the surface again because of the possibility of some oxide layer still remaining. So. it improves chemical reactivity on the surface so that there is a formation of a strong bond between the surface and the electroplated zinc-nickel layer.

3. Electroplating
Here the activated metal is immersed in an electroplating bath which has a zinc-nickel electrolyte solution. Electrolysis is used whereby an electric current is passed through the bath via a cathode which attracts and adheres the zinc and nickel ions to the surface of the metal. This leads to the formation of a uniform protective layer of zinc-nickel alloy on the surface of the metal, which provides, in addition to corrosion protection, increased service life.
4. Post-treatment
Following electroplating, post-treatment is mainly exercised to enhance the quality of the deposit formed upon the substrate. These may include:
- Passivation: This process also provides a very thin layer of zinc that helps to prevent corrosion.
- Chromatin: It is one of the regular treatments that improve the anti-corrosive properties of the coating as well as its appearance; it is available in different colors.
- Sealant Coating: Finally, a topcoat may be used to enhance the durability of the plating especially for those to be used in very corrosive environments.
Tools Used in Zinc Metal Plating
The following are the different tools’ name and their description in detail;

- Plating Bath: A vessel where the zinc-nickel plating solution is stored and from which the substrate to be plated is immersed.
- Power Supply: An AC to DC converter or a power supply unit that delivers the correct current for electroplating.
- Anodes: Zinc or zinc alloy, anodes are employed in the plating bath and disperse the metal ions for the plating process.
- Cathodes: In the electroplating process the substrate to be plated takes the reductive site of the half-cell or acts as the cathode.
- pH Meter: An item used to measure the pH of the plating solution because it has a direct influence on the quality of the plating.
- Heating Elements: Formerly used to control the required temperature of the plating solution to achieve the appropriate deposition rate.
- Agitation Equipment: Special discharge nozzles or mechanical stirs that keep the solution within the plating bath moving in such a way as to obtain uniform metallic deposition and, equally, the plating metal ions.
- Cleaning Equipment: Equipment like ultrasonic cleaners, brushes, or blast cabinets which are the general preparation surface before the plating process.
- Testing Equipment: Apparatus such as thickness gauge, and salt spray testers, which measure the thickness and corrosion ability of the plated surface respectively.
Specifications of High Zinc-Nickel Alloy
The corrosion resistance of zinc-nickel alloy with a higher Ni content is even better than that of the above alloy. High zinc-nickel alloy is used in industries that demand the maximum endurance as in offshore oil drilling equipment and other military use.
| Parameter | Specification |
| Hardness | 350-400 HV |
| Nickel Content | 7-15% |
| Thickness | 8-20 microns |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, marine |
| Corrosion Resistance | Up to 1000 hours (ASTM B117) |
| Zinc Content | 85-93% |
| Finish | Bright, matte, chromate |
| Temp. Resistance | Up to 120°C |
What is Zinc Plating color?
Actual zinc plating may be of any color that is determined by the post-electroplating treatment given to the zinc-plated article. So, its common colors include:

- Clear: A shiny silver finish.
- Yellow: An orange color that is usually obtained after chromate treatments.
- Black: Addition of black chromate which increases its corrosion ability.
- Olive Drab: A dull green color for industrial applications.
What is the major difference between Chrome Plating vs. Zinc-Nickel Plating
The following table concisely describes the major comparison aspects of chrome plating and zinc-nickel plating;

| Feature | Chrome Plating | Zinc-Nickel Plating |
| Composition | Primarily Chromium | 85-93% Zinc, 7-15% Nickel |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (up to 200-500 hours) | Superior (up to 1000 hours, ASTM B117) |
| Coating Thickness | Typically 0.5-10 microns | 8-20 microns |
| Hardness | Very hard (800-1000 HV) | Hard (350-400 HV) |
| Appearance | Bright, mirror-like finish | Bright, matte, or colored finishes |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent (high durability and scratch resistance) | Excellent (good durability and wear resistance) |
| Environmental Resistance | Good, but prone to pitting in extreme environments | High, resistant to saltwater and chemicals |
| Cost | Higher due to chromium and finishing | Moderate |
| Applications | Decorative (automotive trim, tools), industrial (pistons, molds) | Automotive, aerospace, marine |
| Environmental Impact | Toxic chemicals, strict regulations | More environmentally friendly |
Advantages of Zinc Nickel Plating
The following are the different pros/merits of Zinc-Nickel Plating;
- High corrosion resistance.
- Better resistance to the effects of the climate and other unfriendly conditions.
- High heat resistance.
- Better adhesion properties.
- It can be used in conjunction with many post-treatments such as passivation or application of chromate coating.
Disadvantages of Zinc Nickel Plating
Here are some of the limitations of Zinc Nickel plating;
- The major disadvantage is the relatively higher cost of practicing the electroless nickel plating than the typical zinc plating.
- It takes more time and, above all, needs an experienced crew at the helm.
- This information is not freely available in different regions.
- Possible adverse effects of nickel on the environment.
- It demands a special discharging way of plating bath waste.
Applications of Zinc nickel plating
By considering the numerous benefits of zinc nickel plating. Let’s explore the different applications of zinc-nickel plating in various industries;
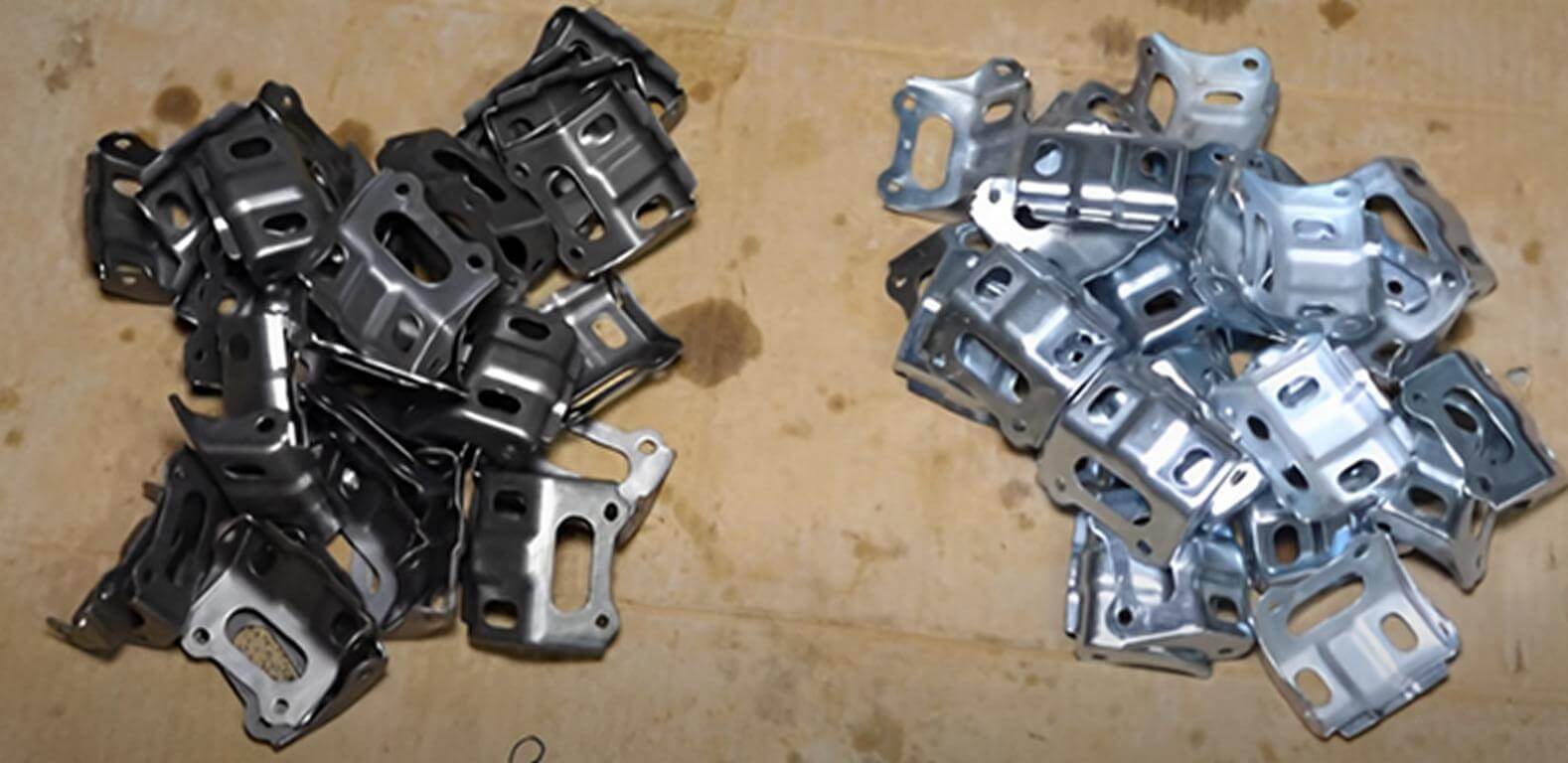

- Automotive Components: This application resists oxidation in highly humid conditions.
- Aerospace Parts: Serves as a shield against severe atmospheric factors.
- Marine Equipment: High levels of standard of resistance to salt water corrosion.
- Electronics: It is used to coat connectors and fasteners to provide a protective layer.
- Heavy Machinery: It offers protection to parts that have to undergo abrasive procedures.
Why Is Zinc-Nickel Resistant to Corrosion?
Due to its rich nickel content, Zinc-Nickel plating hardens to develop a shelter for the base metal from the corrosive factors. This alloy forms a shield that resists chemical solutions, salty water, and rough climate, a reason why it is popular with industries with corrosive characteristics.
Why Zinc Nickel Should Be Used and How to Coat Zinc Nickel Correctly?
Zinc-nickel plating is suitable in cases where one would expect the regular coating solutions to deteriorate as a result of corrosion. To make use of zinc-nickel effectively, then the surface treatment and the electroplating processes have to be done carefully. The electroplating bath must be carefully maintained, the current value must be properly controlled, and protective post-treatments used properly. So, you can achieve a high finish and long-lasting protection.

Choose Sincere Tech for Zinc Plating
If you ever search for the right service provider for zinc plating near me or zinc nickel plating services from China. You should go with experts who ensure the right quality of the finishes. Contact Sincere Tech within your area which deals in zinc or zinc nickel that is well-reviewed and adheres to industrial standards. Besides this, you must trust our furnisher to specialize in various plating processes, particularly zinc-nickel for enhanced corrosion protection.
We are one of the top 10 plastic injection molding companies in China, we offer all in one services from design, prototype, testing, plastic mold manufacturing, die casting making, production, surface finish, assmebly and delivery, we offer many types of surface finish like zinc plating, nickel plasting, painting, slick screen ,and so on.
Conclusion
In conclusion, zinc-nickel plating offers a strong poster for industries requiring robust anticorrosive apps. It has high-impact performance in unfriendly environments, other than that it is more durable, and can be produced in various color variants that may suit a particular manufacturer. While deciding between your standard zinc plating, and going with the advanced features of zinc-nickel allows for better considerations of application and process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the differences between zinc plating and zinc nickel plating?
Compared to just zinc plating, zinc-nickel plating has combined better corrosion resistance by as much as 7-10 times superior.
What is the general use of zinc-nickel plating?
High corrosion protection, increased heat resistance, and stability of material under severe process conditions.
Can zinc-nickel plate be applied on every given type of metal?
Optimal results are achieved on steel and iron but the method can be used in other types of metal if they have been properly pre-treated.
Which industries use zinc-nickel plating?
This plating is widely used in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and marine industry.
What is the durability of zinc-nickel plating?
When maintained properly and applied correctly, zinc-nickel plating can work for many years, and even in certain rough environments.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!